Impact of Government Organizational Reform to Research Legal System and Response Thereto (2) – Observation of the Swiss Research Innovation System

Impact of Government Organizational Reform to Research Legal System and Response Thereto (2) – Observation of the Swiss Research Innovation System
I. Foreword
Switzerland is a landlocked country situated in Central Europe, spanning an area of 41,000 km2, where the Alps occupy 60% of the territory, while it owns little cultivated land and poor natural resources. In 2011, its population was about 7,950,000 persons[1]. Since the Swiss Federal was founded, it has been adhering to a diplomatic policy claiming neutrality and peace, and therefore, it is one of the safest and most stable countries in the world. Switzerland is famous for its high-quality education and high-level technological development and is very competitive in biomedicine, chemical engineering, electronics and metal industries in the international market. As a small country with poor resources, the Swiss have learnt to drive their economic and social development through education, R&D and innovation a very long time ago. Some renowned enterprises, including Nestle, Novartis and Roche, are all based in Switzerland. Meanwhile, a lot of creative small-sized and medium-sized enterprises based in Switzerland are dedicated to supporting the export-orientation economy in Switzerland.
Switzerland has the strongest economic strength and plentiful innovation energy. Its patent applications, publication of essay, frequencies of quotation and private enterprises’ innovation performance are remarkable all over the world. According to the Global Competitiveness Report released by the World Economic Forum (WEF), Switzerland has ranked first among the most competitive countries in the world for four years consecutively since 2009[2]. Meanwhile, according to the Global Innovation Index (GII) released by INSEAD and the World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO) jointly, Switzerland has also ranked first in 2011 and 2012 consecutively[3]. Obviously, Switzerland has led the other countries in the world in innovation development and economic strength. Therefore, when studying the R&D incentives and boosting the industrial innovation, we might benefit from the experience of Switzerland to help boost the relevant mechanism in Taiwan.
Taiwan’s government organization reform has been launched officially and boosted step by step since 2012. In the future, the National Science Council will be reformed into the “Ministry of Science and Technology”, and the Ministry of Economic Affairs into the “Ministry of Economy and Energy”, and the Department of Industrial Development into the “Department of Industry and Technology”. Therefore, Taiwan’s technology administrative system will be changed materially. Under the new government organizational framework, how Taiwan’s technology R&D and industrial innovation system divide work and coordinate operations to boost the continuous economic growth in Taiwan will be the first priority without doubt. Support of innovation policies is critical to promotion of continuous economic growth. The Swiss Government supports technological research and innovation via various organizations and institutions effectively. In recent years, it has achieved outstanding performance in economy, education and innovation. Therefore, we herein study the functions and orientation of the competent authorities dedicated to boosting research and innovation in Switzerland, and observe its policies and legal system applied to boost the national R&D in order to provide the reference for the functions and orientation of the competent authorities dedicated to boosting R&D and industrial innovation in Taiwan.
II. Overview of Swiss Federal Technology Laws and Technology Administrative System
Swiss national administrative organization is subject to the council system. The Swiss Federal Council is the national supreme administrative authority, consisting of 7 members elected from the Federal Assembly and dedicated to governing a Federal Government department respectively. Switzerland is a federal country consisting of various cantons that have their own constitutions, councils and governments, respectively, entitled to a high degree of independence.
Article 64 of the Swiss Federal Constitution[4] requires that the federal government support research and innovation. The “Research and Innovation Promotion Act” (RIPA)[5] is dedicated to fulfilling the requirements provided in Article 64 of the Constitution. Article 1 of the RIPA[6] expressly states that the Act is enacted for the following three purposes: 1. Promoting the scientific research and science-based innovation and supporting evaluation, promotion and utilization of research results; 2. Overseeing the cooperation between research institutions, and intervening when necessary; 3. Ensuring that the government funding in research and innovation is utilized effectively. Article 4 of the RIPA provides that the Act shall apply to the research institutions dedicated to innovation R&D and higher education institutions which accept the government funding, and may serve to be the merit for establishment of various institutions dedicated to boosting scientific research, e.g., the National Science Foundation and Commission of Technology & Innovation (CTI). Meanwhile, the Act also provides detailed requirements about the method, mode and restriction of the government funding.
According to the RIPA amended in 2011, the Swiss Federal Government’s responsibility for promoting innovation policies has been extended from “promotion of technology R&D” to “unification of education, research and innovation management”, making the Swiss national industrial innovation framework more well-founded and consistent[8] . Therefore, upon the government organization reform of Switzerland in 2013, most of the competent authorities dedicated to technology in Swiss have been consolidated into the Federal Department of Economic Affairs, Education and Research.
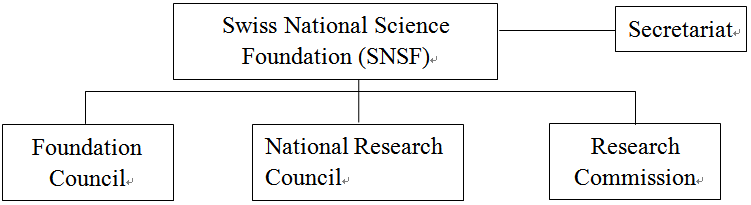
Under the framework, the Swiss Federal Government assigned higher education, job training, basic scientific research and innovation to the State Secretariat for Education, Research and Innovation (SERI), while the Commission of Technology & Innovation (CTI) was responsible for boosting the R&D of application scientific technology and industrial technology and cooperation between the industries and academy. The two authorities are directly subordinate to the Federal Department of Economic Affairs, Education and Research (EAER). The Swiss Science and Technology Council (SSTC), subordinate to the SERI is an advisory entity dedicated to Swiss technology policies and responsible for providing the Swiss Federal Government and canton governments with the advice and suggestion on scientific, education and technology innovation policies. The Swiss National Science Foundation (SNSF) is an entity dedicated to boosting the basic scientific R&D, known as the two major funding entities together with CTI for Swiss technology R&D. The organizations, duties, functions and operations of certain important entities in the Swiss innovation system are introduced as following.
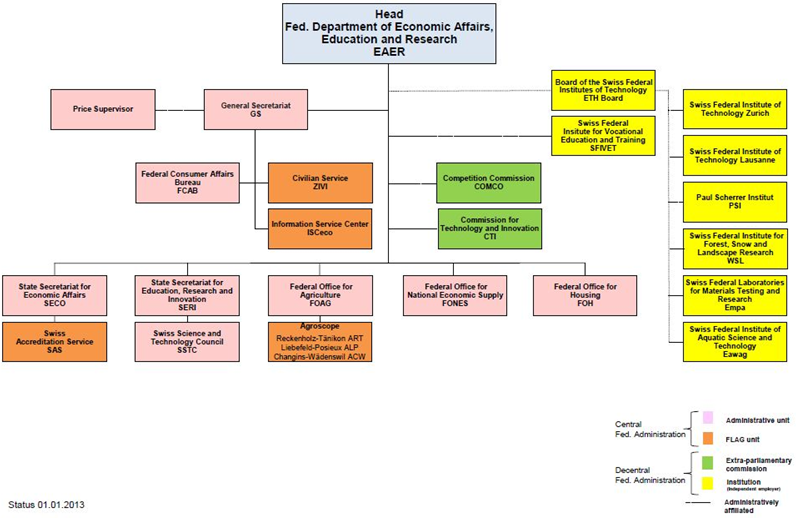
Date source: Swiss Federal Department of Economic Affairs, Education and Research official website
Fig. 1 Swiss Innovation Framework Dedicated to Boosting Industries-Swiss Federal Economic, Education and Research Organizational Chart
1. State Secretariat of Education, Research and Innovation (SERI)
SERI is subordinate to the Department of Economic Affairs, Education and Research, and is a department of the Swiss Federal Government dedicated to managing research and innovation. Upon enforcement of the new governmental organization act as of January 1, 2013, SERI was established after the merger of the State Secretariat for Education and Research, initially subordinate to Ministry of Interior, and the Federal Office for Professional Education and Technology (OEPT), initially subordinated to Ministry of Economic Affairs. For the time being, it governs the education, research and innovation (ERI). The transformation not only integrated the management of Swiss innovation system but also unified the orientations toward which the research and innovation policy should be boosted.
SERI’s core missions include “enactment of national technology policies”, “coordination of research activities conducted by higher education institutions, ETH, and other entities of the Federal Government in charge of various areas as energy, environment, traffic and health, and integration of research activities conducted by various government entities and allocation of education, research and innovation resources. Its functions also extend to funding the Swiss National Science Foundation (SNSF) to enable SNSF to subsidize the basic scientific research. Meanwhile, the international cooperation projects for promotion of or participation in research & innovation activities are also handled by SERI to ensure that Switzerland maintains its innovation strength in Europe and the world.
The Swiss Science and Technology Council (SSTC) is subordinate to SERI, and also the advisory unit dedicated to Swiss technology policies, according to Article 5a of RIPA[9]. The SSTC is responsible for providing the Swiss Federal Government and canton governments with advice and suggestion about science, education and innovation policies. It consists of the members elected from the Swiss Federal Council, and a chairman is elected among the members.
2. Swiss National Science Foundation (SNSF)
The Swiss National Science Foundation (SNSF) is one of the most important institutions dedicated to funding research, responsible for promoting the academic research related to basic science. It supports about 8,500 scientists each year. Its core missions cover funding as incentives for basic scientific research. It grants more than CHF70 million each year. Nevertheless, the application science R&D, in principle, does not fall in the scope of funding by the SNSF. The Foundation allocates the public research fund under the competitive funding system and thereby maintains its irreplaceable identity, contributing to continuous output of high quality in Switzerland.
With the support from the Swiss Federal Government, the SNSF was established in 1952. In order to ensure independence of research, it was planned as a private institution when it was established[10]. Though the funding is provided by SERI, the SNSF still has a high degree of independence when performing its functions. The R&D funding granted by the SNSF may be categorized into the funding to free basic research, specific theme-oriented research, and international cooperative technology R&D, and the free basic research is granted the largest funding. The SNSF consists of Foundation Council, National Research Council and Research Commission[11].
Data source: prepared by the Study
Fig. 2 Swiss National Science Foundation Organizational Chart(1) Foundation Council
The Foundation Council is the supreme body of the SNSF[12], which is primarily responsible for making important decisions, deciding the role to be played by the SNSF in the Swiss research system, and ensuring SNSF’s compliance with the purpose for which it was founded. The Foundation Council consists of the members elected from the representatives from important research institutions, universities and industries in Swiss, as well as the government representatives nominated by the Swiss Federal Council. According to the articles of association of the SNSF[13], each member’s term of office should be 4 years, and the members shall be no more than 50 persons. The Foundation Council also governs the Executive Committee of the Foundation Council consisting of 15 Foundation members. The Committee carries out the mission including selection of National Research Council members and review of the Foundation budget.
(2) National Research Council
The National Research Council is responsible for reviewing the applications for funding and deciding whether the funding should be granted. It consists of no more than 100 members, mostly researchers in universities and categorized, in four groups by major[14], namely, 1. Humanities and Social Sciences; 2. Math, Natural Science and Engineering; 3. Biology and Medical Science; and 4. National Research Programs (NRPs)and National Centers of Competence in Research (NCCRs). The NRPs and NCCRs are both limited to specific theme-oriented research plans. The funding will continue for 4~5years, amounting to CHF5 million~CHF20 million[15]. The specific theme-oriented research is applicable to non-academic entities, aiming at knowledge and technology transfer, and promotion and application of research results. The four groups evaluate and review the applications and authorize the funding amount.
Meanwhile, the representative members from each group form the Presiding Board dedicated to supervising and coordinating the operations of the National Research Council, and advising the Foundation Council about scientific policies, reviewing defined funding policies, funding model and funding plan, and allocating funding by major.
(3) Research Commissions
Research Commissions are established in various higher education research institutions. They serve as the contact bridge between higher education academic institutions and the SNSF. The research commission of a university is responsible for evaluating the application submitted by any researcher in the university in terms of the school conditions, e.g., the school’s basic research facilities and human resource policies, and providing advice in the process of application. Meanwhile, in order to encourage young scholars to attend research activities, the research committee may grant scholarships to PhD students and post-doctor research[16].
~to be continued~
[1] SWISS FEDERAL STATISTICS OFFICE, Switzerland's population 2011 (2012), http://www.bfs.admin.ch/bfs/portal/en/index/news/publikationen.Document.163772.pdf (last visited Jun. 1, 2013).
[2] WORLD ECONOMIC FORUM [WEF], The Global Competiveness Report 2012-2013 (2012), http://www3.weforum.org/docs/WEF_GlobalCompetitivenessReport_2012-13.pdf (last visited Jun. 1, 2013); WEF, The Global Competiveness Report 2011-2012 (2011), http://www3.weforum.org/docs/WEF_GCR_Report_2011-12.pdf (last visited Jun. 1, 2013); WEF, The Global Competiveness Report 2010-2011 (2010), http://www3.weforum.org/docs/WEF_GlobalCompetitivenessReport_2010-11.pdf (last visited Jun. 1, 2013); WEF, The Global Competiveness Report 2009-2010 (2009),. http://www3.weforum.org/docs/WEF_GlobalCompetitivenessReport_2009-10.pdf (last visited Jun. 1, 2013).
[3] INSEAD, The Global Innovation Index 2012 Report (2012), http://www.globalinnovationindex.org/gii/GII%202012%20Report.pdf (last visited Jun. 1, 2013); INSEAD, The Global Innovation Index 2011 Report (2011), http://www.wipo.int/freepublications/en/economics/gii/gii_2011.pdf (last visited Jun. 1, 2013).
[4] SR 101 Art. 64: “Der Bund fördert die wissenschaftliche Forschung und die Innovation.”
[5] Forschungs- und Innovationsförderungsgesetz, vom 7. Oktober 1983 (Stand am 1. Januar 2013). For the full text, please see www.admin.ch/ch/d/sr/4/420.1.de.pdf (last visited Jun. 3, 2013).
[6] Id.
[7] Id.
[8] CTI, CTI Multi-year Program 2013-2016 7(2012), available at http://www.kti.admin.ch/?lang=en&download=NHzLpZeg7t,lnp6I0NTU042l2Z6ln1ad1IZn4Z2qZpnO2Yuq2Z6gpJCDeYR,hGym162epYbg2c_JjKbNoKSn6A-- (last visited Jun. 3, 2013).
[9] Supra note 5.
[10] Swiss National Science Foundation, http://www.snf.ch/E/about-us/organisation/Pages/default.aspx (last visited Jun. 3, 2013).
[11] Id.
[12] Foundation Council, Swiss National Science Foundation, http://www.snf.ch/E/about-us/organisation/Pages/foundationcouncil.aspx (last visited Jun. 3, 2013).
[13] See Statutes of Swiss National Science Foundation Art.8 & Art. 9, available at http://www.snf.ch/SiteCollectionDocuments/statuten_08_e.pdf (last visited Jun. 3, 2013).
[14] National Research Council, Swiss National Science Foundation, http://www.snf.ch/E/about-us/organisation/researchcouncil/Pages/default.aspx (last visted Jun.3, 2013).
[15] Theres Paulsen, VISION RD4SD Country Case Study Switzerland (2011), http://www.visionrd4sd.eu/documents/doc_download/109-case-study-switzerland (last visited Jun.6, 2013).
[16] Research Commissions, Swiss National Science Foundation, http://www.snf.ch/E/about-us/organisation/Pages/researchcommissions.aspx (last visted Jun. 6, 2013).
The opening and sharing of scientific data- The Data Policy of the U.S. National Institutes of Health Li-Ting Tsai Scientific research improves the well-being of all mankind, the data sharing on medical and health promote the overall amount of energy in research field. For promoting the access of scientific data and research findings which was supported by the government, the U.S. government affirmed in principle that the development of science was related to the retention and accesses of data. The disclosure of information should comply with legal restrictions, and the limitation by time as well. For government-sponsored research, the data produced was based on the principle of free access, and government policies should also consider the actual situation of international cooperation[1]Furthermore, the access of scientific research data would help to promote scientific development, therefore while formulating a sharing policy, the government should also consider the situation of international cooperation, and discuss the strategy of data disclosure based on the principle of free access. In order to increase the effectiveness of scientific data, the U.S. National Institutes of Health (NIH) set up the Office of Science Policy (OSP) to formulate a policy which included a wide range of issues, such as biosafety (biosecurity), genetic testing, genomic data sharing, human subjects protections, the organization and management of the NIH, and the outputs and value of NIH-funded research. Through extensive analysis and reports, proposed emerging policy recommendations.[2] At the level of scientific data sharing, NIH focused on "genes and health" and "scientific data management". The progress of biomedical research depended on the access of scientific data; sharing scientific data was helpful to verify research results. Researchers integrated data to strengthen analysis, promoted the reuse of difficult-generated data, and accelerated research progress.[3] NIH promoted the use of scientific data through data management to verify and share research results. For assisting data sharing, NIH had issued a data management and sharing policy (DMS Policy), which aimed to promote the sharing of scientific data funded or conducted by NIH.[4] DMS Policy defines “scientific data.” as “The recorded factual material commonly accepted in the scientific community as of sufficient quality to validate and replicate research findings, regardless of whether the data are used to support scholarly publications. Scientific data do not include laboratory notebooks, preliminary analyses, completed case report forms, drafts of scientific papers, plans for future research, peer reviews, communications with colleagues, or physical objects, such as laboratory specimens.”[5] In other words, for determining scientific data, it is not only based on whether the data can support academic publications, but also based on whether the scientific data is a record of facts and whether the research results can be repeatedly verified. In addition, NIH, NIH research institutes, centers, and offices have had expected sharing of data, such as: scientific data sharing, related standards, database selection, time limitation, applicable and presented in the plan; if not applicable, the researcher should propose the data sharing and management methods in the plan. NIH also recommended that the management and sharing of data should implement the FAIR (Findable, Accessible, Interoperable and Reusable) principles. The types of data to be shared should first in general descriptions and estimates, the second was to list meta-data and other documents that would help to explain scientific data. NIH encouraged the sharing of scientific data as soon as possible, no later than the publication or implementation period.[6] It was said that even each research project was not suitable for the existing sharing strategy, when planning a proposal, the research team should still develop a suitable method for sharing and management, and follow the FAIR principles. The scientific research data which was provided by the research team would be stored in a database which was designated by the policy or funder. NIH proposed a list of recommended databases lists[7], and described the characteristics of ideal storage databases as “have unique and persistent identifiers, a long-term and sustainable data management plan, set up metadata, organizing data and quality assurance, free and easy access, broad and measured reuse, clear use guidance, security and integrity, confidentiality, common format, provenance and data retention policy”[8]. That is to say, the design of the database should be easy to search scientific data, and should maintain the security, integrity and confidentiality and so on of the data while accessing them. In the practical application of NIH shared data, in order to share genetic research data, NIH proposed a Genomic Data Sharing (GDS) Policy in 2014, including NIH funding guidelines and contracts; NIH’s GDS policy applied to all NIHs Funded research, the generated large-scale human or non-human genetic data would be used in subsequent research. [9] This can effectively promote genetic research forward. The GDS policy obliged researchers to provide genomic data; researchers who access genomic data should also abide by the terms that they used the Controlled-Access Data for research.[10] After NIH approved, researchers could use the NIH Controlled-Access Data for secondary research.[11] Reviewed by NIH Data Access Committee, while researchers accessed data must follow the terms which was using Controlled-Access Data for research reason.[12] The Genomic Summary Results (GSR) was belong to NIH policy,[13] and according to the purpose of GDS policy, GSR was defined as summary statistics which was provided by researchers, and non-sensitive data was included to the database that was designated by NIH.[14] Namely. NIH used the application and approval of control access data to strike a balance between the data of limitation access and scientific development. For responding the COVID-19 and accelerating the development of treatments and vaccines, NIH's data sharing and management policy alleviated the global scientific community’s need for opening and sharing scientific data. This policy established data sharing as a basic component in the research process.[15] In conclusion, internalizing data sharing in the research process will help to update the research process globally and face the scientific challenges of all mankind together. [1]NATIONAL SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY COUNCIL, COMMITTEE ON SCIENCE, SUBCOMMITEE ON INTERNATIONAL ISSUES, INTERAGENCY WORKING GROUP ON OPEN DATA SHARING POLICY, Principles For Promoting Access To Federal Government-Supported Scientific Data And Research Findings Through International Scientific Cooperation (2016), 1, organized from Principles, at 5-8, https://obamawhitehouse.archives.gov/sites/default/files/microsites/ostp/NSTC/iwgodsp_principles_0.pdf (last visited December 14, 2020). [2]About Us, Welcome to NIH Office of Science Policy, NIH National Institutes of Health Office of Science Policy, https://osp.od.nih.gov/about-us/ (last visited December 7, 2020). [3]NIH Data Management and Sharing Activities Related to Public Access and Open Science, NIH National Institutes of Health Office of Science Policy, https://osp.od.nih.gov/scientific-sharing/nih-data-management-and-sharing-activities-related-to-public-access-and-open-science/ (last visited December 10, 2020). [4]Final NIH Policy for Data Management and Sharing, NIH National Institutes of Health Office of Extramural Research, Office of The Director, National Institutes of Health (OD), https://grants.nih.gov/grants/guide/notice-files/NOT-OD-21-013.html (last visited December 11, 2020). [5]Final NIH Policy for Data Management and Sharing, NIH National Institutes of Health Office of Extramural Research, Office of The Director, National Institutes of Health (OD), https://grants.nih.gov/grants/guide/notice-files/NOT-OD-21-013.html (last visited December 12, 2020). [6]Supplemental Information to the NIH Policy for Data Management and Sharing: Elements of an NIH Data Management and Sharing Plan, Office of The Director, National Institutes of Health (OD), https://grants.nih.gov/grants/guide/notice-files/NOT-OD-21-014.html (last visited December 13, 2020). [7]The list of databases in details please see:Open Domain-Specific Data Sharing Repositories, NIH National Library of Medicine, https://www.nlm.nih.gov/NIHbmic/domain_specific_repositories.html (last visited December 24, 2020). [8]Supplemental Information to the NIH Policy for Data Management and Sharing: Selecting a Repository for Data Resulting from NIH-Supported Research, Office of The Director, National Institutes of Health (OD), https://grants.nih.gov/grants/guide/notice-files/NOT-OD-21-016.html (last visited December 13, 2020). [9]NIH Genomic Data Sharing, National Institutes of Health Office of Science Policy, https://osp.od.nih.gov/scientific-sharing/genomic-data-sharing/ (last visited December 15, 2020). [10]NIH Genomic Data Sharing Policy, National Institutes of Health (NIH), https://grants.nih.gov/grants/guide/notice-files/NOT-OD-14-124.html (last visited December 17, 2020). [11]NIH Genomic Data Sharing Policy, National Institutes of Health (NIH), https://grants.nih.gov/grants/guide/notice-files/NOT-OD-14-124.html (last visited December 17, 2020). [12]id. [13]NIH National Institutes of Health Turning Discovery into Health, Responsible Use of Human Genomic Data An Informational Resource, 1, at 6, https://osp.od.nih.gov/wp-content/uploads/Responsible_Use_of_Human_Genomic_Data_Informational_Resource.pdf (last visited December 17, 2020). [14]Update to NIH Management of Genomic Summary Results Access, National Institutes of Health (NIH), https://grants.nih.gov/grants/guide/notice-files/NOT-OD-19-023.html (last visited December 17, 2020). [15]Francis S. Collins, Statement on Final NIH Policy for Data Management and Sharing, National Institutes of Health Turning Discovery Into Health, https://www.nih.gov/about-nih/who-we-are/nih-director/statements/statement-final-nih-policy-data-management-sharing (last visited December 14, 2020).
Research on Taiwan’s Policies of Innovative Industry Development in Recent Years (2015-2016)Research on Taiwan’s Policies of Innovative Industry Development in Recent Years (2015-2016) 1. “Five plus Two” Innovative Industries Policy On June 15, 2016, Premier Lin Chuan met with a group of prominent business leaders to talk about a government project on five innovative industries, which aim to drive the next generation of businesses in R.O.C.. Subsequently the program was expanded to include “new agriculture” and the “circular economy” as the “+2.” The program was then broadened even further to include the Digital Economy and Cultural Innovation, with even Semiconductors and IC Design included, although the name of the policy remains 5+2. Speaking at the Third Wednesday Club in Taipei, Premier Lin said the industries require more investment to drive the next generation of industry growth momentum in R.O.C., create high-quality jobs, and upgrade the industrial competitiveness. Executive Yuan has selected the five innovative industries of Asia Silicon Valley, smart machinery, green energy, biotech & pharmaceutical industry, and national defense, which will be the core for pushing forward the next-generation industrial growth and improve overall environment by creating a cluster effect that links local and global industries, while simultaneously raising wages and stimulating employment. Premier Lin said, regarding industrial competitiveness and investment issues the lackluster economy has stifled investment opportunities, and with limited government budgets, the private sector must play the larger role in investments. Regarding the “Five major Innovative Industries” project, Premier Lin said the National Development Council is currently drafting long-term plan to attract talent, create a thriving working environment, and infuse companies with more innovation, entrepreneurship and young workers. In addition, R.O.C. must also cultivate a strong software industry, without which it would be difficult to build a highly intelligent infrastructure. The National Development Council said the program possess both the capacity of domestic demand and local characteristics, as the core for pushing forward the next-generation industrial growth. The government aims to promote a seamless synergy of investment, technology, and the talent, in order to develop innovative industrial clusters for furthering global linkage and nurturing international enterprises. In the meantime, the government also aims at achieving the enhancement of technology levels, balanced regional development, as well as realizing the benefits of job creation. 2. The Asia Silicon Valley Development Plan In September 2016 the government approved the Asia Silicon Valley Development Plan, which connect Taiwan to global tech clusters and create new industries for the next generation. By harnessing advanced technological research and development results from around the world, the plan hopes to promote innovation and R&D for devices and applications of the internet of things (IoT), and upgrade Taiwan’s startup and entrepreneurship ecosystem. The four implementation strategies are as follows: (1) Building a comprehensive ecosystem to support innovation and entrepreneurship (2) Connect with international research and development capabilities (3) Create an IoT value chain (4) Construct diversified test beds for smart products and services by establishing a quality internet environment Taiwan’s first wave of industrial development was driven by continuous technological innovation, and the wave that followed saw the information industry become a major source of economic growth. 3. Global Hub for Smart Machinery On July 21, 2016, Premier Lin Chuan said at a Cabinet meeting, the government aims to forge Taiwan into a global manufacturing hub for intelligent machinery and high-end equipment parts. Upgrading from precision machinery to intelligent machinery is the main goal of putting intelligent machinery industry into focal execution area expecting to create jobs and to maximize the production of production line as well as to forge central Taiwan into a global manufacturing hub for smart machinery. The Ministry of Economic draws up the Intelligent Machinery Promotion Program to establish the applications of the technology and capacity of services that fit the demand of the market. The program embodies two parts. The first is to accelerate the industrialization of intelligent machinery for building an ecosystem. The second is to improve intelligentization by means of introducing the intelligent machinery into the industries. The execution policy of the Intelligent Machinery Promotion Program is to integrate the intelligent functions such as malfunctions predictions, accuracy compensation, and automatic parameter setting into the machinery industry so as to have the ability to render the whole solutions to the problem. Simultaneously, the program employs three strategies, which are connecting with the local industries, connecting with the future, and connecting with the world, to develop the mentioned vision and objectives. Especially, the way to execute the strategy of connecting with the local industries consists of integrating the capabilities of industry, research organization and the government. At the meantime, the government will encourage the applications of smart vehicles and unmanned aerial vehicles and train the talents as well. The thinking of connecting with the future lies in the goal of deepening the technologies, establishing systematic solutions, and providing a testing areas, which focus on the related applications such as aerospace, advanced semiconductor, smart transportation, green vehicles, energy industry, whole solutions between factories, intelligent man-machine coordination, and robots of machine vision combined with intelligent machinery applications. The government would strengthen the cross-cutting cooperation to develop machines for aerospace and integrate the system of industrial division to form a cluster in order to create Taiwanese IoT technology. Eventually, Taiwan will be able to connect with the world, enhance international cooperation, expand export trade and push industry moving toward the age of information and digital economy and break the edge of industry technology to make the industry feel the goodwill of the government. 4. Green energy innovations The government’s “five plus two” innovative industries program includes a green energy industrial innovation plan passed October 27, 2016 that will focus on Taiwan’s green needs, spur extensive investments from within and outside the country, and increase quality employment opportunities while supporting the growth of green energy technologies and businesses. The government is developing the Shalun Green Energy Science City. The hub’s core in Shalun will house a green energy technology research center as well as a demo site, providing facilities to develop research and development (R&D) capabilities and conduct the requisite certification and demonstration procedures. The joint research center for green energy technologies will integrate the efforts of domestic academic institutions, research institutes, state-run enterprises and industry to develop green energy technologies, focusing on four major functions: creating, conserving and storing energy, as well as system integration. Development strategies include systems integration and finding better ways to conserve, generate and store energy by promoting green energy infrastructure, expanding renewable energy capabilities and cooperating with large international firms. The emergence of the green economy has prompted the government to build infrastructure that will lay the foundation for Taiwan’s green energy sector, transform the nation into a nuclear-free society, and spur industrial innovation. For innovative technology industries, green energy industries can drive domestic economic development by attracting more venture capital and creating more employment opportunities. 5. Biomedical Industry Innovation Program To facilitate development of Taiwan’s biomedical industry, the government proposed a “biomedical industrial innovation promotion program” on November 10, 2016 to serve as the nation’s new blueprint for innovative biomedical research and development (R&D). To facilitate development of the biomedical industry, the government proposed a “biomedical industrial innovation promotion program”. The program centered on the theme of “local, global and future links,” “the biomedical industrial innovation promotion program” includes four action plans: (1) Build a comprehensive ecosystem To address a rapidly ageing global population, Taiwan will enhance the biomedical industry’s capacity for innovation by focusing on talent, capital, topic selection, intellectual property, laws and regulations, and resources. (2) Integrate innovative business clusters Established by the Ministry of Science and Technology and based in Hsinchu Biomedical Science Park, the center will serve as a government think tank on related issues. It is also tasked with initiating and advancing exchanges among local and foreign experts, overseeing project implementation, promoting investment and recruiting talents. Equally important, it will play a central role in integrating resources from other biomedical industry clusters around the country, including Nangang Software Park in Taipei City, Central Taiwan Science Park in Taichung City and Southern Science Park in Tainan City. (3) Connect global market resources Building on Taiwan’s advantages, promote M&A and strategic alliances, and employ buyout funds and syndicated loans to purchase high-potential small and medium-sized international pharmaceutical companies, medical supply companies, distributors and service providers. Use modern mosquito-borne disease control strategies as the foundation of diplomatic cooperation, and promote the development of Taiwan’s public health care and medical services in Southeast Asian countries. (4) Promote specialized key industries Promote niche precision medical services, foster clusters of world-class specialty clinics, and develop industries in the health and wellness sectors. 6. DIGITAL NATION AND INNOVATIVE ECONOMIC DEVELOPMENT PLAN On November 24, 2016, the Executive Yuan promote the Digital Nation and Innovative Economic Development Plan (2017-2025) (DIGI+ program), the plan’s main goals for 2025 are to grow R.O.C.’s digital economy to NT $ 6.5 trillion (US$205.9 billion), increase the digital lifestyle services penetration rate to 80 percent, speed up broadband connections to 2 Gbps, ensure citizens’ basic rights to have 25 Mbps broadband access, and put R.O.C. among the top 10 information technology nations worldwide. In addition to the industrial economy, the program can jump off bottlenecks in the past industrial development, and promote the current Internet of things, intelligent machinery, green energy, medical care and other key national industries, but also attaches great importance to strengthening the digital infrastructure construction, the development of equal active, as well as the creation of a service-oriented digital government. It is also hoped that through the construction of a sustainable and intelligent urban and rural area, the quality of life will be improved and the people will enjoy a wealthy and healthy life. Over the next 8 years, the government will spend more than NT $ 150 billion. The plan contains several important development strategies: DIGI+Infrastructure: Build infrastructure conducive to digital innovation. DIGI+Talent: Cultivate digital innovation talent. DIGI+Industry: Support cross-industry transformation through digital innovation. DIGI+Rights: Make R.O.C. an advanced society that respects digital rights and supports open online communities. DIGI+Cities: Build smart cities through cooperation among central and local governments and the industrial, academic and research sectors. DIGI+Globalization: Boost R.O.C.’s standing in the global digital service economy. The program aims to build a favorable environment for digital innovation and to create a friendly legal environment to complete the draft amendments to the Digital Communications Law and the Telecommunications Act as soon as possible, foster cross-domain digital talents and develop advanced digital technologies, To create a digital economy, digital government, network society, smart urban and rural and other national innovation ecological environment in order to achieve "the development of active network society, promote high value innovation economy, open up rich countries of the policy vision. In order to achieve the overall effectiveness of the DIGI + program, interdisciplinary, inter-ministerial, inter-departmental and inter-departmental efforts will be required to collaborate with the newly launched Digital National Innovation Economy (DIGI +) Promotion Team. 7. “NEW AGRICULTURE” PROMOTION PROJECT At a Cabinet meeting On December 08, 2016, Premier Lin Chuan underscored the importance of a new agricultural paradigm for Taiwan’s economic development, adding that new agriculture is an integral part of the “five plus two” industrial innovation projects proposed by President Tsai Ing-wen. The “new agriculture” promotion project uses innovation technology to bring value to agricultural, and build new agricultural paradigm, agricultural safety systems and promote agricultural marketing. This project also takes resources recycling and environmental sustainability into consideration to promote agricultural transformation, and build a robust new agricultural system. This agricultural project is expected to increase food self-sufficiency rate to 40%, level up agricultural industry value by NT$43.4 billion, create 370,000 jobs and increase portion of total agricultural exports to new overseas markets to 57% by 2020. This project contains three aspects: First is “building new agricultural paradigm”: to protect farmers, agricultural development and ensure sustainability of the environment. Second is “building agricultural safety systems”: Ensuring product safety and quality, and building a certification system which can be trust by the consumers and is consistent with international standards. Last but not least is “leveling up agricultural marketing and promotions”: enhancing promotion, making the agricultural industry become profitable and sustainable. Council of Agriculture’s initiatives also proposed 10 policies to leverage agricultural industry, not only just use the passive subsidies measure of the past. These policies including promoting environmentally friendly farming practices; giving farmers that are beneficial(green) to the land payments; stabilizing farmers’ incomes; increasing the competitiveness of the livestock and poultry industries; using agricultural resources sustainably; ensuring the safety of agricultural products; developing technological innovation; leveling up food security; increasing diversification of domestic and external marketing channels; and increasing agriculture industry added value. In this statutes report, Council of Agriculture said this project will accelerate reforms, create new agricultural models and safety systems, but also build a new sustainable paradigm of agricultural. Premier Lin Chuan also backed this “five plus two innovative industries” program and “new agriculture” project, and asked Council of Agriculture to reviewing the possible legal changes or amendment that may help to enhance the transformation of agricultural sector.
The Key Elements for Data Intermediaries to Deliver Their PromiseThe Key Elements for Data Intermediaries to Deliver Their Promise 2022/12/13 As human history enters the era of data economy, data has become the new oil. It feeds artificial intelligence algorithms that are disrupting how advertising, healthcare, transportation, insurance, and many other industries work. The excitement of having data as a key production input lies in the fact that it is a non-rivalrous good that does not diminish by consumption.[1] However, the fact that people are reluctant in sharing data due to privacy and trade secrets considerations has been preventing countries to realize the full value of data. [2] To release more data, policymakers and researchers have been exploring ways to overcome the trust dilemma. Of all the discussions, data intermediaries have become a major solution that governments are turning to. This article gives an overview of relevant policy developments concerning data intermediaries and a preliminary analysis of the key elements that policymakers should consider for data intermediaries to function well. I. Policy and Legal developments concerning data intermediaries In order to unlock data’s full value, many countries have started to focus on data intermediaries. For example, in 2021, the UK’s Department for Digital, Culture, Media and Sport (DCMS) commissioned the Centre for Data Ethics and Innovation (CDEI) to publish a report on data intermediaries[3] , in response to the 2020 National Data Strategy.[4] In 2020, the European Commission published its draft Data Governance Act (DGA)[5] , which aims to build up trust in data intermediaries and data altruism organizations, in response to the 2020 European Strategy for Data.[6] The act was adopted and approved in mid-2022 by the Parliament and Council; and will apply from 24 September 2023.[7] The Japanese government has also promoted the establishment of data intermediaries since 2019, publishing guidance to establish regulations on data trust and data banks.[8] II. Key considerations for designing effective data intermediary policy 1.Evaluate which type of data intermediary works best in the targeted country From CDEI’s report on data intermediaries and the confusion in DGA’s various versions of data intermediary’s definition, one could tell that there are many forms of data intermediaries. In fact, there are at least eight types of data intermediaries, including personal information management systems (PIMS), data custodians, data exchanges, industrial data platforms, data collaboratives, trusted third parties, data cooperatives, and data trusts.[9] Each type of data intermediary was designed to combat data-sharing issues in specific countries, cultures, and scenarios. Hence, policymakers need to evaluate which type of data intermediary is more suitable for their society and market culture, before investing more resources to promote them. For example, data trust came from the concept of trust—a trustee managing a trustor’s property rights on behalf of his interest. This practice emerged in the middle ages in England and has since developed into case law.[10] Thus, the idea of data trust is easily understood and trusted by the British people and companies. As a result, British people are more willing to believe that data trusts will manage their data on their behalf in their best interest and share their valuable data, compared to countries without a strong legal history of trusts. With more people sharing their data, trusts would have more bargaining power to negotiate contract terms that are more beneficial to data subjects than what individual data owners could have achieved. However, this model would not necessarily work for other countries without a strong foundation of trust law. 2.Quality signals required to build trust: A government certificate system can help overcome the lemon market problem The basis of trust in data intermediaries depends largely on whether the service provider is really neutral in its actions and does not reuse or sell off other parties’ data in secret. However, without a suitable way to signal their service quality, the market would end up with less high-quality service, as consumers would be reluctant to pay for higher-priced service that is more secure and trustworthy when they have no means to verify the exact quality.[11] This lemon market problem could only be solved by a certificate system established by actors that consumers trust, which in most cases is the government. The EU government clearly grasped this issue as a major obstacle to the encouragement of trust in data intermediaries and thus tackles it with a government register and verification system. According to the Data Government Act, data intermediation services providers who intend to provide services are required to notify the competent authority with information on their legal status, form, ownership structure, relevant subsidiaries, address, public website, contact details, the type of service they intend to provide, the estimated start date of activities…etc. This information would be provided on a website for consumers to review. In addition, they can request the competent authority to confirm their legal compliance status, which would in turn verify them as reliable entities that can use the ‘data intermediation services provider recognised in the Union’ label. 3.Overcoming trust issues with technology that self-enforces privacy: privacy-enhancing technologies (PETs) Even if there are verified data intermediation services available, businesses and consumers might still be reluctant to trust human organizations. A way to boost trust is to adopt technologies that self-enforces privacy. A real-world example is OpenSAFELY, a data intermediary implementing privacy-enhancing technologies (PETs) to provide health data sharing in a secure environment. Through a federated analytics system, researchers are able to conduct research with large volumes of healthcare data, without the ability to observe any data directly. Under such protection, UK NHS is willing to share its data for research purposes. The accuracy and timeliness of such research have provided key insights to inform the UK government in decision-making during the COVID-19 pandemic. With the benefits it can bring, unsurprisingly, PETs-related policies have become quite popular around the globe. In June 2022, Singapore launched its Digital Trust Centre (DTC) for accelerating PETs development and also signed a Memorandum of Understanding with the International Centre of Expertise of Montreal for the Advancement of Artificial Intelligence (CEIMIA) to collaborate on PETs.[12] On September 7th, 2022, the UK Information Commissioners’ Office (ICO) published draft guidance on PETs.[13] Moreover, the U.K. and U.S. governments are collaborating on PETs prize challenges, announcing the first phase winners on November 10th, 2022.[14] We could reasonably predict that more PETs-related policies would emerge in the coming year. Reference: [1] Yan Carrière-Swallow and Vikram Haksar, The Economics of Data, IMFBlog (Sept. 23, 2019), https://blogs.imf.org/2019/09/23/the-economics-of-data/#:~:text=Data%20has%20become%20a%20key,including%20oil%2C%20in%20important%20ways (last visited July 22, 2022). [2] Frontier Economics, Increasing access to data across the economy: Report prepared for the Department for Digital, Culture, Media, and Sport (2021), https://assets.publishing.service.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploads/attachment_data/file/974532/Frontier-access_to_data_report-26-03-2021.pdf (last visited July 22, 2022). [3] The Centre for Data Ethics and Innovation (CDEI), Unlocking the value of data: Exploring the role of data intermediaries (2021), https://assets.publishing.service.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploads/attachment_data/file/1004925/Data_intermediaries_-_accessible_version.pdf (last visited June 17, 2022). [4] Please refer to the guidelines for the selection of sponsors of the 2022 Social Innovation Summit: https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/uk-national-data-strategy/national-data-strategy(last visited June 17, 2022). [5] Regulation of the European Parliament and of the Council on European data governance and amending Regulation (EU) 2018/1724 (Data Governance Act), 2020/0340 (COD) final (May 4, 2022). [6] Communication from the Commission to the European Parliament, the Council, the European Economic and Social Committee and The Committee of the Regions— A European strategy for data, COM/2020/66 final (Feb 19, 2020). [7] Proposal for a Regulation on European Data Governance, European Parliament Legislative Train Schedule, https://www.europarl.europa.eu/legislative-train/theme-a-europe-fit-for-the-digital-age/file-data-governance-act(last visited Aug 17, 2022). [8] 周晨蕙,〈日本資訊信託功能認定指引第二版〉,科技法律研究所,https://stli.iii.org.tw/article-detail.aspx?no=67&tp=5&d=8422(最後瀏覽日期︰2022/05/30)。 [9] CDEI, supra note 3. [10] Ada Lovelace Institute, Exploring legal mechanisms for data stewardship (2021), 30~31,https://www.adalovelaceinstitute.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/03/Legal-mechanisms-for-data-stewardship_report_Ada_AI-Council-2.pdf (last visited Aug 17, 2022). [11] George A. Akerlof, The Market for "Lemons": Quality Uncertainty and the Market Mechanism, THE QUARTERLY JOURNAL OF ECONOMICS, 84(3), 488-500 (1970). [12] IMDA, MOU Signing Between IMDA and CEIMIA is a Step Forward in Cross-border Collaboration on Privacy Enhancing Technology (PET) (2022),https://www.imda.gov.sg/-/media/Imda/Files/News-and-Events/Media-Room/Media-Releases/2022/06/MOU-bet-IMDA-and-CEIMIA---ATxSG-1-Jun-2022.pdf (last visited Nov. 28, 2022). [13] ICO publishes guidance on privacy enhancing technologies, ICO, https://ico.org.uk/about-the-ico/media-centre/news-and-blogs/2022/09/ico-publishes-guidance-on-privacy-enhancing-technologies/ (last visited Nov. 27, 2022). [14] U.K. and U.S. governments collaborate on prize challenges to accelerate development and adoption of privacy-enhancing technologies, GOV.UK, https://www.gov.uk/government/news/uk-and-us-governments-collaborate-on-prize-challenges-to-accelerate-development-and-adoption-of-privacy-enhancing-technologies (last visited Nov. 28, 2022); Winners Announced in First Phase of UK-US Privacy-Enhancing Technologies Prize Challenges, NIST, https://www.nist.gov/news-events/news/2022/11/winners-announced-first-phase-uk-us-privacy-enhancing-technologies-prize (last visited Nov. 28, 2022).
Analyzing the Framwork of the Regulation「Act For The Development of Biotech And New Pharmaceuticals Industry」in TaiwanTaiwan Government passed The「Act for the Development of Biotech and New Pharmaceuticals Industry」for supporting the biopharmaceutical industry. The purpose of the Act is solely for biopharmaceutical industry, and building the leading economic force in Taiwan. To fulfill this goal, the Act has enacted regulations concerning funding, taxation and recruitment especially for the biopharmaceutical industry. The Act has been seen as the recent important law in the arena of upgrading industry regulation on the island. It is also a rare case where single legislation took place for particular industry. After the Act came into force, the government has promulgated further regulations to supplement the Act, including Guidance for MOEA-Approved Biotech and New Pharmaceuticals Company Issuing Stock Certificate, Deductions on Investments in R&D and Personnel Training of Biotech and New Pharmaceuticals Company, Guidance for Deduction Applicable to Shareholders of Profit-Seeking Enterprises -Biotech and New Pharmaceuticals Company etc. The following discussions are going to introduce the Act along with related incentive measures from an integrated standpoint. 1 、 Scope of Application According to Article 3 of the Act, 「Biotech and New Pharmaceuticals Industry」 refers to the industry that deals in New Rugs and High-risk Medical devices used by human beings, animals, and plants; 「Biotech and New Pharmaceuticals Company」 refers to a company in the Biotech and New Pharmaceuticals Industry that is organized and incorporated in accordance with the Company Act and engages in the research, development, and manufacture of new drugs and high-risk medical devices. Thus, the Act applies to company that conducts research and manufacture product in new drug or high-risk medical devices for human and animal use. Furthermore, to become a Biotech and New Pharmaceuticals Company stipulated in the Act, the Company must receive letter of approval to establish as a Biotech and New Pharmaceuticals Company valid for five years. Consequently, company must submit application to the authority for approval by meeting the following requirements: (1) Companies that conduct any R&D activities or clinical trials must receive permission, product registration, or proof of manufacture for such activities from a competent authority. However, for those conducted these activities outside the country will not apply. (2) When applied for funding for the previous year or in the same year, the expense on R&D in the previous year exceeds 5% of the total net revenue within the same year; or the expenses exceeds 10% of the total capital of the company. (3) Hired at least five R&D personnel majored in biotechnology. For New Drug and High-Risk Medical Device are confined in specific areas. New Drug provided in the Act refers to a drug that has a new ingredient, a new therapeutic effect or a new administration method as verified by the central competent authorities. And High-Risk Medical Device refers to a type of Class III medical devices implanted into human bodies as verified by the central competent authorities. Therefore, generic drug, raw materials, unimplanted medical device, and medical device are not qualified as type III, are all not within the scope of the Act and are not the subject matter the Act intends to reward. 2 、 Tax Benefits Article 5, 6 and 7 provided in the Act has followed the footsteps of Article 6 and 8 stipulated of the Statute, amending the rules tailored to the biopharmaceutical industry, and provided tax benefits to various entities as 「Biotech and New Pharmaceuticals Company」, 「Investors of Biotech and New Pharmaceuticals Industry」, 「Professionals and Technology Investors」. (1) Biotech and New Pharmaceuticals Company In an effort to advance the biopharmaceutical industry, alleviate financial burden of the companies and strengthen their R&D capacity. The Act has provided favorable incentive measures in the sector of R&D and personnel training. According to Article 5: 「For the purpose of promoting the Biotech and New Pharmaceuticals Industry, a Biotech and New Pharmaceuticals Company may, for a period of five years from the time it is subject to profit-seeking enterprise income tax payable, enjoy a reduction in its corporate income tax payable, for up to 35% of the total funds invested in research and development (R&D) and personnel training each year.」 Consequently, company could benefit through tax deduction and relieve from the stress of business operation. Moreover, in supporting Biotech and New Pharmaceutical Company to proceed in R&D and personnel training activities, the Act has set out rewards for those participate in ongoing R&D and training activities. As Article 5 provided that」 If the R&D expenditure of a particular year exceeds the average R&D expenditure of the previous two years, or if the personnel training expenditure of a particular year exceeds the average personnel training expenditure of the pervious two years, 50% of the exceed amount in excess of the average may be used to credit against the amount of profit-seeking enterprise income tax payable. 「However, the total amount of investment credited against by the payable corporate income tax in each year shall not exceed 50% of the amount of profit-seeking enterprise income tax payable by a Biotech and New Pharmaceuticals Company in a year, yet this restriction shall not apply to the amount to be offset in the last year of the aforementioned five-year period. Lastly, Article 5 of the Act shall not apply to Biotech and New Pharmaceutical Company that set up headquarters or branches outside of Taiwan. Therefore, to be qualified for tax deduction on R&D and personnel training, the headquarters or branches of the company must be located in Taiwan. (2) Investors of Biotech and New Pharmaceuticals Company To raise funding, expand business development, and attract investor continuing making investments, Article 6 of the Act has stated that 「In order to encourage the establishment or expansion of Biotech and New Pharmaceuticals Companies, a profit-seeking enterprise that subscribes for the stock issued by a Biotech and New Pharmaceuticals Company at the time of the latter's establishment or subsequent expansion; and has been a registered shareholder of the Biotech and New Pharmaceuticals Company for a period of 3 years or more, may, for a period of five years from the time it is subject to corporate income tax, enjoy a reduction in its profit-seeking enterprise income tax payable for up to 20% of the total amount of the price paid for the subscription of shares in such Biotech and New Pharmaceuticals Company.」 Yet 「If the afore-mentioned profit-seeking enterprise is a venture capital company (「VC」), such VC corporate shareholders may, for a period of five years from the fourth anniversary year of the date on which the VC becomes a registered shareholder of the subject Biotech and New Pharmaceuticals Company, enjoy a reduction in their profit-seeking enterprise income tax payable based on the total deductible amount enjoyed by the VC under Paragraph 1 hereof and the shareholders' respective shareholdings in the VC.」 The government enacted this regulation to encourage corporations and VC to invest in biotech and new pharmaceutical company, and thus provide corporate shareholders with 20% of profit-seeking enterprise income tax payable deduction, and provide VC corporate shareholders tax deduction that proportion to its shareholdings in the VC. (3) Top Executives and Technology Investors Top Executives refer to those with biotechnology background, and has experience in serving as officer of chief executive (CEO) or manager; Technology Investors refer to those acquire shares through exchange of technology. As biopharmaceutical industry possesses a unique business model that demands intensive technology, whether top executives and technology investors are willing to participate in a high risk business and satisfy the needs of industry becomes a critical issue. Consequently, Article 7 of the Act stated that 「In order to encourage top executives and technology investors to participate in the operation of Biotech and New Pharmaceuticals Companies and R&D activities, and to share their achievements, new shares issued by a Biotech and New Pharmaceuticals Company to top executives and technology investors (in return of their knowledge and technology) shall be excluded from the amount of their consolidated income or corporate income of the then current year for taxation purposes; provided, however, that if the title to the aforesaid shares is transferred with or without consideration, or distributed as estate, the total purchase price or the market value of the shares at the time of transfer as a gift or distribution as estate shall be deemed income generated in that tax year and such income less the acquisition cost shall be reported in the relevant income tax return.」 Additionally, 「For the title transfer of shares under the preceding paragraph, the Biotech and New Pharmaceuticals Company concerned shall file a report with the local tax authorities within thirty 30 days from the following day of the title transfer.」 Purpose of this regulation is to attract top executives and technology personnel for the company in long-term through defer taxation. Moreover, the Biotech and New Pharmaceutical Company usually caught in a prolong period of losses, and has trouble financing through issuing new shares, as stipulated par value of each share cannot be less than NTD $10.Thus, in order to offer top executive and technology investors incentives and benefits under such circumstances, Article 8 has further provided that」Biotech and New Pharmaceutical Companies may issue subscription warrants to its top executives and technology investors, provided that the proposal for the issuance of the aforesaid subscription warrants shall pass resolution adopted by a majority votes of directors attended by at least two-thirds (2/3) of all the directors of the company; and be approved by the competent authorities. Holders of the subscription warrants may subscribe a specific number of shares at the stipulated price. The amount of stipulated price shall not be subject to the minimum requirement, i.e. par value of the shares, as prescribed under Article 140 of the Company Act. Subscription of the shares by exercising the subscription warrant shall be subject to income tax in accordance with Article 7 hereof. if a Biotech and New Pharmaceutical Company issue new shares pursuant to Article 7 hereof, Article 267 of the Company Act shall not apply. The top executives and technology investors shall not transfer the subscription warrant acquired to pursuant to this Article.」 These three types of tax benefits are detailed incentive measures tailor to the biopharmaceutical industry. However, what is noteworthy is the start date of the benefits provided in the Act. Different from the Statue, the Act allows company to enjoy these benefits when it begins to generate profits, while the Statute provides company tax benefits once the authority approved its application in the current year. Thus, Biotech and New Pharmaceuticals Company enjoys tax benefits as the company starts to make profit. Such approach reflects the actual business operation of the industry, and resolves the issue of tax benefits provided in the Statue is inapplicable to the biopharmaceutical industry. 3 、 Technical Assistance and Capital Investment Due to the R&D capacity and research personnel largely remains in the academic circle, in order to encourage these researchers to convert R&D efforts into commercial practice, the government intends to enhance the collaboration among industrial players, public institutions, and the research and academic sectors, to bolster the development of Biotech and New Pharmaceuticals Company. However, Article 13 of Civil Servants Service Act prohibits officials from engaging in business operation, the Act lifts the restriction on civil servants. According to Article 10 of the Act provided that」For a newly established Biotech and New Pharmaceuticals Company, if the person providing a major technology is a research member of the government research organization, such person may, with the consent of the government research organization, acquired 10% or more of the shares in the Biotech and New Pharmaceuticals Company at the time of its establishment, and act as founder, director, or technical adviser thereof. In such case, Article 13 of the Civil Servants Service Act shall not apply. And the research organization and research member referred to thereof shall be defined and identified by the Executive Yuan, in consultation with the Examination Yuan.」 This regulation was enacted because of the Civil Servants Services Act provided that public officials are not allowed to be corporate shareholders. However, under certain regulations, civil servants are allowed to be corporate shareholders in the sector of agriculture, mining, transportation or publication, as value of the shares cannot exceed 10% of the total value of the company, and the civil servant does not served in the institution. In Taiwan, official and unofficial research institution encompasses most of the biotechnology R&D capacity and research personnel. If a researcher is working for a government research institution, he would be qualified as a public servant and shall be governed by the Civil Servants Service Act. As a result of such restriction, the Act has lifted the restriction and encouraged these researchers to infuse new technologies into the industry. At last, for advancing the development of the industry, Article 11 also provided that 」R&D personnel of the academic and research sectors may, subject to the consent of their employers, served as advisors or consultants for a Biotech and New Pharmaceuticals Company.」 4 、 Other Regulations For introducing and transferring advanced technology in support of the biopharmaceutical industry, Article 9 stated that 「Organization formed with government funds to provide technical assistance shall provide appropriate technical assistance as may be necessary.」 Besides technical assistance, government streamlines the review process taken by various regulatory authorities, in order to achieve an improved product launch process result in faster time-to-market and time-to profit. As Article 12 provided that 「the review and approval of field test, clinical trials, product registration, and others, the central competent authorities shall establish an open and transparent procedure that unifies the review system.」
- Impact of Government Organizational Reform to Scientific Research Legal System and Response Thereto (1) – For Example, The Finnish Innovation Fund (“SITRA”)
- The Demand of Intellectual Property Management for Taiwanese Enterprises
- Blockchain in Intellectual Property Protection
- Impact of Government Organizational Reform to Research Legal System and Response Thereto (2) – Observation of the Swiss Research Innovation System
- Recent Federal Decisions and Emerging Trends in U.S. Defend Trade Secrets Act Litigation
- The effective and innovative way to use the spectrum: focus on the development of the "interleaved/white space"
- Copyright Ownership for Outputs by Artificial Intelligence
- Impact of Government Organizational Reform to Research Legal System and Response Thereto (2) – Observation of the Swiss Research Innovation System