| LATEST LEGAL NEWS
|
|
|
|
| THE NATIONAL COMMUNICATIONS COMMISSION ESTABLISHED THE "TELECOMMUNICATIONS DISPUTE RESOLUTION INSTITUTIONS", EXPECTING TO SPEED UP THE HANDLING OF TELECOMMUNICATIONS CONSUMPTION DISPUTES AND TO IMPROVE THE QUALITY OF TELECOMMUNICATIONS SERVICES |
|
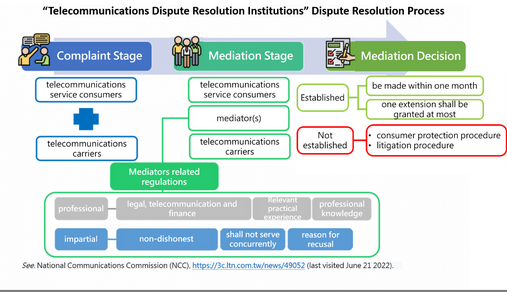
On May 11, 2022, the National Communications Commission (NCC) adopted the Articles of Incorporation of "Telecommunications Dispute Resolution Institutions", and would jointly establish by seven telecommunications carriers. It is expected that disputes over telecommunication consumption can be handled fairly and reasonably, and the overall quality of telecommunications services will be improved.
In order to effectively handle telecommunication consumption disputes and protect the rights and interests of consumers, under Article 20(1) of the Telecommunications Management Act, telecommunications enterprises determined by the competent authority shall co-establish complaint handling channels for telecommunications consumers, submit the articles of incorporation to the competent authority, and have them implemented upon receipt of approval. Therefore, according to the resolution of the 967th meeting of the NCC on June 9, 2021, seven carriers, including Chunghwa Telecom, Asia Pacific Telecom, Taiwan Mobile, Far Eas Tone Telecom, Taiwan Star Telecom, Taiwan Fixed Network, and New Century InfoComm Tech, will jointly set up a telecommunications dispute resolution institutions. According to Article 14 of Regulations Governing the Establishment, Supervision and Management of Telecommunications Dispute Resolution Institutions, The mediators shall be selected from among law, telecommunications, finance or consumer protection.
According to NCC statistics, in addition to more than 7,000 cases in 2018, there are more than 5,000 cases of telecommunications consumption disputes received in the past, and 60% of them are "poor connection quality". In the past, there were four channels for handling related disputes, including NCC, telecommunications carriers, consumer protection groups, and local government consumer service centers. After the establishment of the Institutions, the complaint cases will be directly handled by the Institutions. NCC will supervise the operation of the Institutions, upon request of the Institution and may directly intervene in the case to handle the disputes as the complaint is serious or emergent. In the future, it is hoped that with the assistance of the Institutions, consumers and the telecommunications carriers will be able to resolve consumer disputes in a self-determined and mutually agreed manner in a simple and quick non- contentious.
Reference
1.Telecommunications Management Act, available at https://law.moj.gov.tw/ENG/LawClass/LawAll.aspx?pcode=K0060111 (last visited June 21 2022).
2.Regulations Governing the Establishment, Supervision and Management of Telecommunications Dispute Resolution Institutions, available at https://law.moj.gov.tw/ENG/LawClass/LawAll.aspx?pcode=K0060132 (last visited June 21 2022).
3.The resolution of the 967th meeting of the NCC, available at https://www.ncc.gov.tw/chinese/files/21061/67_46168_210616_1.pdf (last visited June 21 2022).
4.The National Communications Commission adopted the Articles of Incorporation of the "Telecommunications Dispute Resolution Institutions", expecting to speed up the handling of telecommunications consumption disputes and to improve the quality of telecommunications services, National Communications Commission, available at https://www.ncc.gov.tw/chinese/news_detail.aspx?site_content_sn=8&cate=0&keyword=&is_history=0&pages=0&sn_f=47502 (last visited June 21 2022).
|
|
| [Top] |
|
| TAIWAN’S LEGISLATIVE YUAN PASSED THE AMENDMENTS TO THE NATIONAL SECURITY ACT AND THE CROSS-STRAIT ACT TO REINFORCE PROTECTION FOR NATIONAL SECURITY RELATED CORE TECHNOLOGIES |
|
On May 20, 2022, Taiwan’s Legislative Yuan passed the partial amendments to the National Security Act and the Act Governing Relations between the People of the Taiwan Area and the Mainland Area (the Cross-Strait Act). Given that the high-tech industry is an important foundation for Taiwan’s economic development, any theft or illicit leakage could pose a national security threat. Therefore, from the standpoint of national legal interests, it is necessary for the government to treat related issues as a national security issue and ramp up legal protection for national security related core technologies. As far as the specifics defining “national security related core technologies” and “certain standards” , due to the technical nature of these matters, the amendments to Article 3 of the the National Security Act and Article 9 of the Cross-Strait Act then give authority to the Ministry of Science and Technology to establish details in consultation with relevant agencies.
The main points of the amendments to the National Security Act and the Cross-Strait Act are as follow:
(1)the National Security Act
Taiwan’s Legislative Yuan passed amendment to the National Security Act to make economic espionage a crime punishable by a jail term of up to 12 years and a fine of NT$100 million. A provision was also added to the amendment setting a punishment of up to 10 years in prison and a fine of up to NT$50 million for extraterritorial misappropriation of trade secrets in key technologies.
The high-tech industry is the lifeline of Taiwan, but the infiltration of this industry by China's "red supply chain", which refers to a fast-growing cluster of tech companies cultivated by the Chinese government to replace foreign competitors, has become increasingly serious in recent years. China uses various means to poach Taiwan's high-tech talents and steal its core and key technologies. By circumventing Taiwan's laws and regulations, these companies conduct business activities without permission or illegally invest in Taiwan by using Taiwanese licenses, adding that this presented a risk to Taiwan's information security, economic gains, and national security. As a result, the National Security Act were drawn up to prevent Taiwan's critical technologies from theft.
(2)the Cross-Strait Act
At the same time, Taiwan’s Legislative Yuan also passed amendment to the Act Governing Relations between the People of the Taiwan Area and the Mainland Area in a bid to deter Chinese capital from infiltrating Taiwan. Under the amendment, for-profit Chinese businesses based outside of China cannot conduct business operations in Taiwan unless authorized and all subsidiaries established in Taiwan by these companies must comply with the Company Act. Those found in violation of the rules would face up to three years in prison or a fine of up to NT$15 million. The amendment also stipulates that Taiwanese companies which are found to be a front for Chinese firms or lending their licenses to Chinese for making unauthorized investments in Taiwan will face a fine of up to NT$25 million.
The Cross-Strait Act apply to the individuals or those affiliated with non-governmental organizations, legal persons, or institutions involved in affairs regarding national security related core technologies if they are commissioned by or receive research grant from government agencies (institutions) to certain standards.
Reference
1.Reinforce Protection for National Security Related Core Technologies: MAC Approves Draft Amendments to Article 9 and Article 91 of the Cross-Strait Act at the 27th Council Meeting, Mainland Affairs Council, available at https://www.mac.gov.tw/en/News_Content.aspx?n=2BA0753CBE348412&sms=E828F60C4AFBAF90&s=AD0C3117E8FF5F53 (last visited June 21 2022).
2.29th MAC Council Meeting Approves Draft Amendments to Article 40-1, Article 93-1, and Article 93-2 of the Cross-Strait Act to Maintain the Order and Normal Operation of Taiwan's Economy, Mainland Affairs Council, available at https://www.mac.gov.tw/en/News_Content.aspx?n=2BA0753CBE348412&sms=E828F60C4AFBAF90&s=3BE258902CCFAD81 (last visited June 21 2022).
3.Cabinet approves bill to toughen penalties for economic espionage, Focus Taiwan, available at https://focustaiwan.tw/politics/202202170010 (last visited June 21 2022).
|
|
| [Top] |
|
| THE FINANCIAL SUPERVISORY COMMISSION AMENDED THE REGULATIONS GOVERNING PUBLIC DISCLOSURE OF INFORMATION IN INSURANCE INDUSTRY |
|
On May 25, 2022, the Financial Supervisory Commission (金融監督與管理委員會,"FSC") amended Article 8 of the Regulations Governing Public Disclosure of Information by Life Insurance Enterprises (人身保險業辦理資訊公開管理辦法) and Article 8 of the Regulations Governing Public Disclosure of Information by Non-life Insurance Enterprises (財產保險業辦理資訊公開管理辦法) , requiring the insurance enterprises to concretely disclose the diversity policies of board of directors, cyber security risk management structure and programs, as well as the operation of ethical management and the reporting system.
Corporate Governance
In order to strengthen corporate governance, FSC amended Article 8, Paragraph 1, Subparagraph 3 of the Regulations Governing Public Disclosure of Information by Life Insurance Enterprises and Article 8, Paragraph 1, Subparagraph 3 of Regulations Governing Public Disclosure of Information by Non-life Insurance Enterprises.
These amendments stipulate that the insurance enterprises shall disclose the diversity policy of the board of directors, and state the specific goals of the company and the current achievements of the policy, so as to promote the sound development of the composition and structure of the board of directors of the insurance enterprises.
Cyber Security
Cyber security is a key topic of corporate governance, and is desperate for legal reinforcement. Therefore, FSC added Article 8, Paragraph 1, Subparagraph 20 of the Regulations Governing Public Disclosure of Information by Life Insurance Enterprises and Article 8, Paragraph 1, Subparagraph 20 of the Regulations Governing Public Disclosure of Information by Non-life Insurance Enterprises.
These additions stipulate that the insurance industry should disclose information including the cyber security risk management structure, policies, programs and resources invested, such as the number of personnel or the number of related meetings. The insurance enterprises should also disclose the loss, potential impact and countermeasures of major cyber security incidents.
In order to strengthen the awareness of the importance of cyber security and implement the risk disclosure of cyber security, the insurance enterprises shall disclose the impact of cyber security risks on financial business and related countermeasures.
Sustainable Development
FSC also revised Article 8, Paragraph 1, Subparagraph 15 of the Regulations Governing Public Disclosure of Information by Life Insurance Enterprises and Article 8, Paragraph 1, Subparagraph 15 of the Regulations Governing Public Disclosure of Information by Non-life Insurance Enterprises. The terms “social responsibility” in the provisions are replaced by "sustainable development" to comply with global trends and “Sustainable Development Roadmap” (公司治理 3.0-永續發展藍圖) formulated by FSC.
Lastly, in order to strengthen the implementation of ethical management, the insurance enterprise shall state its ethical policies and plans, as well as its actual ethical management and the operation of the reporting system.
Reference
1.The announcement of the amendment of Regulations Governing Public Disclosure of Information by Life Insurance Enterprises and the Regulations Governing Public Disclosure of Information by Non-life Insurance Enterprises, available at https://www.fsc.gov.tw/ch/home.jsp?id=128&parentpath=0,3&mcustomize=lawnew_view.jsp&dataserno=202205250001&dtable=Law (last visited June 13, 2022).
|
|
| [Top] |
|
|
|
|
|