Impact of Government Organizational Reform to Research Legal System and Response Thereto (2) – Observation of the Swiss Research Innovation System

3.Commission of Technology and Innovation (CTI)
The CTI is also an institution dedicated to boosting innovation in Switzerland. Established in 1943, it was known as the Commission for the Promotion of Scientific Research[1]. It was initially established for the purpose of boosting economy and raising the employment rate, and renamed after 1996. The CTI and SNSF are two major entities dedicated to funding scientific research in Switzerland, and the difference between both resides in that the CTI is dedicated to funding R&D of the application technology and industrial technology helpful to Switzerland’s economic development.
Upon enforcement of the amended RIPA 2011, the CTI was officially independent from the Federal Office for Professional Education and Technology (OEPT) and became an independent entity entitled to making decisions and subordinated to the Federal Department of Economic Affairs (FDEA) directly[2]. The CTI is subject to the council system, consisting of 65 professional members delegated from industrial, academic and research sectors. The members assume the office as a part time job. CTI members are entitled to making decisions on funding, utilization of resources and granting of CTI Start-up Label independently[3].
The CTI primarily carries out the mission including promotion of R&D of industrial technology, enhancement of the market-orientation innovation process and delivery of R&D energy into the market to boost industrial innovation. For innovation, the CTI's core mission is categorized into[4]:
(1)Funding technology R&D activities with market potential
The CTI invests considerable funds and resources in boosting the R&D of application technology and industrial technology. The CTI R&D Project is intended to fund private enterprises (particularly small-sized and medium-sized enterprises) to engage in R&D of innovation technology or product. The enterprises may propose their innovative ideas freely, and the CTI will decide whether the funds should be granted after assessing whether the ideas are innovative and potentially marketable[5].
CTI’s funding is conditioned on the industrial and academic cooperation. Therefore, the enterprises must work with at least one research institution (including a university, university of science and technology, or ETH) in the R&D. Considering that small-sized and medium-sized enterprises usually do not own enough working funds, technology and human resources to commercialize creative ideas, the CTI R&D Project is intended to resolve the problem about insufficient R&D energy and funds of small- and medium-sized enterprises by delivering the research institutions’ plentiful research energy and granting the private enterprises which work with research institutions (including university, university of science and technology, or ETH) the fund. Notably, CTI’s funding is applicable to R&D expenses only, e.g., research personnel’s salary and expenditure in equipment & materials, and allocated to the research institutions directly. Meanwhile, in order to enhance private enterprises' launch into R&D projects and make them liable for the R&D success or failure, CTI’s funding will be no more than 50% of the total R&D budget and, therefore, the enterprises are entitled to a high degree of control right in the process of R&D.
The industrial types which the CTI R&D Project may apply to are not limited. Any innovative ideas with commercial potential may be proposed. For the time being, the key areas funded by CTI include the life science, engineering science, Nano technology and enabling sciences, etc.[6] It intends to keep Switzerland in the lead in these areas. As of 2011, in order to mitigate the impact of drastic CHF revaluation to the industries, the CTI launched its new R&D project, the CTI Voucher[7]. Given this, the CTI is not only an entity dedicated to funding but also plays an intermediary role in the industrial and academic sectors. Enterprises may submit proposals before finding any academic research institution partner. Upon preliminary examination of the proposals, the CTI will introduce competent academic research institutions to work with the enterprises in R&D, subject to the enterprises' R&D needs. After the cooperative partner is confirmed, CTI will grant the fund amounting to no more than CHF3,500,000 per application[8], provided that the funding shall be no more than 50% of the R&D project expenditure.
The CTI R&D Project not only boosts innovation but also raises private enterprises’ willingness to participate in the academic and industrial cooperation, thereby narrowing the gap between the supply & demand of innovation R&D in the industrial and academic sectors. Notably, the Project has achieved remarkable effect in driving private enterprises’ investment in technology R&D. According to statistical data, in 2011, the CTI solicited additional investment of CHF1.3 from a private enterprise by investing each CHF1[9]. This is also one of the important reasons why the Swiss innovation system always acts vigorously.
Table 1 2005-2011 Passing rate of application for R&D funding
|
Year |
2011 |
2010 |
2009 |
2008 |
2007 |
2006 |
2005 |
|
Quantity of applications |
590 |
780 |
637 |
444 |
493 |
407 |
522 |
|
Quantity of funded applications |
293 |
343 |
319 |
250 |
277 |
227 |
251 |
|
Pass rate |
56% |
44% |
50% |
56% |
56% |
56% |
48% |
Data source: Prepared by the Study
(2)Guiding high-tech start-up
Switzerland has learnt that high-tech start-ups are critical to the creation of high-quality employment and boosting of economic growth, and start-ups were able to commercialize the R&D results. Therefore, as of 2001, Switzerland successively launched the CTI Entrepreneurship and CTI Startup to promote entrepreneurship and cultivate high-tech start-ups.
1.CTI Entrepreneurship
The CTI Entrepreneurship was primarily implemented by the Venture Lab founded by CTI investment. The Venture Lab launched a series of entrepreneurship promotion and training courses, covering day workshops, five-day entrepreneurship intensive courses, and entrepreneurship courses available in universities. Each training course was reviewed by experts, and the experts would provide positive advice to attendants about innovative ideas and business models.
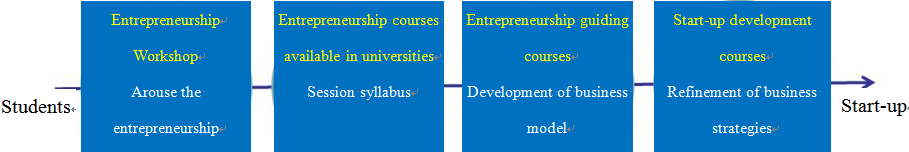
Data source: Venture Lab Site
Fig. 3 Venture Lab Startup Program
2.CTI Startup
The CTI is dedicated to driving the economy by virtue of innovation as its priority mission. In order to cultivate the domestic start-ups with high growth potential in Switzerland, the CTI Startup project was launched in 1996[10] in order to provide entrepreneurs with the relevant guidance services. The project selected young entrepreneurs who provided innovative ideas, and guided them in the process of business start to work their innovative ideas and incorporate competitive start-ups.
In order to enable the funding and resources to be utilized effectively, the CTI Startup project enrolled entrepreneurs under very strict procedure, which may be categorized into four stages[11]:
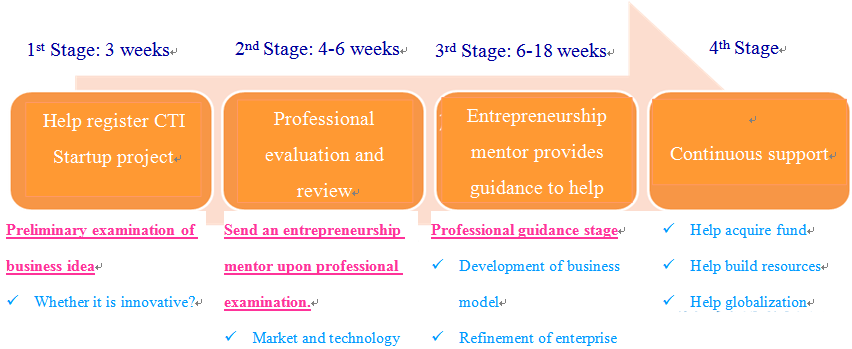
Data source: CTI Startup Site
Fig. 4 Startup Plan Flow Chart
In the first stage, the CTI would preliminarily examine whether the applicant’s idea was innovative and whether it was technologically feasible, and help the applicant register with the CTI Startup project. Upon registration, a more concrete professional examination would be conducted at the second stage. The scope of examination included the technology, market, feasibility and management team’s competence. After that, at the stage of professional guidance, each team would be assigned a professional “entrepreneurship mentor”, who would help the team develop further and optimize the enterprise’s strategy, flow and business model in the process of business start, and provide guidance and advice on the concrete business issues encountered by the start-up. The stage of professional guidance was intended to guide start-ups to acquire the CTI Startup Label, as the CTI Startup Label was granted subject to very strict examination procedure. For example, in 2012, the CTI Startup project accepted 78 applications for entrepreneurship guidance, but finally the CTI Startup Label was granted to 27 applications only[12]. Since 1996, a total of 296 start-ups have acquired the CTI Startup Label, and more than 86% thereof are still operating now[13]. Apparently, the CTI Startup Label represents the certification for innovation and on-going development competence; therefore, it is more favored by investors at the stage of fund raising.
Table 2 Execution of start-up plans for the latest three years
|
|
Quantity of application |
Quantity of accepted application |
Quantity of CTI Label granted |
|
2012 |
177 |
78 |
27 |
|
2011 |
160 |
80 |
26 |
|
2010 |
141 |
61 |
24 |
Data source: CTI Annual Report, prepared by the Study
Meanwhile, the “CTI Invest” platform was established to help start-up raise funds at the very beginning to help commercialize R&D results and cross the valley in the process of R&D innovation. The platform is a private non-business-making organization, a high-tech start-up fund raising platform co-established by CTI and Swiss investors[14]. It is engaged in increasing exposure of the start-ups and contact with investors by organizing activities, in order to help the start-ups acquire investment funds.
(3)Facilitating transfer of knowledge and technology between the academic sector and industrial sector
KTT Support (Knowledge & Technology Transfer (KTT Support) is identified as another policy instrument dedicated to boosting innovation by the CTI. It is intended to facilitate the exchange of knowledge and technology between academic research institutions and private enterprises, in order to transfer and expand the innovation energy.
As of 2013, the CTI has launched a brand new KTT Support project targeting at small-sized and medium-sized enterprises. The new KTT Support project consisted of three factors, including National Thematic Networks (NTNs), Innovation Mentors, and Physical and web-based platforms. Upon the CTI’s strict evaluation and consideration, a total of 8 cooperative innovation subjects were identified in 2012, namely, carbon fiber composite materials, design idea innovation, surface innovation, food study, Swiss biotechnology, wood innovation, photonics and logistics network, etc.[15] One NTN would be established per subject. The CTI would fund these NTNs to support the establishment of liaison channels and cooperative relations between academic research institutions and industries and provide small- and medium-sized enterprises in Switzerland with more rapid and easy channel to access technologies to promote the exchange of knowledge and technology between both parties. Innovation Mentors were professionals retained by the CTI, primarily responsible for evaluating the small-sized and medium-sized enterprises’ need and chance for innovation R&D and helping the enterprises solicit competent academic research partners to engage in the transfer of technology. The third factor of KTT Support, Physical and web-based platforms, is intended to help academic research institutions and private enterprises establish physical liaison channels through organization of activities and installation of network communication platforms, to enable the information about knowledge and technology transfer to be more transparent and communicable widely.
In conclusion, the CTI has been dedicated to enhancing the link between scientific research and the industries and urging the industrial sector to involve and boost the R&D projects with market potential. The CTI’s business lines are all equipped with corresponding policy instruments to achieve the industrial-academic cooperation target and mitigate the gap between the industry and academic sectors in the innovation chain. The various CTI policy instruments may be applied in the following manner as identified in the following figure.
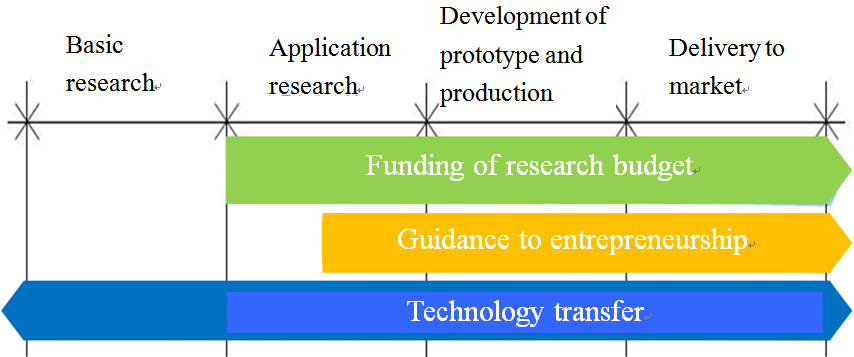
Data source: CTI Annual Report 2011
Fig. 5 Application of CTI Policy Instrument to Innovation Chain
III. Swiss Technology R&D Budget Management and Allocation
The Swiss Federal Government has invested considerable expenditures in technology R&D. According to statistic data provided by Swiss Federal Statistical Office (FSO) and OECD, the Swiss research expenditures accounted for 2.37% of the Federal Government’s total expenditures, following the U.S.A. and South Korea (see Fig. 6). Meanwhile, the research expenditures of the Swiss Government grew from CHF2.777 billion in 2000 to CHF4.639 billion in 2010, an average yearly growth rate of 5.9% (see Fig. 7). It is clear that Switzerland highly values its technology R&D.
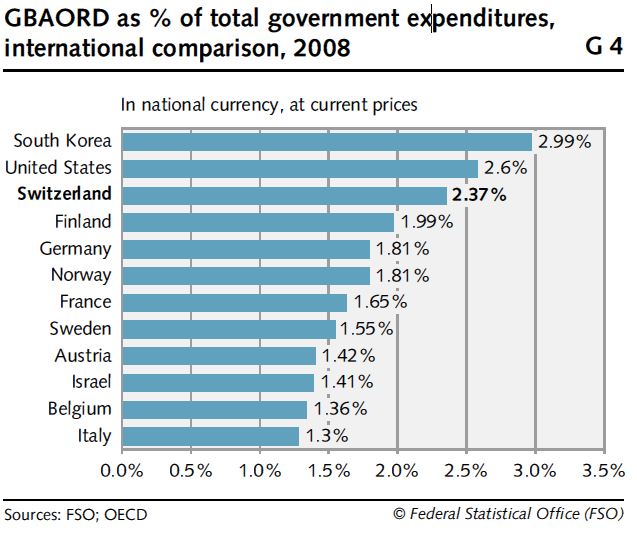.jpg)
Data source: FSO and OECD
Fig. 6 Percentage of Research Expenditures in Various Country Governments’ Total Expenditures (2008)
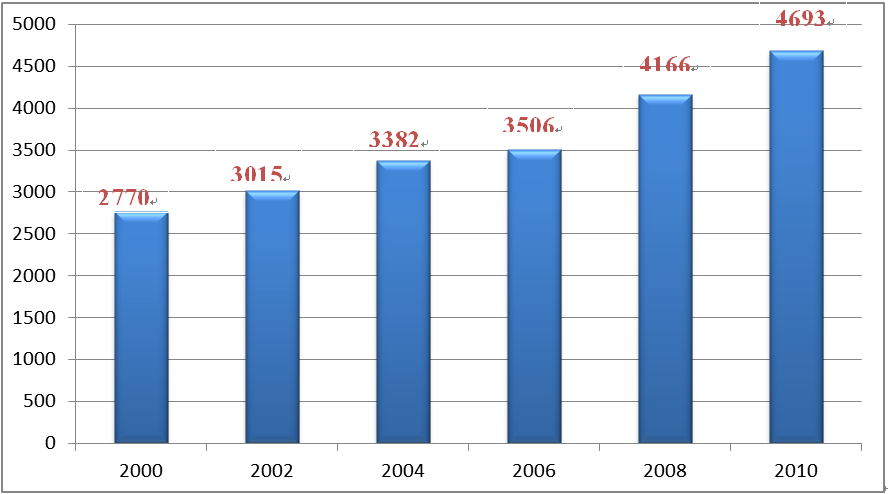
Data source: FSO and OECD
Fig. 7 Swiss Government Research Expenditures 2000-2010
1.Management of Swiss Technology R&D Budget
Swiss research expenditures are primarily allocated to the education, R&D and innovation areas, and play an important role in the Swiss innovation system. Therefore, a large part of the Swiss research expenditures are allocated to institutions of higher education, including ETH, universities, and UASs. The Swiss research expenditures are utilized by three hierarchies[16] (see Fig. 8):
- Government R&D funding agencies: The Swiss research budget is primarily executed by three agencies, including SERI, Federal Department of Economic Affairs, Education and Research, and Swiss Agency for Development and Cooperation (SDC).
- Intermediary R&D funding agencies: Including SNSC and CTI.
- Funding of R&D performing institutions: Including private enterprises, institutions of higher education and private non-profit-making business, et al.
Therefore, the Swiss Government research expenditures may be utilized by the Federal Government directly, or assigned to intermediary agencies, which will allocate the same to the R&D performing institutions. SERI will allocate the research expenditures to institutions of higher education and also hand a lot of the expenditures over to SNSF for consolidated funding to the basic science of R&D.
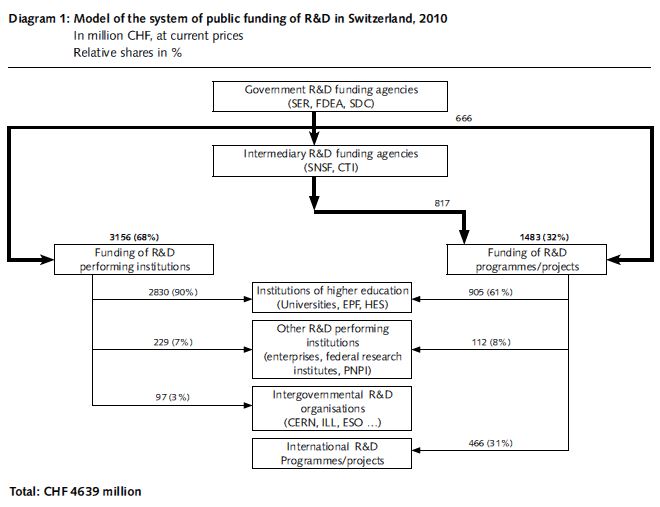
Data source: FSO
Fig. 8 Swiss Research Fund Utilization Mechanism
~to be continued~
[1] ORGANIZATION FOR ECONNOMIC CO-OPERATION AND DEVELOPMENT [OECD], OECD Reviews of Innovation Policy: Switzerland 27 (2006).
[2] As of January 1, 2013, the Federal Ministry of Economic Affairs was reorganized, and renamed into Federal Department of Economic Affairs, Education and Research (EAER).
[3] The Commission for Technology and Innovation CTI, THE COMMISSION FOR TECHOLOGY AND INNOVATION CTI, http://www.kti.admin.ch/org/00079/index.html?lang=en (last visited Jun. 3, 2013).
[4] Id.
[5] CTI INVEST, Swiss Venture Guide 2012 (2012), at 44, http://www.cti-invest.ch/getattachment/7f901c03-0fe6-43b5-be47-6d05b6b84133/Full-Version.aspx (last visited Jun. 4, 2013).
[6] CTI, CTI Activity Report 2012 14 (2013), available at http://www.kti.admin.ch/dokumentation/00077/index.html?lang=en&download=NHzLpZeg7t,lnp6I0NTU042l2Z6ln1ad1IZn4Z2qZpnO2Yuq2Z6gpJCDen16fmym162epYbg2c_JjKbNoKSn6A-- (last visited Jun. 3, 2013).
[7] CTI Voucher, THE COMMISSION FOR TECHOLOGY AND INNOVATION CTI, http://www.kti.admin.ch/projektfoerderung/00025/00135/index.html?lang=en (last visited Jun. 3, 2013).
[8] Id.
[9] CTI, CTI Activity Report 2011 20 (2012), available at http://www.kti.admin.ch/dokumentation/00077/index.html?lang=en&download=NHzLpZeg7t,lnp6I0NTU042l2Z6ln1ad1IZn4Z2qZpnO2Yuq2Z6gpJCDeYR,gWym162epYbg2c_JjKbNoKSn6A--(last visited Jun. 3, 2013).
[10] CTI Start-up Brings Science to Market, THE COMMISSION FOR TECHOLOGY AND INNOVATION CTI, http://www.ctistartup.ch/en/about/cti-start-/cti-start-up/ (last visited Jun. 5, 2013).
[11] Id.
[12] Supra note 8, at 45.
[13] Id.
[14] CTI Invest, http://www.cti-invest.ch/About/CTI-Invest.aspx (last visited Jun. 5, 2013).
[15] KTT Support, CTI, http://www.kti.admin.ch/netzwerke/index.html?lang=en (last visited Jun.5, 2013).
[16] Swiss Federal Statistics Office (SFO), Public Funding of Research in Switzerland 2000–2010 (2012), available at http://www.bfs.admin.ch/bfs/portal/en/index/themen/04/22/publ.Document.163273.pdf (last visited Jun. 20, 2013).
- Fig. 3 Venture Lab Startup Program [ png ]
- Fig. 4 Startup Plan Flow Chart [ png ]
- Fig. 5 Application of CTI Policy Instrument to Innovation Chain [ png ]
- Fig. 6 Percentage of Research Expenditures in Various Country Governments’ Total Expenditures (2008) [ jpg ]
- Fig. 7 Swiss Government Research Expenditures 2000-2010 [ png ]
- Fig. 8 Swiss Research Fund Utilization Mechanism [ jpg ]
Adopting Flexible Mechanism to Promote Public Procurement of Innovation—the Amendment of Article 27 of the Statute for Industrial Innovation I.Introduction To further industrial innovation, improve industrial environment, and enhance industrial competitiveness through a systematic long-term approach, the Statute for Industrial Innovation (hereinafter referred to as the Statute) has been formulated in Taiwan. The central government authority of this Statute is the Ministry of Economic Affairs, and the Industrial Development Bureau of the Ministry of Economic Affairs (henceforth referred to as the IDB) is the administrative body for the formulation of this Statute. Since its formulation and promulgation in 2010, the Statute has undergone four amendments. The latest amendment, passed by the Legislative Yuan on November 3, 2017, on the third reading, is a precipitate of the international industrial development trends. The government is actively encouraging the investment in industrial innovation through a combination of capital, R&D, advanced technologies and human resources to help the promotion of industrial transformation, hence this large scale amendment is conducted. The amendment, promulgated and enacted on November 22, 2017, focuses on eight key points, which include: state-owned businesses partaking in R&D (Article 9-1 of the amended provisions of the Statute), the tax concessions of the limited partnership venture capital businesses (Article 2, Article 10, Article 12-1 and Article 23-1 of the amended provisions of the Statute), the tax concessions of Angel Investors (Article 23-2 of the amended provisions of the Statute), applicable tax deferral of employees' stock compensation (Article 19-1 of the amended provisions of the Statute), tax deferral benefit of stocks given to research institution creators (Article 12-2 of the amended provisions of the Statute), the promotion of flexible mechanism for innovation procurement (Article 27 of the amended provisions of the Statute), the establishment of evaluation mechanism for intangible assets (Article 13 of the amended provisions of the Statute), and forced sale auction of idled land for industrial use (Article 46-1 of the amended provisions of the Statute). This paper focuses on the amendment of Article 27 of the Fourth Revision of the Statute, which is also one of the major focuses of this revision—promoting flexible mechanism for innovation procurement, using the mass-market purchasing power of the government as the energetic force for the development of industrial innovation. II.Explanation of the Amendment of Article 27 of the Statute 1.Purposes and Descriptions of the Amendment of Article 27 of the Statute The original intent of Article 27 (hereinafter referred to as the Article) of the Statute, prior to the latest amendment (content of the original provisions is shown in Table 1), was to encourage government agencies and enterprises to give a priority to using green products through the "priority procurement" provisions of Paragraph 2, which allow government agencies to award contracts to green product producers using special government procurement procedures, so as to increase the opportunities for government agencies to use green products, and thereby promote the sustainable development of the industry. In view of the inherent tasks of promoting the development of industrial innovation, and considering that, using the large-scale government procurement demand to guide industrial innovation activities, has become the policy instrument accepted by most advanced countries, the IDB expects that, with the latest amendment of Article 27, the procurement mechanism policy for software, innovative products and services, in addition to the original green products, may become influential, and that "innovative products and services" may be included in the scope of "Priority Procurement" of this Article namely, make “priority procurement of innovative products and services” as one of the flexible mechanisms for promoting innovation procurement. A comparison of the amended provisions and the original provisions is shown in Table 1, and an explanation of the amendment is described as follows:[1] Table 1 A Comparison of Article 27 Amendment of the Statute for Industrial Innovation Amended Provisions Original Provisions Article 27 (I) Each central government authority in charge of end enterprises of a specific industry shall encourage government organizations (agencies) and enterprises to procure software, innovative and green products or services. (II) To enhance the procurement efficiencies, as effected by supply and demand, the central government authority shall offer assistance and services to the organizations (agencies) that handle these procurements as described in the preceding paragraph; wherein, Inter-entity Supply Contracts that are required for the aforesaid procurements, the common requirements shall be decided, in accordance with policy requirements, upon consultation between the central government authority and each central government authority in charge of end enterprises of a specific industry. (III) Where the software, innovative and green products or services, as described in Paragraph 1, must be tested, audited, accredited and certified, their associated fees and charges may be reduced, exempted, or suspended. (IV) Government organizations (agencies) may specify in the tender document the priority procurement of innovative and green products or services that have been identified to meet the requirements of paragraph 1. However, such a specification shall not violate treaties or agreements that have been ratified by the Republic of China. The measures concerning specifications, categories, and identification procedures of software, innovative and green products or services as prescribed in Paragraph 1; the testing, auditing criteria, accreditation and certification as prescribed in paragraph 3; and the Priority Procurement in paragraph 4 and other relevant items, shall be established by each central government authority in charge of end-enterprises of a specific industry. Article 27 (I) Each central government authority in charge of end enterprises shall encourage government agencies and enterprises to give priority to green products that are energy/resources recyclable/renewable, energy and water saving, non-toxic, less-polluting, or able to reduce the burden on the environment. (II) Agencies may specify in the tender documents that priority is given to green products meeting the requirement set forth in the preceding Paragraph. (III) The regulations governing the specifications, categories, certification procedures, review standards, and other relevant matters relating to the green products as referred to in the preceding Paragraph shall be prescribed by the central government authorities in charge of end enterprises. Source: The Ministry of Economic Affairs (I).Paragraph 1 In order to compel each central government authority in charge of end enterprises of a specific industry to motivate industrial innovation activities and sustainable development on the basis of requirements, and to support the development of the software industry in Taiwan, the provision, that such an authority should encourage government organizations (agencies) and enterprises to procure software and innovative products and services, is added in paragraph 1. (II).Paragraph 2 This procurement, as described in paragraph 1, is different from the property or services procurement of general affairs as handled by various organizations. To enhance procurement efficiencies, as effected by supply and demand, the central government authority, i.e., the Ministry of Economic Affairs, shall provide relevant assistance and services to organizations (agencies) handling these procurements, hence the added provisions in paragraph 2. For purchases using inter-entity supply contracts, which are bound by the requirements of this Article, due to their prospective nature, and that the common demand of each organization is difficult to make an accurate estimate by using a demand survey or other method, the Ministry of Economic Affairs shall discuss the issues with each central government authority in charge of end-enterprises of a specific industry, who consult or promote policies, and are in charge of end enterprises of a specific industry, and then make decisions in accordance with the policy promotion requirements. (III).Paragraph 3 The fee schedule for testing, auditing, accrediting and certifying software, innovative and green products or services is covered by Article 7, Administrative Fees of the Charges And Fees Act. The authorities in charge should determine relevant fee standards.However, considering that the test, audit, accreditation and certification may be conducted during a trial or promotional period, or circumstances dictate that it is necessary to motivate tenderer participation, the fee may be reduced, waived or suspended; hence, paragraph 3 is added. (IV).Paragraph 4 Paragraph 2 of the original provision is moved to paragraph 4 with the revisions made to paragraph 1, accordingly, and the provision for using Priority Procurement to handle innovative products or services is added. However, for organizations covered by The Agreement on Government Procurement (GPA), due to Taiwan's accession to the WTO, ANZTEC, and ASTEP, their procurement of items covered in the aforesaid agreements with a value reaching the legislated threshold, shall be handled in accordance with the regulations stipulated in the aforesaid agreements; hence the stipulation in the proviso that the procurement must not violate the provisions of treaties or agreements ratified by the Taiwan government. (V).Paragraph 5 Paragraph 3 of the original Article is moved to paragraph 5 with the revisions made to paragraph 1, accordingly, and the provision, that authorizes each central government authority in charge of end enterprises of a specific industry to determine appropriate measures concerning the methods of defining software, innovative and green products and services, as well as matters relating to test, accreditation, certification and priority procurement, is added. 2.The Focus of the Amendment of Article 27 of the Statute—Promoting a Flexible Mechanism for Innovation Procurement As previously stated, the amendment of this Article aims to stimulate activities of industrial innovation by taking advantage of the huge demand from government agencies. With the government agencies being the users of the innovative products or services, government's procurement market potential is tapped to support the development of industrial innovation. The original intention of amendment is to incorporate the spirit of Public Procurement of Innovation[2] into this Article, and to try to introduce EU's innovation procurement mechanism[3] into our laws. So that, a procurement procedure, that is more flexible and not subject to the limitation of procurement procedures currently stipulated by the Government Procurement Act, may be adopted to facilitate government sector action in taking the lead on adopting innovative products or services that have just entered their commercial prototype stage, or utilizing the demand for innovation in the government sector to drive industry's innovative ideas or R&D (that can not be satisfied with the existing solutions in the marketplace). However, while it is assessing the relevant laws and regulations of our government procurement system and the practice of implementation, the use of the current government procurement mechanism by organizations in the public sector to achieve the targets of innovation procurement is still in its infancy. It is difficult to achieve the goal, in a short time, of establishing a variety of Public Procurement of Innovation Solutions (PPI Solutions) as disclosed in the EU's Directive 2014/24 / EU, enacted by the EU in 2014, in ways that are not subject to current government procurement legislation. Hence, the next best thing: Instead of setting up an innovative procurement mechanism in such a way that it is "not subject to the restrictions of the current government procurement law", we will focus on utilizing the flexible room available under the current system of government procurement laws and regulations, and promoting the "flexible mechanism for innovation procurement” paradigm. With the provisions now provided in Article 27 of the Statute for Industrial Innovation, the government sector is authorized to adopt the "Priority Procurement" method on innovative products and services, thus increasing the public sector's access to innovative products and services. With this amendment, in addition to the "green products" listed in the original provisions of paragraph 1 of the Statute, "software" and "innovative products or services"[4] are now incorporated into the target procurement scope and each central government authority in charge of end enterprises of a specific industry should now encourage government organizations and enterprises to implement; however, the provisions of this paragraph do not have the specific effect of law, they are declaratory provisions. Two priorities are the1 primary focus of the provisions of paragraph 2 and paragraph 4 of this Article for promoting flexible mechanism for innovation procurement: (I)The procurement of software, innovative and green products or services that uses Inter-entity Supply Contracts may rely on the "policy requirement" to establish the common demand. According to the first half of the provisions of paragraph 2 of this Article, the Ministry of Economic Affairs, being the central government authority of the Statute, may provide assistance and services to organizations dealing with the procurement of software, innovative and green products and services.This is because the procurement subjects, as pertaining to software, products or services that are innovative and green products (or services), usually have the particularities (especially in the software) of the information professions; different qualities (especially in innovative products or services), and are highly profession-specific. They are different from the general affairs goods and services procured by most government agencies. Hence, the Ministry of Economic Affairs may provide assistance and service to these procurement agencies, along with the coordination of relevant organizations, in matters relating to the aforesaid procurement process in order to improve procurement efficiency as relates to supply and demand. Pursuant to the second half of Paragraph 2 of this Article, if the inter-entity supply contract method is used to process the procurement of software, innovative products and services, green products (or services) and other related subjects, there could be "Commonly Required" by two or more organizations concerning the procurement subjects, so in accordance with the stipulations of Article 93 of the Government Procurement Act, and Article 2 of the Regulations for The Implementation of Inter-entity Supply Contracts[5], an investigation of common requirements should be conducted first. However, this type of subject is prospective and profession-specific (innovative products or services in particular), and government organizations are generally not sure whether they have demand or not, which makes it difficult to reliably estimate the demand via the traditional demand survey method[6], resulting in a major obstacle for the procurement process. Therefore, the provisions are now revised to allow the Ministry of Economic Affairs to discuss procurement with each central government authority in charge of end enterprises of a specific industry, who consult or promote policies (such as the National Development Council, or central government authority in charge of end enterprises of a specific industry relevant to the procurement subjects), and then make decisions based on the quantities of goods and services of common requirements in accordance with the demand for promoting the policy. The provisions explicitly stipulate such flexibility in adopting methods other than the "traditional demand survey" method, as is required by laws for the common demand of Inter-entity Supply Contracts. Thus, agencies currently handling procurement of prospective or innovative subjects using inter-entity supply contracts, may reduce the administrative burden typically associated with conducting their own procurement. In addition, with a larger purchase quantity demand, as generated from two or more organizations, the process can more effectively inject momentum into the industry, and achieve a win-win situation for both supply and demand. (II)Government organizations may adopt "Priority Procurement" when handling procurement of innovative and green products or services. Prior to the amendment, the original provision of paragraph 2 of this Article stipulates that organizations may specify in the tender document Priority Procurement of certified green products; Additionally, a provision of paragraph 3 of the original Article stipulates that each central government authority in charge of end enterprises of a specific industry is authorized to establish the specifications, categories and other relevant matters of the green products[7] (according to the interpretation of the original text, it should include "Priority Procurement" in paragraph 3 of the Article).After the amendment of the Article, paragraph 2 of the original Article is moved to paragraph 4. In addition to the original green products, "innovative products or services" are included in the scope of "Priority Procurement" that organizations are permitted to adopt (but, the "software" in paragraph 1 was not included[8]). However, for organizations covered by The Agreement on Government Procurement (GPA), due to Taiwan's accession to the WTO, ANZTEC, and ASTEP, their procurement of items covered by the aforesaid agreements with a value reaching the stated threshold, shall be handled in accordance with the regulations stipulated in the aforesaid agreements; hence the stipulation in the proviso that the procurement must not violate the provisions in treaties or agreements ratified by the Taiwan government. Additionally, paragraph 3 of the original Article is moved to paragraph 5. Each central government authority in charge of end enterprises of a specific industry is authorized to use their own judgment on matters concerning the specifications, categories, certification processes of software, innovative and green products or services and the method for Priority Procurement of paragraph 4. In accordance with the authorization in paragraph 5 of the amended provision of this Article, each central government authority in charge of end enterprises of a specific industry may, depending on the specific policy requirement that promotes innovation development of its supervised industry, establish methods of identification and the processes of Priority Procurement for “Specific categories of innovative products or services", especially on products or services fitting the requirements of the method of using the demands of government organizations to stimulate industrial innovation. The established "Regolations for priority procurement of Specific categories of innovative products or services" is essentially a special regulation of the government procurement legislation, which belongs to the level of regulations, that is, it allows the organizations to apply measures other than the government procurement regulations and its related measures to the procurement process, and adopt "Preferential Contract Awarding" for qualified innovative products or services. Any government agency that has the need to procure a particular category of innovative product or service may, in accordance with the provisions of paragraph 4 of this Article, specify the use of Priority Procurement in the tender document, and administer the procurement, in accordance with the process of this particular category of innovative products, or priority procurement. The agency is now enabled to follow a more flexible procurement process than that of the government procurement regulations to more smoothly award contracts for qualified innovative products or services. Citing two examples of this applied scenario: Example one, "innovative information services": The central government authority in charge of information services is IDB. Thus, IDB may, according to the authorization provided for in paragraph 5 of the Article, establish the identification methods for innovative information services (the purpose of which is to define the categories and specifications of innovative services covered in the scope of priority procurement) and priority procurement processes, pertaining to emerging information services that are more applicable to the requirements of government agencies, such as: cloud computing services, IoT services, and Big Data analysis services.Example two, "Innovative construction or engineering methods": The central government authority in charge of construction affairs is the Construction and Planning Agency of the Ministry of the Interior. Since the agency has already established the "Guidelines for Approval of Applications for New Construction Techniques, Methods, Equipment and Materials", the agency may establish a priority procurement process for new construction techniques, methods or equipment, in accordance with the stipulations in paragraph 5 of the Article. Government agencies may conduct procurement following any of these priority procurement practices, if there is a requirement for innovative information services, or new construction techniques, methods or equipment. In addition to the two aforementioned flexible mechanisms for innovation procurement, where government agencies are granted flexible procedures to handle the procurement of innovative products or services via the use of the flexible procurement mechanism, paragraph 3, concerning the incentive measures of concessionary deductions, is added to the Article to reduce the bidding costs for tenderers participating in the tender. For the Procurement of software, innovative and green products or services encouraged by each central government authority in charge of end-enterprises of a specific industry (not limited to those handled by the authorities themselves, using inter-entity supply contracts or priority procurement methods), if the procurement subjects are still required to be tested, audited, accredited and certified by the government agencies, such a process falls under the scope of administrative fees collection, pursuant to paragraph 1 Article 7 of the Charges And Fees Act. However, considering that the item subject to test, audit, accreditation and certification may be in a trial or promotional period, or that it may be necessary to motivate tenderer participation, the provisions of paragraph 3 are thusly added to the Article to reduce, waive, or suspend the collection of aforementioned fees. Executive authorities in charge of collecting administrative fees shall proceed to reduce, waive, or suspend the collection pursuant to the stipulations of paragraph 3 of the Article and Article 12 subparagraph 7 of the Charges And Fees Act.[9] III.The direction of devising supporting measures of flexible mechanism for innovation procurement The latest amendment of the Statute for Industrial Innovation was promulgated and enacted on November 22, 2017, it is imperative that supporting measures pertaining to Article 27 of the Statute be formulated. As previously stated, the flexible mechanism for innovation procurement, as promoted in this Article, is designed specifically for the products or services that are pertinent to the government procurement requirements and are capable of stimulating industrial innovation, and providing a more flexible government procurement procedure for central authorities in charge of a specific industry as a policy approach in supporting industry innovation. Thus, the premise of devising relevant supporting measures is dependent on whether the specific industry, as overseen by the particular central authority, has a policy in place for promoting the development of industrial innovation, and on whether it is suitable in promoting the flexible mechanism for innovation procurement as described in this Article. The purpose of this Article is to promote the flexible mechanism for innovation procurement. Supporting measures pertaining to this Article will focus on the promotion of devising an "Innovation Identification Method", and of the "Priority Procurement Process" of the innovative products or services of each industry that central government authorities oversee. The former will rely on each central government authority in charge of a specific industry to charter an industry-appropriate and profession-specific planning scheme; while, for the latter, the designing of a priority procurement process, in accordance with the nature of the various types of innovative products or services, does not have to be applicable to all. However, regardless what type of innovative products or services the priority procurement process is designed for, the general direction of consideration should be given to - taking the different qualities of innovative products or services as the core consideration. Additionally, the attribute of the priority procurement procedures focusing specifically on the different qualities of the innovative subjects relates to the special regulation relevant to the government procurement regulations. Thus, the procurement procedures should follow the principle that if no applicable stipulation is found in the special regulation, the provisions of the principal regulation shall apply. The so-called "Priority Procurement" process refers to the "Preferential Contract Awarding" on tenders that meet certain criteria in a government procurement procedure. The existing Government Procurement Act (GPA, for short) and its related laws that have specific stipulations on "Priority Procurement" can be found in the "Regulations for Priority Procurement of Eco-Products" (Regulations for Eco-Products Procurement, for short), and the "Regulations for Obliged Purchasing Units / Institutions to Purchase the Products and Services Provided by Disabled Welfare Institutions, Organizations or Sheltered Workshops" (Regulations for Priority Procurement of Products or Services for Disabled or Shelters, for short). After studying these two measures, the priority procurement procedures applicable to criteria-conformed subjects can be summarized into the following two types: 1.The first type: Giving preferential contract awarding to the tenderer who qualifies with "the lowest tender price”, as proposed in the tender document, and who meets a certain criteria (for example, tenderers of environmental products, disabled welfare institutions, or sheltered workshops). There are two scenarios: When a general tenderer and the criteria-conformed tenderer both submit the lowest tender price, the criteria-conformed tenderer shall obtain the right to be the "preferential winning tender" without having to go through the Price Comparison and Reduction Procedures. Additionally, if the lowest tender price is submitted by a general tenderer, then the criteria-conformed tenderers have the right to a "preferential price reduction” option, that is, the criteria-conformed tenderers can be contacted, in ascending order of the tender submitted, with a one time option to reduce their bidding prices. The first tenderer who reduces their price to the lowest amount shall win the tender. Both the Regulations for Eco-Products Procurement[10] and Regulations for Priority Procurement of Products or Services for Disabilities or Shelters[11] have such relevant stipulations. 2.The second type: It is permitted to give Preferential Contract Awarding to a criteria-conformed tenderer, when the submitted tender is within the rate of price preference. When the lowest tenderer is a general tenderer, and the tender submitted by the criteria-conformed tenderer is higher than the lowest tender price, the law permits that if the tender submitted is "within the rate of price preference ", as set by the procuring entity, the procuring entity may award the contract preferentially to "the tender submitted by the criteria-conformed tenderer." The premise for allowing this method is that the tender submitted by the criteria-conformed tenderer must be within the preferential price ratio. If the submitted tender is higher than the preferential price ratio, then the criteria-conformed tenderer does not have the right to preferential contract awarding. The contract will be awarded to theother criteria-conformed tenderer, or to a general tenderer. This method is covered in the provisions of the Regulations for Eco-Products Procurement[12]. However, the important premise for the above two priority procurement methods is that the nature of the subject matter of the tender is suitable for adopting the awarding principle of the lowest tender (Article 52, Paragraph 1, Subparagraphs 1 and 2 of the Procurement Act), that is, it is difficult to apply these methods to the subjects if they are different qualities. Pursuant to the provisions of Article 66 of the Enforcement Rules of the Government Procurement Act, the so-called "different qualities" refers to the construction work, property or services provided by different suppliers that are different in technology, quality, function, performance, characteristics, commercial terms, etc. Subjects of different qualities are essentially difficult to compare when based on the same specifications. If just looking at pricing alone it is difficult to identify the advantages and disadvantages of the subjects, hence, the awarding principle of the lowest tender is not appropriate. The innovative subjects are essentially subjects of different qualities, and under the same consideration, they are not suitable for applying the awarding principle of the lowest tender. Therefore, it is difficult to adopt the lowest-tender-based priority procurement method for the procurement of innovative subjects. In the case of innovative subjects with different qualities, the principle of the most advantageous tender should be adopted (Article 52 Paragraph 1 Subparagraph 3 of the Procurement Act) to identify the most qualified vender of the subjects through open selection. Therefore, the procedure for the priority procurement of innovative subjects with different qualities should be based on the most advantageous tender principle with focus on the "innovativeness" of the subjects, and consideration on how to give priority to tenderers, who qualify with the criteria of innovation. Pursuant to the provisions of Article 56 Paragraph 4 of the Procurement Act, the Procurement and Public Construction Commission has established the "Regulations for Evaluation of the Most Advantageous Tender". The tendering authorities adopting the most advantageous tender principle should abide by the evaluation method and procedures delineated in the method, and conduct an open selection of a winning tender. According to the Regulations for Evaluation of the Most Advantageous Tender, in addition to pricing, the tenderers' technology, quality, function, management, commercial terms, past performance of contract fulfillment, financial planning, and other matters pertaining to procurement functions or effectiveness, maybe chosen as evaluation criteria and sub-criteria. According to the three evaluation methods delineated in the provisions of Article 11 of the Regulations for Evaluation of the Most Advantageous Tender (overall evaluation score method, price per score point method, and ranking method), pricing could not been included in the scoring. That is, "the prices of the subjects" is not the absolute criterion of evaluation of the most advantageous tender process. The priority procurement procedures designed specifically for innovative subjects with different qualities may adopt an evaluation method that excludes "pricing" as part of the scoring criterion so as to give innovative subject tenderers the opportunity to be more competitive in the bidding evaluation process, and due to the extent of their innovativeness, obtain the right to preferential tenders. If it must be included in the scoring, the percentage of the total score for pricing should be reduced from its usual ratio[13], while stipulating explicitly that "innovation" must be included as part of the evaluation criteria. In addition, its weight distribution should not be less than a ratio that highlights the importance of innovation in the evaluation criteria. Furthermore, when determining how to give preference to tenderers who meet certain innovation criteria in the contract awarding procedures, care should be taken to stay on focus with the degree of innovation of the subject (the higher the degree of innovation, the higher the priority), rather than giving priority to arbitrary standards. In summary, with consideration of priority procurement procedures designed specifically for innovative subjects with different qualities, this paper proposes the following preliminary regulatory directions: 1.Adopt the awarding principle of the most advantageous tender. 2.Explicitly stipulate the inclusion of "innovation" in the evaluation criteria and sub-criteria, and its ratio, one that indicates its importance, should not be less than a certain percentage of the total score (for example 20%). 3.Reduce the distributed ratio of "price" in the scoring criteria in the open selection. 4.After the members of the evaluation committee have concluded the scoring, if more than two tenderers have attained the same highest overall evaluated score or lowest quotient of price divided by overall evaluated score, or more than two tenderers have attained the first ranking, the contract is awarded preferentially to the tenderer who scores the highest in the "innovation" criterion. 5.When multiple awards (according to Article 52 Paragraph 1 Subparagraph 4 of the Procurement Act) are adopted, that is, there is more than one final winning tender, the procuring entity may select the tenderers with higher innovation scores as the price negotiation targets for contract awarding, when there are more than two tenderers with the same ranking. Using the above method to highlight the value of innovative subjects will make these suppliers more competitive, because of their innovativeness ratings in the procurement procedures, and not confine them to the limitation of price-determination. So that, subject suppliers with a high degree of innovation, may attain the right to the preferential contract awarding that they deserve due to their innovativeness, and the procuring entity can purchase suitable innovative products in a more efficient and easy process. It also lowers the threshold for tenderers with innovation energy to enter the government procurement market, thus achieving the goal of supporting industrial innovation and creating a win-win scenario for supply and demand. [1] Cross-reference Table of Amended Provisions of the Statute for Industrial Innovation, The Ministry of Economic Affairs, https://www.moea.gov.tw/MNS/populace/news/wHandNews_File.ashx?file_id=59099 (Last viewed date: 12/08/2017). [2] According to the Guidance for public authorities on Public Procurement of Innovation issued by the Procurement of Innovation Platform in 2015, the so-called innovation procurement in essence refers to that the public sector can obtain innovative products, services, or work by using the government procurement processes, or that the public sector can administer government procurement with a new-and-better process. Either way, the implementation of innovation procurement philosophy is an important link between government procurement, R & D and innovation, which shortens the distance between the foresighted emerging technologies/processes and the public sector/users. [3] The EU's innovative procurement mechanism comprises the "Public Procurement of Innovation Solutions" (PPI Solutions) and "Pre-Commercial Procurement" (PCP). The former is one of the government procurement procedures, explicitly regulated in the new EU Public Procurement Directive (Directive 2014/24 / EU), for procuring solutions that are innovative, near or in preliminary commercial prototype; The latter is a procurement process designed to assist the public sector in obtaining technological innovative solutions that are not yet in commercial prototype, must undergo research and development process, and are not within the scope of EU Public Procurement Directive. [4] The "software, innovative and green products or services", as described in paragraph 1 of Article 27 of the amended Statute for Industrial Innovation, refers to, respectively, "software", "innovative products or services", and "green products or services" in general. There is no co-ordination or subordination relationship between the three; the same applies to "innovative and green products or services" in paragraph 4. [5] Article 93 of the Government Procurement Act stipulates: "An entity may execute an inter-entity supply contract with a supplier for the supply of property or services that are commonly needed by entities." Additionally, Article 2 of the Regulations for The Implementation of Inter-entity Supply Contracts stipulates: "The term 'property or services that are commonly needed by entities' referred to in Article 93 of the Act means property or services which are commonly required by two or more entities. The term 'inter-entity supply contract (hereinafter referred to as the “Contract”)' referred to in Article 93 of the Act means that an entity, on behalf of two or more entities, signs a contract with a supplier for property or services that are commonly needed by entities, so that the entity and other entities to which the Contract applies can utilize the Contract to conduct procurements." Therefore, according to the interpretation made by the Public Construction Commission, the Executive Yuan (PCC, for short), organizations handling inter-entity supply contracts should first conduct a demand investigation. [6] In general, organizations in charge of handling the inter-entity supply contracts will disseminate official documents to applicable organizations with an invitation to furnish information online about their interests and estimated requirement (for budget estimation) at government's e-procurement website. However, in the case of more prospective subjects (such as cloud services of the emerging industry), it may be difficult for an organization to accurately estimate the demand when filling out the survey, resulting in a mismatch of data between the demand survey and actual needs. [7] In accordance with the authorization of paragraph 3 of the Article, the IDB has established "Regulations Governing Examination and Identification of Advanced Recycled Products by Ministry of Economic Affairs" (including an appendix: Identification Specification for Resource Regenerating Green Products), except that the priority procurement process was not stipulated, because the Resource Regenerating Green Products, that meet the requirements of the Ministry of Economic Affairs, are covered by the "Category III Products" in the provisions of Article 6 of the existing "Regulations for Priority Procurement of Eco-Products", set forth by the PPC and The Environmental Protection Administration of the Executive Yuan. Hence, organizations that have the requirement to procure green products, may proceed with priority procurement by following the regulations in the "Regulations for Priority Procurement of Eco-Products". [8] After the amendment of the Article, the "software" in the provisions of paragraph 1 was excluded in paragraph 4, because the objective of paragraph 4 is to promote industry innovation and sustainable development with the use of a more flexible government procurement procedure. Thus, the subjects of the priority procurement mechanism are focused on "innovative" and "green" products or services, which exclude popular "software" that has a common standard in the market. However, if it is an "innovative software", it may be included in the "innovative products or services" in the provisions of paragraph 4. [9] According to the provisions of Article 12 of the Charges And Fees Act: "In any of the following cases, the executive authority in charge of the concerned matters may waive or reduce the amount of the charges and fees, or suspend the collection of the charges and fees: 7. Waiver, reduction, or suspension made under other applicable laws." [10] Refer to Article 12, Paragraph 1, Subparagraphs 1 and Article 13, Paragraph 1 and 2 of Regulations for Priority Procurement of Eco-Products. [11] Refer to Article 4 of Regulations for Obliged Purchasing Units / Institutions to Purchase the Products and Services Provided by Disabled Welfare Institutions, Organizations or Sheltered Workshops. [12] Refer to Article 12, Paragraph 1, Subparagraphs 2 and Article 13, Paragraph 3 of Regulations for Priority Procurement of Eco-Products. [13] The provisions of paragraph 3 Article 16 of the Regulations for Evaluation of the Most Advantageous Tender stipulates: Where price is included in scoring, its proportion of the overall score shall be not less than 20% and not more than 50%.
Legal Opinion Led to Science and Technology Law: By the Mechanism of Policy Assessment of Industry and Social NeedsWith the coming of the Innovation-based economy era, technology research has become the tool of advancing competitive competence for enterprises and academic institutions. Each country not only has begun to develop and strengthen their competitiveness of industrial technology but also has started to establish related mechanism for important technology areas selected or legal analysis. By doing so, they hope to promote collaboration of university-industry research, completely bring out the economic benefits of the R & D. and select the right technology topics. To improve the depth of research cooperation and collect strategic advice, we have to use legislation system, but also social communication mechanism to explore the values and practical recommendations that need to be concerned in policy-making. This article in our research begins with establishing a mechanism for collecting diverse views on the subject, and shaping more efficient dialogue space. Finally, through the process of practicing, this study effectively collects important suggestions of practical experts.
A Discussion on Introducing the Concept of “Government Procurement Innovation” and Suggestions for LegislationI. Introduction In Finland, the Finnish Funding Agency for Technology and Innovation, or TEKES1, has proposed the Innovations in Public Procurement, or IPP2, which can be seen as the origin of innovative government procurement solutions all over the world. As such, this paper is an attempt to explore the possibility of introducing improvements to government innovation, within procurement in the Republic of China (ROC). The IPP scheme of Finland may be used as an observational tool for the analysis of innovative ideas within the international community, for comparison with government procurement, the legislation of the scientific research subsidy, and scientific research procurement currently effective in ROC. The findings could serve as a reference for related government agencies. The concept of Public Procurement of Innovation, or PPI, in the EU could serve as the benchmark for the ROC on studying the feasibility of introducing this system. In this paper an analysis of the legal system of the ROC will be conducted in the first place to clarify the objective of introducing the concept of PPI into existing legal procedures. This is particularly the case, since that subsidy and procurement do indeed form the two-pronged policy that is currently in effect. First of all, is PPI essential to the systems that could be or could only be enforced under “government procurement”? Secondly, could PPI be introduced into relevant procedures, as explained in preceding sections? Are there any provisions of law that could be amended for such a purpose? And in what direction should we focus our attention? The concept of PPI is a solution under rapid social change, certain products or services are scarce or absent for coping with the needs of rapid social change, to the extent that an innovative solution is necessary. In addition, government procurement is the tool for encouraging the proposal of innovative solutions to mold a friendly market through the participation of the users. (But we have to be cautious. This need is different from green procurement, which requires government procurement to create a market of pre-commercialized purchase 3.) The procurement and innovation subsidy by TEKES of Finland takes the public sector as the recipients of subsidy so that the recipients of subsidy could introduce the mode of dialogue between the users and the suppliers in the course of procurement. At the planning stage of the IPP in Finland, government agencies could receive a subsidy ranging from 25% to 75% of expenditure (including the provision of technology dialogue with different targets, long-term development analysis, the design of the specification for the subject matter that is purchased comparison of different solutions) for the service programs provided by the suppliers. During the implementation stage of procurement, purchasing government agencies could also receive a subsidy of 75% for expenditure on innovation projects procured by the government under subsidy at planning stage, on the performance of tasks during research and development at the implementation stage. Or, they could be subsidized up to 50% for spending on tasks beyond research and development. The content of subsidy includes equipment, service (including management fees), travelling expenses, and other necessary expenses. The recipients of a subsidy from TEKES at these two stages, is dictated by the extent to which these government agencies are able to introduce the spirit of procurement innovation at planning and implementation stages. As such, the legal foundation for the introduction of PPI into scientific research subsidy within the ROC will be an immediate concern. In concrete terms, this is the legality of the agency for advocacy of industrial technology research and development in subsidizing government agencies using national science and technology development funds of the Executive Yuan (also known as Science Development Fund); the legality of the authority of Industrial Technology Department in subsidizing other departments of the public sector, and the issues of the applicability of the Scientific Research Procurement Monitoring Regulation to the appointment of external institutions for conducting market surveys on such needs by the public sector (collectively known as “the issues of subsidizing for innovation”). In seeking a solution on subsidy, we still have to fit dialogue between the recipients of a subsidy during the course of a ‘procurement’ project, within the legal framework currently in force. The fundamental spirit and primary concern for government procurement in the ROC, for example, will be the prevention of misconduct and corruption during the procurement procedure4. It is necessary to state such a requirement within the law, in order to avoid allegations of manipulation during the bidding process. Only by so doing could the spirit of PPI be introduced into the process. In other words, it would be a matter of sorting out the recipients of scientific research subsidy, government procurement, and scientific research procurement without causing a contradiction between “the participation of the suppliers and users of the end-requirement or service, in the determination of the specification, terms and conditions of the procurement” from the PPI of Finland and the applicable laws currently in force. It would be necessary to design the details of the procedures (collectively known as the “issues of innovation dialogue”), which takes up the second part of this research. In summary, this paper aims to explore the dialogue of aspects of government procurement, scientific research subsidy, and scientific research procurement. It is also an attempt to analyze the gravity of PPI and the dialogue. Finally, the findings of the discussion on the introduction of the concept of PPI to science and technology projects of the ROC (which may also be extended to the subsidy of the research and development in science and technology by the public sector of the ROC) will be presented, with consultation and recommendations for legislation. II. Analysis of the dialogue in the process of government procurement, scientific research subsidy, and scientific research procurement in the ROC (I) There is more than one tool within the ROC for the encouragement of research and development in science and technology Governments of different countries possess different policy tools to support or encourage the private sector in the research and development of science and technology in order to shore-up insufficient resources. From the perspective of government budgeting, the design of procedures may be identical or different. For example, the US federal government instituted the Federal Acquisition Regulation, FAR, and defined “acquisition” as “the acquiring by contract with appropriated funds of supplies or services (including construction) by and for the use of the Federal Government through purchase or lease, whether the supplies or services are already in existence or must be created, developed, demonstrated, or evaluated” 5. In light of the variation between its specific features and other services, Research and Development Contracting has been specifically regulated in section 35 of FAR, which states: “The primary purpose of contracted R&D programs is to advance scientific and technical knowledge and apply that knowledge to the extent necessary to achieve agency and national goals. Unlike contracts for supplies and services, most R&D contracts are directed toward objectives for which the work or methods cannot be precisely described in advance. It is difficult to judge the probabilities of success or required effort for technical approaches, some of which offer little or no early assurance of full success. The contracting process shall be used to encourage the best sources from the scientific and industrial community to become involved in the program and must provide an environment in which the work can be pursued with reasonable flexibility and minimum administrative burden. 6” In the EU, they defined research and development beyond government procurement regulation: According to Council Directive 92/50/EEC, or known as EU Directive, the scope of application as stated in paragraph (a) of article 1, “public service contracts shall mean contracts for pecuniary interest concluded in writing between a service suppliers and a contracting authority” with list of the exclusion conditions, where clause (ix) states: “research and development service contracts other than those where the benefits accrue exclusively to the contracting authority for its use in the conduct of its own affairs, on condition that the service supplied is wholly remunerated by the contracting authority. 7” As such, we can see the difference in legal requirements between the EU and USA. Whether such procurement is a special form of government procurement, or whether research and development falls beyond the regulation of government procurement procedure, it nonetheless falls under a government budget for the encouragement of technology research and development, and said research and development “cannot be forecast and not to be directly used by the procurement agency8 ”. Under the legal system of the ROC, it is a policy tool for the encouragement of research and development in science and technology, and could be classified as government procurement, scientific research subsidy, and scientific research procurement. For scientific research subsidy, Article 9 of the Industrial Innovation Statue of the ROC 9 provides the legal origin. For example, the technology projects administered by the Ministry of Economic Affairs have been established under this law. Accordingly, the Regulation Governing the Subsidy of Research Institutions in Industrial Innovation and Research and Development Advocated by Ministry of Economic Affairs (hereinafter, “institutional scientific project regulation”), the “Ministry of Economic Affairs Regulation Governing the Subsidy and Supervision for Assistance of Industrial Innovation (hereinafter, “Industrial Scientific Project Regulation”), and the “Regulation Governing the Subsidy of Academic Institutions in Industrial Innovation and Research and Development Advocated by Ministry of Economic Affairs (hereinafter, “Academic Scientific Project Regulation” for subsidizing research and development in industrial technologies10. The result of research and development shall be released to the administering body as required by Article 6 of the Fundamental Science and Technology Act 11. In the ROC, the result of science and technology projects shall be transferred to Ministry of Economic Affairs 12, which is similar to the requirement in the EU. This could be exemplified by the EU example as mentioned13 that the appointing agency is not entitled to any interest of the result. Government procurement is a vital policy tool of the government in subsidizing research and development. According to Article 2 of the Government Procurement Act 14, procurement as referred to in this law covers the outsourcing of service. Article 7 (paragraph 3) of the same law also requires that, service shall cover professional service, research and development. As such, the government will naturally adopt the means of government procurement in promoting its policy for encouragement of research and development in science and technology. Procurement is different from subsidy. The former entails an “inspection for acceptance” procedure, and the end users of the latter may not be the government. This point is different from the EU Directive in procurement 15. The third kind of tool in the ROC for the encouragement of research and development is scientific research procurement. According to Article 6 (paragraph 4 16) of the Fundamental Science and Technology Act, public schools, public research agencies (institutions), non-profit organizations or groups receiving a government subsidy or appointed by the government as stated in paragraph 1, or public research agencies (institutions) proceed to procurement by preparing a budget for research and development in science and technology under law. We could analyze this issue from three aspects: 1. Public schools, public research agencies (institutions), non-profit organizations or groups may receive government subsidy as stated in paragraph 1, Article 6 of the Fundamental Science and Technology Act for procurement; 2. Public schools, public research agencies (institutions), non-profit organizations or groups may proceed to procurement at the appointment of the government as stated in paragraph 1, Article 6 of the Fundamental Science and Technology Act for procurement; and 3. Public research agencies (institutions) proceed to procurement by preparing a budget for research and development in science and technology under the law 17. In detail, this specific mode of scientific research procurement has its origin in Article 4 of the Government Procurement Act. The cause of the legislation for this article, dated May 27 1998, specified that: “When non-profit organizations or groups receive government subsidy for procurement, and if the amount of subsidy exceeds half of the total amount of procurement and the amount of subsidy is subject to announcement, such procurement shall be governed by this article and subject to the monitoring of the subsidizing agencies to prevent misconduct and corruption”. As such, the recipients of subsidies shall be governed by the Government Procurement Act after passing through the due procedure of subsidy if the amount of procurement meets the standard for announcement. The purpose is to prevent misconduct and corruption. Or it would not be necessary for the government to intervene, given the subsidy has been supported by its legal source in the determination of the recipients and the procedure for entering into subsidy agreement. Indeed, this is the specific feature of the Government Procurement Act of the ROC. The same principle applies to scientific research procurement in the ROC (excluded from the application of Article 4 of the Government Procurement Act), and not the exclusion of the application of the Government Procurement Act to the subsidy procedure 18. (II) Analysis of the dialogue in the process of government procurement, scientific research subsidy, and scientific research procurement III. The dialogue of government procurement In government procurement, the regulations governing an invitation to tender and decision of award require that the party for the design of the content of procurement shall be the same party in the bidding process, to avoid alleged manipulation of the bidding process. For example, Article 39 of the Government Procurement Act (paragraph 2 and 3) requires that, “The deputy agent or partners of contractor undertaking the project management shall not be the deputy agent or partners in the planning, design, construction, or of the suppliers”. Article 38 of the Enforcement Rules of the Government Procurement Act requires that, “In tender invitation, the entity shall require explicitly in the tender invitation documents that if any of the following applies to a specific bidder, such bidder shall not participate in the bidding process, as the recipient of the award, or subcontractors of the award, or assisting the bidder: 1. The contractor that provides the planning and design service shall proceed to procurement on the basis of the planning and design result”. As such, the purpose of the Government Procurement Act aims at the impartiality and neutrality of the planning of project “to prevent funneling of interest, helping each other in manipulation of the bidding process, and the bidder also assumes the role of judge during the bidding process 19”. Indeed, there is still the possibility for hearing opinions from outside the procurement entity in the procurement cases under the Government Procurement Act. The government procurement system of the ROC could be seen as a system featuring a mechanism for dialogue. The “Particulars for Implementation of Public Viewing of Documents of Public Work Tender Invitation” 20 (hereinafter, Public Viewing Particulars) could serve as an example for the introduction of user needs dialogue. The Public Viewing Particulars require that the documents for public viewing shall include the schematics of the project, the sample version of contract, sample of affidavit, sample of important notice to bidding, bill of quantities and specifications, and other documents related to the specific characters of the projects (Number 3 of the Public Viewing Particulars). The purpose of viewing is an invitation for the opinions from the contractors or the public, which will be compiled and forwarded to the organizer of the project for processing before making an announcement for invitation to tender (Number 8 of the Public Viewing Particulars). As such, public opinions could be presented at this stage as a response to the content of the aforementioned documents in addition to the contractors. There is no delineated scope of public opinion, and could cover the objective content of the procurement. However, the type of projects subject to public viewing are of a specific nature or the amount of the engineering projects shall be subject to an audit (Number 2 of the Public Viewing Particulars), which excludes the procurement of research and development. In addition, the purpose of the Public Viewing Particulars is the transparency and openness of the tender invitation process for public work. Through the public viewing of tender invitation documents, the opinions from the contractors or the public can be heard. This can help to upgrade the quality of the planning and design of public works projects and reduce possible disputes deriving from tender invitations or performance of contract (Number 2 of the Public Viewing Particulars). As such, the purpose of this arrangement is not aimed at the necessity of the procurement of engineering projects. The possibility of applying the concept of PPI to this system of public viewing could be considered. If we think of the content for public viewing as including the schematics of the projects, the subject matter of the purchase is very substantive. In the future, it is expected that the objective of public viewing shall include subject matters that do not yet have a concrete plan, but still the opinions of the user and producer would be properly heard. 1. The dialogue of scientific research subsidy In the domain of scientific research subsidy of the ROC, the topics for subsidy are selected through the top-down mode. According to Article 7 of the institutional scientific project regulation, “The MOEA shall invite the experts from the industry, government agencies (institutions), academic and research institutions to meetings for strategic planning of industrial innovation and research and development, and consider the opinions from these social sectors to design for the direction of industrial innovation and research and development in the future”. Article 11 of the same regulation also requires that, “The MOEA may unleash the urgent industrial technology development plan on industrial technology that needs to be launched urgently as approved by MOEA or Executive Yuan”. As such, the law has already included the opinions and thoughts from the industry, government, and the academeia in designing of the recipient of subsidy. As compared with the measures adopted in Finland, this regulation is different, and the practice of Finland aims at obtaining suggestions during the course of “procurement”. Or, we could say that the introduction of the PPI concept in the subsidy mechanism could help to broaden the scope of the legal adjustment. Under the scientific project subsidy mechanism currently in effect, if we do not cut into the problem from the aforementioned mode of topic selection for subsidy, the cooperative education activities in the course of the execution of the subsidy plan are emphasized in the subsidy of scientific project for the institutions, academia, and industry 21. Further to the requirements of the regulation in principle, a variety of options could be used for integrating the needs of the industry in order to achieve the goal of the dialogue for “encouraging” research and development and the needs of the industry in practice. Individual agreements can help to achieve this goal. Currently, there are requirements specified in the notice to applicants for scientific projects within the field of academia, which feature detailed requirements for our analysis. We could take the prototype important notice to applicants (general academic scientific project) and the requirements therein commonly used in the development of industrial technology projects by the academic circle. To encouraging close cooperation between schools and the industry and research institutions, the source of funding for the projects shall be incorporated with the fees for supporting bodies with the requirements for the relevant proportion of funding on the basis of the domain of the subject matter of the project topic and the geographic location of the schools 22. If we take a closer look at the important notice of the application for a local academic development of an industrial technology project (local academic technology project), we could see that the system design features the needs of local industry. A local academic technology project is positioned for the upgrading of the research and development of specific technologies of local industries and the advocacy of regional industrial development with regional characteristics. As such, the items eligible for subsidy are innovative, prospective or critical technologies required by the industry, or modes of operation, corporate management skills or innovative service advantageous for industrial development 23. As such, the applicants must attach the letter of intent issued by at least three enterprises in the application procedure, and can prove that the objective of the project for subsidy is to a certain extent meeting the needs of local industry. 2. The dialogue of scientific research procurement For scientific research procurement, the “Regulations Governing Procurements for Scientific and Technological Research and Development” (hereinafter, “Monitoring Regulation”) instituted at the authorization of the Fundamental Science and Technology Act serves as the legal source for the entities or procurement authority to undertake scientific research procurement. The Monitoring Regulation aims at monitoring and management and also provides the legal environment for dialogue for scientific research procurement. This could be the starting point for scientific research procurement innovation. According to Article 7 of the Monitoring Regulation, “Where necessary, public schools, public research agencies (institutions), non-profit organizations or groups may proceed to consultation with the suppliers respecting the works for procurement, the specifications of properties or service needs before entering into agreement on scientific research procurement”. As such, the requirements under the Monitoring Regulations allow flexibility for the procurement authority in pursuing scientific research procurement, as they can engage in consultation with the ‘suppliers’. The topics for consultation covered the works for procurements, the specification of properties or service needs. There is one thing that needs to be differentiated, the mechanism of “consultation”, which is different from the consultation under the Government Procurement Act. Consultation as specified in the Government Procurement Act is a kind of supplementary measure applicable only when no decision of award can be made to the best bid 24, or it is difficult to determine the best bid 25. In addition, only the provisions contained in the original documents labeled as amendable could fall into the scope of consultation 26. As such, the subject matter of procurement specified in the tender invitation document shall be the fundamental requirement of the procurement case. In other words, the procurement authority has already known the purchase needs, which is different from the tentative IPP scheme of Finland. The latter aims at the encouragement for the participation of the suppliers of the service and the users in the process of determining the specification for procurement, and the terms and conditions of procurement, which is an immediate concern of the government for solutions and the development of the state to tackle challenges in the future. In other words, the IPP scheme of Finland aims at providing a solution for the procurement authority and the content of procurement is uncertain or is difficult to define due to the rapid change in the environment. (III) Concluding remarks─ the subject matter of dialogue under the concept of PPI and the possibility of preventing misconduct and corruption The study of this section leads to a preliminary conclusion that the legal framework of ROC for scientific research subsidy, government procurement, and scientific research procurement provides the mechanism for possible dialogues between the subsidy providers/procurement authority and the recipients of subsidy/bidders. Even the public viewing system of government procurement could incorporate the channels for public opinions. These could serve as the starting points for the introduction of PPI concept. Yet, there are two points to be clarified and resolved if we compare the aforementioned legal system and the PPI concept of the EU or the implementation of the IPP scheme in Finland if we are to introduce related practices First of all, if we elect to understand the aforementioned mechanism of government procurement and scientific research procurement from the perspective of dialogue/participation mechanism, the participants in the dialogues are still the subsidy providers or procurement authority and the service/goods suppliers. It is not a dialogue directly involving the users of public service (at this point, we could see the eventual purpose of the result of research and development as a form of public service). However, the spirit of the system currently in effect aims at matching the users for an indirect dialogue through this mode to a certain extent. For example, the integration of the academic scientific research project with the intent of the general and local participating firms as a necessary condition in the application, which approximates the mode of dialogue with the users of public service in the future. This arrangement is made in consideration that the firms and the market are the closest entities in the process, and is incorporated as a part of the user needs (of course, if we equate the two parties, there is the risk that the firms orchestrate market needs or making profits as the primary goal). Secondly, the gravity of the law in the ROC rests with the prevention of misconduct and corruption. This is particularly the case in the Government Procurement Act. Therefore, the foremost issue of introducing the concept of government procurement innovation to the ROC, that is the design of a system that features a mechanism for the prevention of misconduct and corruption to avoid “manipulation of the bidding process”, is yet to be resolved, and will be discussed later in this paper. IV. Analysis of the introduction of PPI into the laws governing scientific research subsidy, government procurement, and scientific research procurement (I) Suggestions and thoughts for the incorporation of PPI into the legal framework of government procurement Article 39 of the Government Procurement Act and Article 38 of its implementation procedure have set forth strict criteria for the prevention of “participants who also act as judges”. Yet, the so-called “contractors providing planning and design service” do not apply to all contractors that have provided planning suggestions but particularly point to the contractors that have been appointed by the entity to engage in the planning, design, or working on the preparation of tender invitation documents 27. In practice, the parties concerned tended to “keep a distance from” the prospective bidders in order to avoid inadvertent violation of the law. As such, there is an exception in law that excludes situations of no conflict of interest or no unfair competition 28. If we are to introduce the concept of PPI into government procurement of science and technology research and development, additional provisions must be added to the aforementioned law to provide explicit legal grounds for practice, before the entities can possibly or willingly introduce dialogue between the supplier and the user. As for the public viewing system in existence, it provides the possibility of a similar setting under the same spirit. As explained, the subject matter for receiving public opinions is still the content of the plan, which is different from the dialogue between the “supplier” and the “users’ being encouraged in the procurement planning stage under IPP in Finland. In summary, suggestions for introducing PPI to government procurement practice of the ROC within the legal framework are detailed below: First, the Government Procurement Act primarily aims at the prevention of misconduct and corruption. The introduction of the PPI concept entails higher cost of legislation, which requires amendment to the procurement act to provide the legal grounds. At the same time, the reconciliation with the rule of avoidance of the conflict of interest current practiced in procurement and the settlement of relate issues shall also be taken in account. Second, it could be possible to include the procurement of professional service or research and development in the Public Viewing Particulars in order to introduce the concept of PPI. In so doing, we must consider the entrance barrier on the procurement of engineering projects previously covered by the Public Viewing Particulars. This may be designed for avoiding the incurrence of additional administrative cost and bolstering administrative efficiency (for example, the procurement of engineering projects not exceeding specific amount, the addition of the requirement of public viewing, may delay the procurement procedure and hamper competition). For the outsourcing of professional services or research and development, appropriate consideration should be taken. (II) Suggestions and thoughts for the incorporation of PPI into the legal framework of scientific research subsidy The legal sources for governing scientific research subsidy are Article 7 and Article 11 of the institutional scientific project regulation, as in the case of the Ministry of Economic Affairs, and the important notice to applicants for general and local academic technology projects in their design. First, Article 7 of the institutional scientific project regulation requires that, Ministry of Economic Affairs shall invite experts from the industry, government agencies (institutions), academia and research institutions to the strategic planning of industrial innovation and research and development and consider the opinions from these experts in order to plan for the direction of industrial innovation and research and development in the future. The planning of the direction for innovation research and development could be included as an item for the development of industrial technology and should be the direction expected by all. For example, the Ministry of Economic Affairs has held the “National Industrial Development Conference” in December 2012, and opened to public opinions on four reformations in three industries on the advocacy of adding value to industrial innovation, structuring of positive investment environment, and other common topics. This is similar to PPI, which may include the absorption of and communication with the opinions of the “users”. But there is one point of variation. This is a matter of the use of planning strategy, and is the planning of the overall industrial technology development direction from top-down. In PPI, this will be the direct dialogue between the suppliers of service/properties and the end users in order to encourage the innovative solutions for the procurement. They may be at different levels. Second, the principle for the subsidy of general and local academic scientific projects requires the funding in proportion of the participating units or the letter of intent signed by the owners of at least three enterprises, which could be stated as the requirement of cooperative education programs. Article 12 of the institutional scientific project regulation, Article 8 of the academic scientific project regulation, and Article 4 of the industrial scientific project regulation have the provisions for encouraging cooperation education and could serve as the legal source for such a purpose. The pilot project of procurement in Finland adopted the dialogue between the prospective suppliers of service providers and the end users at the planning stage of procurement. This may be defying the principle of the procurement act. In the ROC, the subsidy procedure and the procurement procure are governed by different sets of laws. As such, the restriction of the Government Procurement Act does not exist in the legal rules governing the subsidy procedure. As such, there is little concern over the violation of the law. However, we have to pay attention to Article 6 of the Fundamental Science and Technology Act 29 on the issue of the avoidance of interest in the entitlement and use of the result of scientific research under government subsidy, at the appointment of or funded by the government. In other words, the legal rules governing subsidy have not restricted the possibility of dialogue between the “supplier” and “end users” of the science technology research and development project at the preliminary planning stage. The substantive terms of requirement are stated in Article 12-1 of the “Ministry of Economic Affairs Regulation Governing the Entitlement and Use of The Result of Science and Technology Research and Development”, the procurement authority shall establish the management mechanism or regulations, or report to the Ministry for record on the avoidance of the conflict of interest or related disclosure of the result of research and development. Attention is required for possible violation against related requirements of the avoidance of the conflict of interest and disclosure of the procurement authority. But if we take a closer look at the Fundamental Science and Technology Act in the aspect of the avoidance of the conflict of interest, and compare with the dialogue between the procurer and the users at the planning stage, there may be room for legality. It is because the Fundamental Science and Technology Act requires only the entitlement and use of the result of research and development, which is the output of the project, and not the avoidance of the conflict of interest at the planning stage and implementation stage. This is the difference in the substance. Even though there is no dialogue after the outcome of the project, the performer may still have a conflict of interest under certain circumstances, which should also be considered. For example, the procurement authority declares its position on the opinions presented at the planning stage is indeed the suggestion of the result of research and development of the only party that has the technical capacity in the technology market that can undertake the research and development. In summary, suggestions for introducing PPI to government scientific research subsidy projects in the ROC within the legal framework are detailed below: First, we could incorporate relevant dialogue mechanisms at the project planning stage, in a timely fashion and in accordance with the requirements for encouraging cooperative education within the legal framework of scientific research subsidy administered by the Ministry of Economic Affairs currently in effect. Second, legal rules governing scientific research subsidy administered by the Ministry of Economic Affairs currently in effect do not restrict any dialogue between the recipient of subsidy (the so-called “supplier”) and the “end user” at the planning stage or in the future, but whether or not such an act will violate the requirements of relevant procurement authority in the avoidance of conflict of interest, deserves our attention. (III) Suggestions and thoughts for the incorporation of PPI into the legal framework scientific research procurement In the domain of scientific project procurement, Article 7 of the Monitoring Regulation sets forth that suppliers may involved in consultation on issues related to the works for procurement, specification of properties, or service needs. This provides the legal source for the trial use of the IPP scheme of Finland in the ROC, but we have to consider two things. First, the provision sets for the consultation with the supplier only, and it is, by and large, the dialogue mechanism only after the determination of the subject matter of procurement, which is different from the IPP of Finland. Also, the dialogue with the end user does not fall within the scope of such legal source, and, there is still room to define who could be positioned as the “end user”. Yet, it is two sides of the same coin. There is a legal framework in place without detailed requirement. As such, the procurement authority may design the procedure in fuller detail in this space as needed. Finally, the scope of scientific research procurement in the ROC is not as broad as the subsidy cases (refer to the definition of scientific research procurement above). As such, the majority of scientific research procurement is already at the cooperative education stage under individual subsidy or appointment of the government (except the work under the scientific research and development budget prepared by the public research institutions). If we introduce the concept of PPI into the scientific research procurement stage, the content and the scope have already fallen into the framework of the previous subsidy plan, and there is little room for the incorporation of dialogue and opinions. In summary, the suggestions for introducing PPI to scientific research procurement of the ROC within the legal framework are detailed below: First, the Monitoring Regulation of scientific research procurement provides the mechanism for consultation but does not define the subject matter of consultation in procurement. As such, the scope for hearing opinions is limited. Further, the dialogue with the users has not been covered. The overall implementation procedure requires refinement for proper enforcement. Second, the scope of scientific research procurement is limited to the procurement under an individual subsidy program or at the appointment of the government, and falls within the scope of the content for the previous subsidy program or the program at the appointment of the government in principle. As such, the effect of introducing PPI is limited. V. Conclusion – A Discussion on Introducing the PPI into Science and Technology Projects and Suggestions for Legislation within the ROC The above are overall observations on the analysis of the introduction of PPI to scientific research subsidy, government procurement, and scientific research procurement in the ROC. In the “Issue of dialogue for innovation”, we should consider to start with scientific research subsidy. The primary reason is that there is room within the legal framework under the Monitoring Regulations governing scientific research procurement, but in practice, more substantive terms could be developed. However, the scope of the legal framework for the applicability of scientific research procurement is confined to the procurement made under subsidy or at the appointment of the government on specific programs. The effect of trial running PPI is very little under the framework of subsidy or appointment by the government. Finally, the feasibility of introducing PPI to the scientific research projects of the ROC, which is the “subsidy innovation issue”, is analyzed below: First, the legality of using scientific development fund to subsidize other government agencies: Article 5 of the “National Science and Technology Development Fund Management and Utilization Regulation of Executive Yuan” sets forth the use of the fund, including “expenditure on the advocacy of overall technology development of the nation”, “expenditure on the improvement of the research and development environment for science and technology”. As such, the introduction of the trial run of IPP schemes in Finland would comply with the aforementioned provisions. Second, the legality of subsidizing the public sector by advocating science and technology research and development, like the Department of Industrial Technology at the Ministry of Economic Affairs in the future: reference could be taken from Article 9 of the Ministry of Economic and Energy Affairs Articles of Association (Draft) under which the Department of Industrial Technology shall administer, “1. Strategic planning and implementation in technology under the jurisdiction of the ministry”, and the “planning of technology funding resources, and the establishment of implementation system and evaluation system”. As such, the model of the IPP scheme of Finland is not compatible with the authority and function of the Department of Industrial Technology. In other words, the Department of Industrial Technology shall not perform the function of subsidizing/advocating the duties of procurement innovation of other government agencies, but can introduce the concept of PPI for trial running within its scope of legal framework (e.g., scientific research procurement). Third, the issue of outsourcing for survey of market needs by the public sector on the applicability of the Monitoring Regulation. If the work for outsourcing is an item of work under previous subsidy or work at the appointment of the government, and the fund of the project for procurement is regulated by the Monitoring Regulations. However, for survey of market needs purely planned for subsidy by the entity or required by the procurement cases, they fall within the category of general procurement of service and the Government Procurement Act shall be applicable. In sum, the PPI concept under the FP7 of the EU has been subject to trial run through the IPP scheme of Finland. In Finland, the evaluation mechanism has not yet been fully established. Yet, such attempt to provide a solution for specific subject matter of procurement for the country that faces the rapid changing objective environment through the absorption of dialogue and opinions for innovative solutions is new in the world, and could be considered for adoption within the ROC that has similar challenges in the objective environment. As such, we could start with scientific research procurement. The evaluation of the result is promising; this could be incorporated into the design of the mechanism for scientific research subsidy. For the scope governed by the Government Procurement Act, it entails high cost for amendment, and should be left a subsequent choice for review and planning. 1.TEKES Homepage, http://www.tekes.fi/en/community/Home/351/Home/473 (last visited June 15, 2013). 2.The IPP scheme is the response of Finland to FP7 of the EU in proposing the Public Procurement of Innovative Solutions, PPI. In this paper, PPI and IPP share the same concept while the latter is the substantive name of the pilot project in Finland. See Huang Huei-Hsiang, “International Practice and Legal Analysis of the Advocacy of Government Procurement Innovation – a case study on IPP of TEKES, Finland”, Science and Technology Law Review, Vol. 25 No. 10. PP. 27-45 (2013), by. 3.Pre-commercial procurement, PCP, is the procurement of the government for creating a market and appeals mainly to the service supplier with emphasis the difference from the dialogue between the users and the suppliers. 4.Article 1 of the Government Procurement Act, “This law is instituted for the establishment of a government procurement system to the extent of setting up a fair and transparent procurement procedure, upgrade the efficiency and function of procurement, and guarantee the quality of procurement”. Although this law is instituted for achieving the objective of upgrading procurement efficiency and function, and guarantee of procurement quality, the procedure of the Government Procurement Act aims at keeping distance with the prospective contractors in the procurement process to avoid possible allegation of manipulation of the bidding process, monopoly of the tender, and profit seeking. 5.Federal Acquisition Regulation 2.101, “Acquisition’ means the acquiring by contract with appropriated funds of supplies or services (including construction) by and for the use of the Federal Government through purchase or lease, whether the supplies or services are already in existence or must be created, developed, demonstrated, and evaluated.” FAR Home Page, https://www.acquisition.gov/far/current/html/Subpart%202_1.html#wp1145507 (last visited June 15, 2013). 6.Federal Acquisition Regulation 35.002, “The primary purpose of contracted R&D programs is to advance scientific and technical knowledge and apply that knowledge to the extent necessary to achieve agency and national goals. Unlike contracts for supplies and services, most R&D contracts are directed toward objectives for which the work or methods cannot be precisely described in advance. It is difficult to judge the probabilities of success or required effort for technical approaches, some of which offer little or no early assurance of full success. The contracting process shall be used to encourage the best sources from the scientific and industrial community to become involved in the program and must provide an environment in which the work can be pursued with reasonable flexibility and minimum administrative burden.” FAR Home Page, https://www.acquisition.gov/far/current/html/FARTOCP35.html#wp223483 (last visited June 15, 2013). 7.“For the purposes of this Directive: (a) public service contracts shall mean contracts for pecuniary interest concluded in writing between a service provider and a contracting authority, to the exclusion of:…(ix) research and development service contracts other than those where the benefits accrue exclusively to the contracting authority for its use in the conduct of its own affairs, on condition that the service provided is wholly remunerated by the contracting authority;” Council Directive 92/50/EEC, art. 1, 1992 O.J. (L 209) 1,3. 8.In “Critique of Scientific Research Procurement after the Amendment to Article VI of the Fundamental Science and Technology Act ”, in Science and Technology Law, Vol. 24, No. 10, PP, 29-32 (2012), by Chen Shih-Chieh. 9.Article 9 of the Industrial Innovation Statue, “Competent authorities at the central government may advocate the following in the form of subsidy or supervision: I. Encouragement of industrial innovation or research and development. II. Supply or industrial technology and supervision of industrial upgrading. III. Encouragement for the establishment of innovation or research and development center in the enterprises. IV. Assistance in the establishment of innovation or research and development institutions. V. Encouragement of cooperation among the industry, academic circle, and research institutions. VI. Encouragement of the input to schools by enterprises for the training and development of talents. VII. Augmentation of human resources in the industry. VIII. Assistance in the innovation of regional industries. IX. Any others that help to encourage industrial innovation or research and development. The recipients of the aforementioned subsidy or supervision, the qualification requirements, criteria for screening, application procedure, authority for approval, and other related rules and regulation shall be established by respective competent authority of the central government”. 10.For example, Article 4 of the academic scientific project regulation, “The MOEA shall subsidize academic institutions to perform the following research and development for the advocacy of industrial development and reinforcement of innovation capacity for the country…” 11.Article 6 of the Fundamental Science and Technology Act , “The parties for awarding science and technology research and development subsidized, appointed, funded by the government, or under a budget prepared by public research agencies (institutions) on science and technology research and development shall be determined by evaluation or review process with justifiable reasons for the evaluation and review. The resulting intellectual property rights and result in whole or in part shall be entitled to the pursuer of research and development or authorization for use irrespective of the restriction of state-owned properties”. 12.Article 6 of the Ministry of Economic Affairs Regulation Governing the Entitlement and Utilization of Science and Technology Research and Development Result, “The result of science and technology project of the pursuer shall be entitled to the pursuer unless otherwise specified in This Regulation”. 13.In the EU, the provision of “The procurement authority shall be responsible for all the expenses incurred from the service supply and the benefit so generated shall be owned by the procurement authority for its needs in operation” served as an exception of contracted service of research and development. In other words, the interpretation is inversely made to the extent that contracted service of research and development in the EU is not entitled to the procurement authority. 14.Article 2 of the Government Procurement Act, “Procurement as referred in this law shall be job order for work, the purchase, making to order, leasing of properties and the contract for service or employment”. Article 7 of the same law, “Work as referred to in this law shall be act of building, addition, renovation, remodeling, demolition of structures and equipment accessory to the structures above and below ground level, and the act to change the natural environment, including building, civil engineering Hydraulic engineering, water work, environment, transportation, machinery, electric, chemical engineering and any other engineering project recognized by the competent authority. Properties as referred to in this law are items(except fresh agricultural or aquacultural products), materials, equipment, machinery and other movables, real properties, rights, and other properties recognized by the competent authority. Service as referred to in this law shall be professional service, technical service, information service, research and development, corporate management, repair and maintenance, training, labor, and other forms of service recognized by the competent authority. Where the procurement may involve two or more of the aforementioned content, which made it difficult to identify the very nature, the content accounted for a larger proportion of the budget for total work shall stand”. 15.Op. Cit, Note 13. 16.Article 6 – Paragraph 4 of the Fundamental Science and Technology Act , “the Government Procurement Act shall not be applicable to public schools, public research agencies (institutions), non-profit organizations or groups receiving government subsidy or assignment, or procurement of public research agencies (institutions) under a budget of science and technology research and development prepared in compliance with applicable law unless otherwise specified in a treaty or agreement binding the ROC and a third country. Yet, they are subject to the monitoring of the subsidizing, assigning, or the competent authority. The regulation for monitoring and management shall be established by the competent authority in the central government”. 17.Op. Cit. Note 8, PP36-37. 18.Table of “Research and Development Projects” governed by the “Government Procurement Act” under Public Construction Commission, Executive Yuan Letter Chi-Tzi No. 89009844. The Government Procurement Act shall not be applicable to the selection of the recipients of subsidy. 19.The cause of legislation for Article 39 of the Government Procurement Act dated May 27 2998, “II. Paragraph II and III explicitly state that contractors may act on behalf of the entity in project management, and shall be in specific relation with the contractors responsible for the planning, design, construction of the project to avoid funneling of interest, cover up each other, and acting as a participant and the judge at the same time”. 20.Particulars for Public Viewing of Tender Invitation Documents of Public Works, at http://lawweb.pcc.gov.tw/LawContentDetails.aspx?id=FL029347&KeyWordHL=&StyleType=1 (last browsing date: 2013/6/15) 21.Article 12 of the Regulation Governing the Subsidy of Research Institutions in Industrial Innovation and Research and Development Advocated by the Ministry of Economic Affairs, “The MOEA or its functionaries shall encourage research institutions to introduce technologies, joint ventures in the development and participation in the pursuit of technology projects through interdisciplinary or cross-function cooperation for the effective integration of domestic and foreign research and development resources and capacity, the assistance of the upgrading of traditional industries, or advocacy of the development of knowledge service for the best interest of the industry”. Article 8 of the Regulation Governing the Subsidy of Academic Institutions in Industrial Innovation and Research and Development Advocated by the Ministry of Economic Affairs , “The MOEA shall request the applicants of academic technology projects to invite the joint participation of research institutions or companies and execute the academic technology project in interdisciplinary or cross-function mode of operation for the effective integration of research and development resources and capacities at home and abroad and create the optimized result in industry”. Article 4 of the Ministry of Economic Affairs Regulation Governing the Subsidy and Supervision for Assistance of Industrial Innovation, “The MOEA or its functionaries may provide subsidy for the following industrial innovative activities:… IV. Encouragement for joint venture among the industry, academia, and research institutions”. 22.Refer to important notice of application for general type of projects, IV. Types of subsidies for general academic scientific research projects. 23.Refer to important notice of application for local type of projects, III. The positioning, nature, and subsidy for local academic scientific research projects. 24.Article 55 of the Government Procurement Act, “Entities taking minimum offer for procurement and have been approved by the senior authority and announced in the notice of tender and the tender invitation documents and cannot determine the award pursuant to the requirements or preceding two articles may proceed to consultation”. 25.Article 56 of the Government Procurement Act, “ …if the evaluation result cannot determine the best bid on the basis of the decision of the head of entity or more than half of the members of the evaluation committee, proceed to consultation and comprehensive evaluation for determining the best bid”. 26.Article 57 of the Government Procurement Act, “Entity elects to proceed to consultation in accordance to the requirements specified in the previous two articles shall comply with the following principles: … III. The content of the original tender invitation documents to be revised shall be highlighted before proceeding to consultation”. 27.Paragraph 1, Article 39 of the Government Procurement Act, “Entities may assign the duties of project management in planning, design, supply, or performance of contract to a contractor in procurement under this law when making procurement”. 28.Paragraph 2, Article 38 of the Government Procurement Act Implementation Procedure, “Subsequent procurement procedure shall not be applicable to situations specified in I and II of the previous section if there is no alleged conflict of interest or unfair competition and at the approval of the entity”. 29.Paragraph 3, Article 6 of Fundamental Science and Technology Act , “The Executive Yuan shall coordinate and regulate the entitlement and utilization of the intellectual property right and result as mentioned in preceding two sections under the principle of equity and effectiveness, with reference to the proportion and contribution of capital and service, the nature, potential of utilization, social benefit, national security and the effect on the market of the result of science and technology research and development, and on the basis of its purpose, necessary condition, duration, scope, proportion in whole or in part, registration, management, distribution of incomes, avoidance of conflict of interest and the disclosure of related information, the intervention of the subsidizing agent in authorization of a third party, or procedure for nationalization. Respective competent authority at different level shall establish relevant legal rules for such purpose”.
Review of Taiwan's Existing Regulations on the Access to Bioloical ResourcesThe activities of accessing to Taiwan's biological resources can be governed within certain extent described as follows. 1 、 Certain Biological Resources Controlled by Regulations Taiwan's existing regulation empowers the government to control the access to biological resources within certain areas or specific species. The National Park Law, the Forestry Act, and the Cultural Heritage Preservation Act indicate that the management authority can control the access of animals and plants inside the National Park, the National Park Control Area, the recreational area, the historical monuments, special scenic area, or ecological protection area; forbid the logging of plants and resources within the necessary control area for logging and preserved forestry, or control the biological resources inside the natural preserved area. In terms of the scope of controlled resources, according to the guidance of the Wildlife Conservation Act and the Cultural Heritage Preservation Act, governmental management authority is entitled to forbid the public to access the general and protected wild animals and the plant and biological resources that are classified as natural monuments. To analyse the regulation from another viewpoint, any access to resources in areas and of species other than the listed, such as wild plants or microorganism, is not regulated. Therefore, in terms of scope, Taiwan's management of the access to biological resources has not covered the whole scope. 2 、 Access Permit and Entrance Permit Taiwan's current management of biological resources adopts two kinds of schemes: access permit scheme and entrance permit in specific areas. The permit allows management authority to have the power to grant and reject the collection, hunting, or other activities to access resources by people. This scheme is similar to the international standard. The current management system for the access to biological resources promoted by many countries and international organizations does not usually cover the guidance of entrance in specific areas. This is resulting from that the scope of the regulation about access applies for the whole nation. However, since Taiwan has not developed regulations specifically for the access of bio-research resources, the import/export regulations in the existing Wildlife Conservation Act, National Park Law, Forestry Act, and Cultural Heritage Preservation Act may provide certain help if these regulations be properly connected with the principle of access and benefit sharing model, so that they will help to urge people to share the research interests. 3 、 Special Treatments for Academic Research Purpose and Aborigines Comparing to the access for the purpose of business operation, Taiwan's regulations favour the research and development that contains collection and hunting for the purpose of academic researches. The regulation gives permits to the access to biological resources for the activities with nature of academic researches. For instance, the Wildlife Conservation Act, National Park Law, and theCultural Heritage Preservation Act allow the access of regulated biological resources, if the academic research unit obtains the permit, or simply inform the management authority. In addition, the access by the aborigines is also protected by the Forestry Act, Cultural Heritage Preservation Act, and the Aboriginal Basic Act. The aborigines have the right to freely access to biological resources such as plants, animals and fungi. 4 、 The Application of Prior Informed Consent (PIC) In topics of the access to and benefit sharing of biological resources, the PIC between parties of interests has been the focus of international regulation. Similarly, when Taiwan was establishing theAboriginal Basic Act, this regulation was included to protect the aborigines' rights to be consulted, to agree, to participate and to share the interests. This conforms to the objective of access and benefit sharing system. 5 、 To Research and Propose the Draft of Genetic Resources Act The existing Wildlife Conservation Act, National Park Law, Forestry Act,Cultural Heritage Preservation Act, Aboriginal Basic Act provide the regulation guidance to the management of the access to biological resources within certain scope. Comparing to the international system of access and benefit sharing, Taiwan's regulation covers only part of the international guidance. For instance, Taiwan has no regulation for the management of wild plants and micro-organism, so there is no regulation to confine the access to wild plants and microorganism. To enlarge the scope of management in terms of the access to Taiwan's biological resources, the government authority has authorize the related scholars to prepare the draft of Genetic Resources Act. The aim of the Genetic Resources Act is to establish the guidance of the access of genetic resources and the sharing of interests in order to preserve the genetic resources. The draft regulates that the bio-prospecting activity should be classified into business and academic, with the premise of not interfering the traditional usages. After classification, application of the permit should be conducted via either general or express process. During the permit application, the prospector, the management authority, and the owner of the prospected land should conclude an agreement jointly. In the event that the prospector wishes to apply for intellectual property rights, the prospector should disclose the origin of the genetic resources and provide the legally effective documents of obtaining these resources. In addition, a Biodiversity Fund should be established to manage the profits derived from genetic resources. The import/export of genetic resources should also be regulated. Violators should be fined.
- Impact of Government Organizational Reform to Scientific Research Legal System and Response Thereto (1) – For Example, The Finnish Innovation Fund (“SITRA”)
- The Demand of Intellectual Property Management for Taiwanese Enterprises
- Blockchain in Intellectual Property Protection
- Impact of Government Organizational Reform to Research Legal System and Response Thereto (2) – Observation of the Swiss Research Innovation System
- Recent Federal Decisions and Emerging Trends in U.S. Defend Trade Secrets Act Litigation
- The effective and innovative way to use the spectrum: focus on the development of the "interleaved/white space"
- Copyright Ownership for Outputs by Artificial Intelligence
- Impact of Government Organizational Reform to Research Legal System and Response Thereto (2) – Observation of the Swiss Research Innovation System
