Brief Introduction to Taiwan Social Innovation Policies

Brief Introduction to Taiwan Social Innovation Policies
2021/09/13
1. Introduction
The Millennium Development Goals (MDGs)[1] set forth by the United Nations in 2000 are carried out primarily by nations and international organizations. Subsequently, the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) set forth by the United Nations in 2015 started to delegate the functions to organizations of all levels. Presently, there is a global awareness of the importance of balancing “economic growth”, “social progress”, and “environmental protection” simultaneously during development. In the above context, many similar concepts have arisen worldwide, including social/solidarity economy, social entrepreneurship and social enterprise, and social innovation.
Generally, social innovation aims to alter the interactions between various groups in society through innovative applications of technology or business models, and to find new ways to solve social problems through such alterations. In other words, the goal is to use innovative methods to solve social problems. The difference between social innovation and social enterprise is that social enterprise combines commercial power to achieve its social mission under a specific perspective, while social innovation creates social value through cooperation with and coordination among technology, resources, and communities under a diversified nature.
2. Overview of Taiwan Social Enterprise Policy
To integrate into the global community and assist in the development of domestic social innovation, Taiwan’s Executive Yuan launched the “Social Enterprise Action Plan” in 2014, which is the first policy initiative to support social enterprises (from 2014 to 2016). Under this policy initiative, through consulting with various ministries and applying methods such as “amending regulations”, “building platforms”, and “raising funds”, the initiative set to create an environment with favorable conditions for social innovation and start-ups. At this stage, the initiative was adopted under the principle of “administrative guidance before legislation” in order to encourage private enterprise development without excessive burden, and avoid regulations restricting the development of social enterprises, such as excessive definition of social enterprises. Moreover, for preserving the original types of these enterprises, this Action Plan did not limit the types of social enterprises to companies, non-profit organizations, or other specific types of organizations.
To sustain the purpose of the Social Enterprise Action Plan and to echo and reflect the 17 sustainable development goals proposed in SDGs by the United Nations, the Executive Yuan launched the “Social Innovation Action Plan” (effective from 2018 to 2022) in 2018 to establish a friendly development environment for social innovation and to develop diversified social innovation models through the concept of “openness, gathering, practicality, and sustainability”. In this Action Plan, “social innovation” referred to “social innovation organizations” that solve social problems through technology or innovative business models. The balancing of the three managerial goals of society, environment value, and profitability is the best demonstration of the concept of social innovation.
3. Government’s Relevant Social Enterprise Policy and Resources
The ministries of the Taiwan Government have been promoting relevant policies in accordance with the Social Innovation Action Plan issued by the Executive Yuan in 2018, such as the “Registration System for Social Innovation Enterprises” (counseling of social enterprises), the “Buying Power - Social Innovation Products and Services Procurement”, the “Social Innovation Platform” established by the Ministry of Economic Affairs, the “Social Innovation Manager Training Courses”, the “Promoting Social Innovation and Employment Opportunities” administered by the Ministry of Labor, and the “University Social Responsibility Program” published by the Ministry of Education. Among the above policies stands out the measures adopted by the Ministry of Economic Affairs, and a brief introduction of those policies are as follows:
i. Social Innovation Platform
To connect all resources involved in social issues to promote social innovation development in Taiwan, the Ministry of Economic Affairs established the “Social Innovation Platform”.[2] With visibility through the Social Innovation Platform, it has become more efficient to search for targets in a public and transparent way and to assist with the input of resources originally belonging to different fields in order to expand social influence.
As a digital platform gathering “social innovation issues in Taiwan,” the Social Innovation Platform covers multiple and complete social innovation resources, which include the “SDGs Map” constructed on the Social Innovation Platform, by which we can better understand how county and city governments in Taiwan implement SDGs and Voluntary Local Review Reports, and which allow us to search the Social Innovation Database[3] and the registered organizations, by which citizens, enterprises, organizations, and even local governments concerned with local development can find their partners expediently as possible, establish service lines to proactively assist public or private entities with their needs/resources, and continue to enable the regional revitalization organizations, ministries, and enterprises to identify and put forward their needs for social innovation through the function of “Social Innovation Proposals”, which assist social innovation organizations with visibility while advancing cooperation and expanding social influence.
In addition, the “Event Page” was established on the Social Innovation Platform and offers functions, such as the publishing, searching, and sorting of events in four major dimensions with respect to social innovation organization, governments, enterprises, and citizens; and encourages citizens, social innovation organizations, enterprises, and governments to devote themselves via open participation to continuously expande the influence of the (Civic Technology) Social Innovation Platform. The “Corporate Social Responsibility Report” collects the corporate social responsibility reports, observes the distribution of resources for sustainable development by corporations in Taiwan, offers filtering functions by regions, keyword, popular rankings, and or SDGs types, and provides contact information and a download function for previous years’ reports, in order to effectively assist social innovation organizations to obtain a more precise understanding of the status quo, needs, and trends with respect to their development of respective products and services.
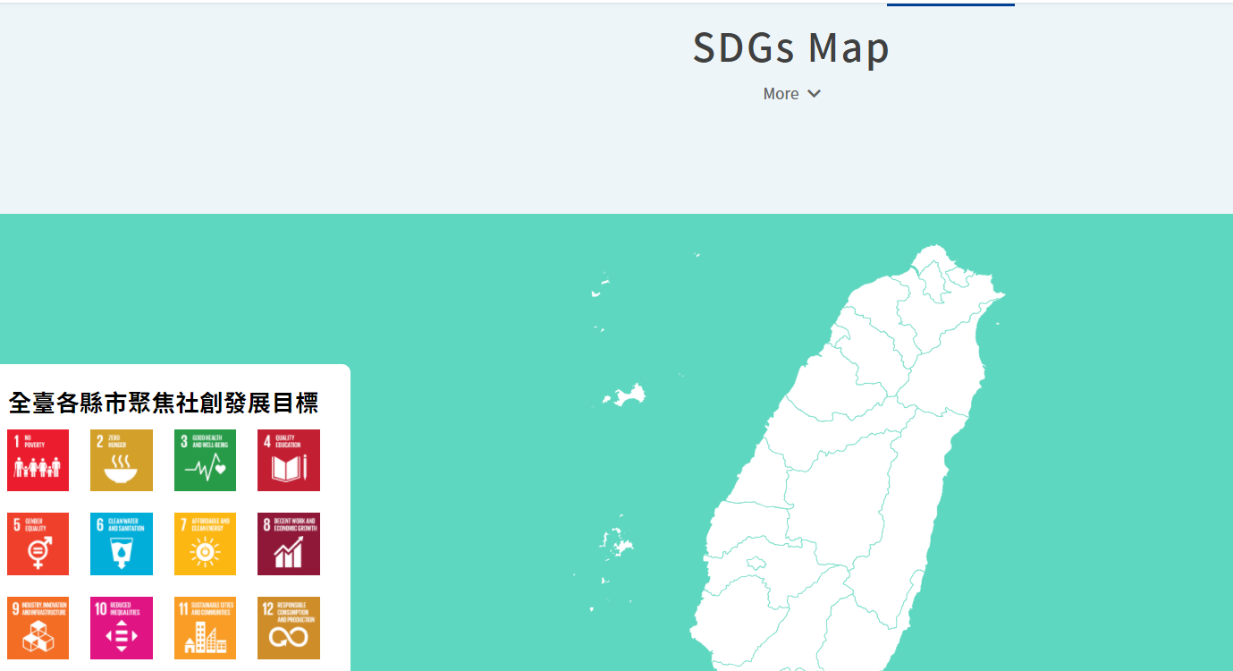
Figure 1: SDGs Map
Reference: Social Innovation Platform (https://si.taiwan.gov.tw/)
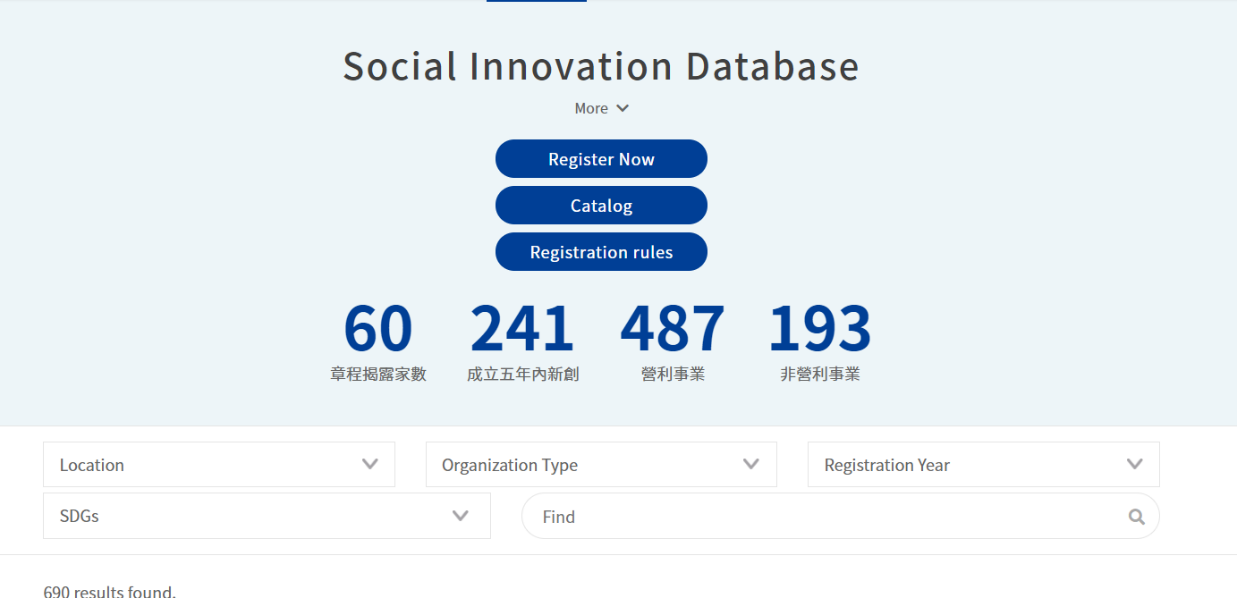
Figure 2: Social Innovation Database
Reference: Social Innovation Platform (https://si.taiwan.gov.tw/)
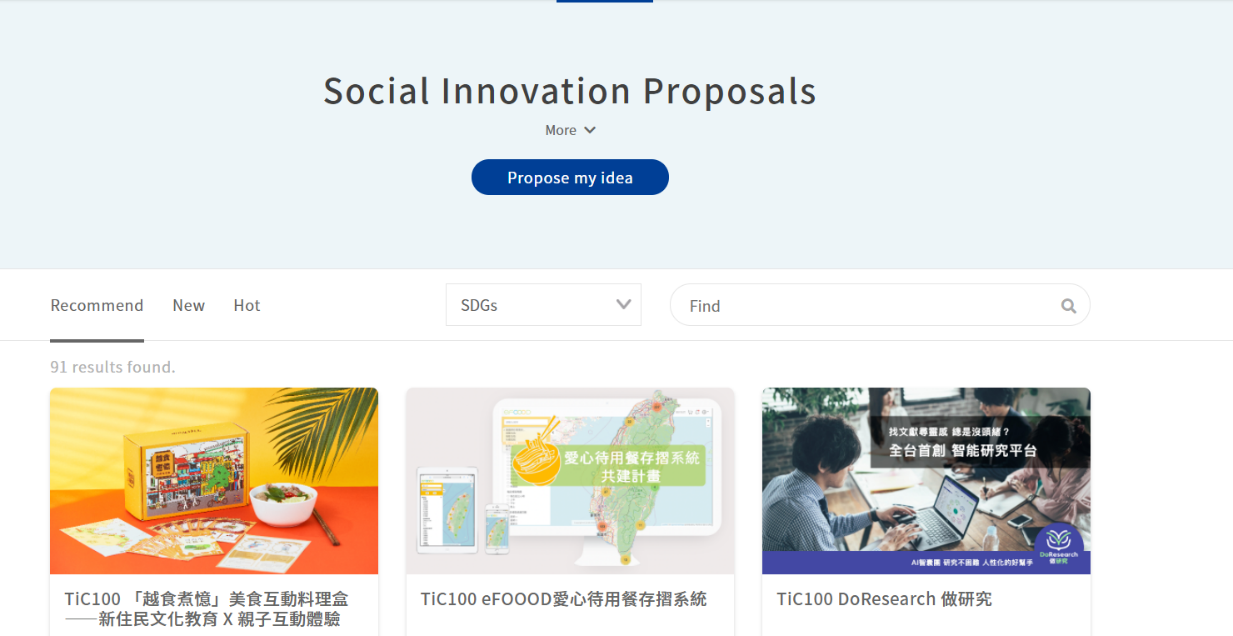
Figure 3: Social Innovation Proposals
Reference: Social Innovation Platform (https://si.taiwan.gov.tw/)
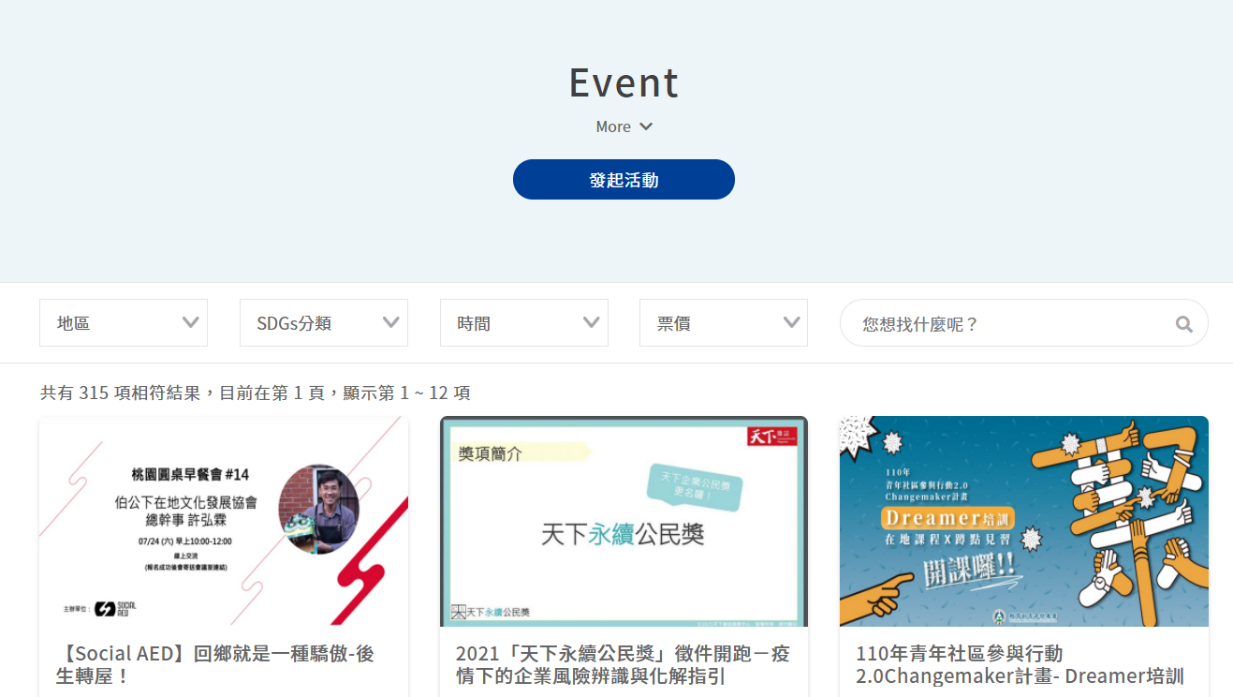
Figure 4: Event Page
Reference: Social Innovation Platform (https://si.taiwan.gov.tw/)

Figure 5: Corporate Social Responsibility Report
Reference: Social Innovation Platform (https://si.taiwan.gov.tw/)
ii. Social Innovation Database
To encourage social innovation organizations to disclose their social missions, products and services, and to guide society to understand the content of social innovation, and to assist the administrative ministries to be able to utilize such information, the Ministry of Economic Affairs issued the “Principles of Registration of Social Innovation Organizations” to establish the “Social Innovation Database”.
Once a social innovation organization discloses the items, such as its social missions, business model, or social influence, it may obtain the relevant promotional assistance resources, including becoming a trade partner with Buying Power (Social Innovation Products and Services Procurement), receiving exclusive consultation and assistance from professionals for social innovation organizations, and becoming qualified to apply to entering into the Social Innovation Lab. Moreover, the Ministry of Economic Affairs is simultaneously consolidating, identifying, and designating the awards and grants offered by the various ministries, policies and measures in respect of investment, and financing and assistance, as resources made available to registered entities.
As of 25 May 2021, there were 658 registered social innovation organizations and 96 Social Innovation Partners (enterprises with CSR or ESG resources that recognize the cooperation with social innovation under the social innovation thinking model may be registered as a “Social Innovation Partner”). The public and enterprises can search for organizations registered in the Social Innovation Database through the above-said Social Innovation Platform, the search ability of which advances the exposure of and the opportunities for cooperation with social innovation organizations.
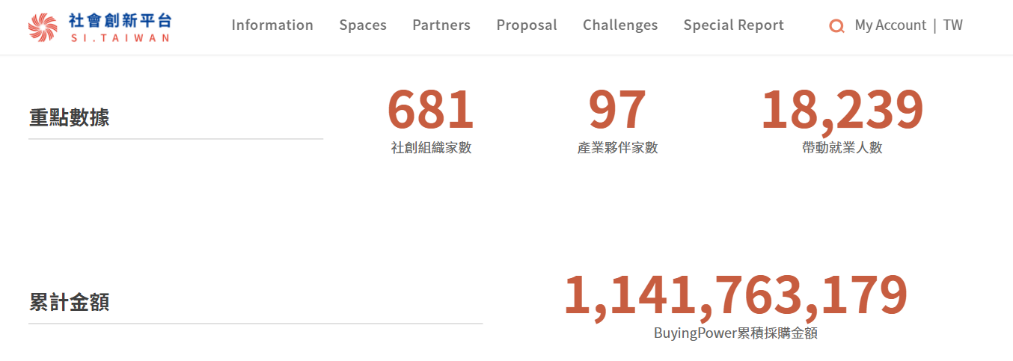
Figure 6: Numbers of registered social innovation organizations and accumulated value of purchases under Buying Power
Reference: Social Innovation Platform(https://si.taiwan.gov.tw/)
iii. Buying Power - Social Innovation Products and Services Procurement
In order to continue increasing the awareness on social innovation organizations and related issues and promote responsible consumption and production in Taiwan, as well as to raise the attention of the commercial sector to the sustainability-driven procurement models, the Ministry of Economic Affairs held the first “Buying Power - Social Innovation Products and Services Procurement” event in 2017. Through the award system under the Buying Power, it continues to encourage the governments, state-owned enterprises, private enterprises, and organizations to take the lead in purchasing products or services from social innovation organizations, to provide the relevant resources so as to assist social innovation organizations to obtain resources and to explore business opportunities in the markets, to practice responsible consumption and production, and to promote innovative cooperation between all industries and commerce and social innovation organizations.
The aim of the implementation of the Buying Power is to encourage the central and local governments, state-owned enterprises, private enterprises, and non-governmental organizations to purchase products or services from organizations registered in the Social Innovation Database, while prizes will be awarded based on the purchase amounts accumulated during the calculation period. The winners can obtain priority in applying for membership in the Social Innovation Partner Group, with corresponding member services, in the future.
Under the Social Innovation Platform, both the amount of purchase awards and the number of applicants for special awards continue to increase. So far, purchases have accumulated to a value of more than NT$1.1 billion (see Figure 6), and more than 300 organizations have proactively participated.
iv. Social Innovation Mark
In order to promote public awareness of social innovation, the Ministry of Economic Affairs has been charged with the commissioned task of promoting the Social Innovation Mark, and issued “ The Small and Medium Enterprise Administration of the Ministry of Economic Affairs Directions for Authorization of the Social Innovation Mark” as the standard for the authorization of the Social Innovation Mark. Social innovation organizations can use the Mark, through obtaining authorization, to hold Social Innovation Summits or other social innovation activities for promoting social innovation concepts.
In order to build the Mark as a conceptual symbol of social innovation, the Ministry of Economic Affairs has been using the Social Innovation Mark in connection with various social innovation activities, such as the Social Innovation Platform, the Buying Power, and the annual Social Innovation Summit. Taking the selection of sponsors of the Social Innovation Summit in 2022 as an example[4], only organizations that have obtained authorization of the Social Innovation Mark can use the Mark to hold the Social Innovation Summit.

Figure 7: The Social Innovation Mark of the Small and Medium Enterprise Administration, Ministry of Economic Affairs
IV. Conclusion
The “Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development” (OECD) regards social innovation as a new strategy for solving future social problems and as an important method for youth entrepreneurship and social enterprise development. Taiwan’s social innovation energy has entered a stage of expansion and development. Through the promotion of the “Social Innovation Action Plan,” the resources from the central and local governments are integrated to establish the Social Innovation Platform, the Social Innovation Database, the Social Innovation Lab, and the Social Innovation Mark. In addition, incentives such as the Buying Power have been created, manifesting the positive influence of Taiwan’s social innovation.
[1] MDGs are put forward by the United Nations in 2000, and are also the goals requiring all the 191 member states and at least 22 international organizations of the United Nations to be committed to on their best endeavors, including: 1. eradicating extreme poverty and hunger, 2. applying universal primary education, 3. promoting gender equality and empowering women, 4. reducing child mortality rates, 5. improving maternal health, 6. combatting HIV/AIDS, malaria, and other diseases, 7. ensuring environmental sustainability, and 8. establishing a global partnership for development.
[2] Please refer to the Social Innovation Platform: https://si.taiwan.gov.tw/.
[3] Please refer to the Social Innovation Database: https://si.taiwan.gov.tw/Home/Org_list.
[4] Please refer to the guidelines for the selection of sponsors of the 2022 Social Innovation Summit: https://www.moeasmea.gov.tw/files/6221/4753E497-B422-4303-A8D4-35AE0B4043A9
Innovative Practice of Israel's Government Procurement Government procurement is an important pillar of government services. Because of the huge number of government purchases, government procurement management play an important role in promoting public sector efficiency and building citizenship. Well-designed government procurement systems also help to achieve policy such as environmental protection, innovation, start-ups and the development of small and medium-sized enterprises. Nowadays, countries in the world, especially OECD countries, have been widely practiced with innovative procurement to stimulate innovation and start-ups, and call Innovation procurement can deliver solutions to challenges of public interest and ICTs can play a major role in this. However, in the OECD countries, in addition to the advanced countries that have been developed, many developing countries have also used government procurement to stimulate national R & D and innovation with remarkable results. Israel is one of the world's leading technology innovation centers, one of the most innovative economies in the world, continues to leverage its own strengths, support of technology entrepreneurship and unique environment, an international reputation in the high-tech industry, the spirit of technological innovation and novelty. Government procurement is a core element of the activities of Israeli government, agreement with suppliers and compliance with the Mandatory Tenders Law. The main challenge is how to ensure efficiency and maintain government performance while ensuring an equitable and transparent procurement process. Israel’s Mandatory Tenders Law has shown the central role played by the Israeli Supreme Court in creating and developing this law, even in the absence of any procurement legislation, based instead on general principles of administrative law. Once the project of creating a detailed body of public tendering law had been completed, and the legislator was about to step in, the Supreme Court was prepared to step out and transferring the jurisdiction to lower courts. The Knesset passed the Mandatory Tenders Law, and based on it the Government issued the various tendering regulations. Besides, Israel's various international agreements on government procurement, mainly GPA and other bilateral international agreements such as free trade agreements with Mexico and Colombia and free trade agreements and memoranda of understanding with the United States. The practical significance of these commitments can only be understood on the backdrop of Israel’s domestic preference and offset policies. These policies were therefore discussed and analyzed as they apply when none of the international agreements applies. The Challenge Tenders "How to solve the problem of overcrowding in the emergency department and the internal medicine department?" is the first of a series of "problem solicitations" released by the Israeli Ministry of Health which seeks to find a digital solution to the public health system problem, questions from the government while avoiding preconceived prejudices affect the nature of the solution, allowing multiple innovative ideas from different fields to enter the health system, make fair and transparent judgments about the ideal solution to the problem. In order to ensure transparency and integrity, equality, efficiency and competition in the decision-making process, the tender proposed by the Israeli Ministry of Health defines a two-stage tender process. The Ministry of Health of Israel, in order to improve the quality of medical care, shorten the waiting time for hospitalized patients, protect the dignity of patients and their families with patients as its center, and ensure their rights, while alleviating the burden of hospital staff, so as to pass the targeted treatment areas reduce the gap between various residential areas. The Israeli government deals with these issues through challenging tenders and offers a digital solution combined with innovative ideas. The initiative proposed through the development of public service projects can raise the level of public services in the country and help the government to reduce costs and achieve the purpose of promoting innovation with limited conceptual, technical and financial capabilities. In addition, due to the online operation of the challenging tender process throughout the entire process, fair and transparent procedures can be ensured, while public-private partnerships are encouraged to facilitate the implementation of the implementation plan.
Research on Taiwan’s Policies of Innovative Industry Development in Recent Years (2015-2016)Research on Taiwan’s Policies of Innovative Industry Development in Recent Years (2015-2016) 1. “Five plus Two” Innovative Industries Policy On June 15, 2016, Premier Lin Chuan met with a group of prominent business leaders to talk about a government project on five innovative industries, which aim to drive the next generation of businesses in R.O.C.. Subsequently the program was expanded to include “new agriculture” and the “circular economy” as the “+2.” The program was then broadened even further to include the Digital Economy and Cultural Innovation, with even Semiconductors and IC Design included, although the name of the policy remains 5+2. Speaking at the Third Wednesday Club in Taipei, Premier Lin said the industries require more investment to drive the next generation of industry growth momentum in R.O.C., create high-quality jobs, and upgrade the industrial competitiveness. Executive Yuan has selected the five innovative industries of Asia Silicon Valley, smart machinery, green energy, biotech & pharmaceutical industry, and national defense, which will be the core for pushing forward the next-generation industrial growth and improve overall environment by creating a cluster effect that links local and global industries, while simultaneously raising wages and stimulating employment. Premier Lin said, regarding industrial competitiveness and investment issues the lackluster economy has stifled investment opportunities, and with limited government budgets, the private sector must play the larger role in investments. Regarding the “Five major Innovative Industries” project, Premier Lin said the National Development Council is currently drafting long-term plan to attract talent, create a thriving working environment, and infuse companies with more innovation, entrepreneurship and young workers. In addition, R.O.C. must also cultivate a strong software industry, without which it would be difficult to build a highly intelligent infrastructure. The National Development Council said the program possess both the capacity of domestic demand and local characteristics, as the core for pushing forward the next-generation industrial growth. The government aims to promote a seamless synergy of investment, technology, and the talent, in order to develop innovative industrial clusters for furthering global linkage and nurturing international enterprises. In the meantime, the government also aims at achieving the enhancement of technology levels, balanced regional development, as well as realizing the benefits of job creation. 2. The Asia Silicon Valley Development Plan In September 2016 the government approved the Asia Silicon Valley Development Plan, which connect Taiwan to global tech clusters and create new industries for the next generation. By harnessing advanced technological research and development results from around the world, the plan hopes to promote innovation and R&D for devices and applications of the internet of things (IoT), and upgrade Taiwan’s startup and entrepreneurship ecosystem. The four implementation strategies are as follows: (1) Building a comprehensive ecosystem to support innovation and entrepreneurship (2) Connect with international research and development capabilities (3) Create an IoT value chain (4) Construct diversified test beds for smart products and services by establishing a quality internet environment Taiwan’s first wave of industrial development was driven by continuous technological innovation, and the wave that followed saw the information industry become a major source of economic growth. 3. Global Hub for Smart Machinery On July 21, 2016, Premier Lin Chuan said at a Cabinet meeting, the government aims to forge Taiwan into a global manufacturing hub for intelligent machinery and high-end equipment parts. Upgrading from precision machinery to intelligent machinery is the main goal of putting intelligent machinery industry into focal execution area expecting to create jobs and to maximize the production of production line as well as to forge central Taiwan into a global manufacturing hub for smart machinery. The Ministry of Economic draws up the Intelligent Machinery Promotion Program to establish the applications of the technology and capacity of services that fit the demand of the market. The program embodies two parts. The first is to accelerate the industrialization of intelligent machinery for building an ecosystem. The second is to improve intelligentization by means of introducing the intelligent machinery into the industries. The execution policy of the Intelligent Machinery Promotion Program is to integrate the intelligent functions such as malfunctions predictions, accuracy compensation, and automatic parameter setting into the machinery industry so as to have the ability to render the whole solutions to the problem. Simultaneously, the program employs three strategies, which are connecting with the local industries, connecting with the future, and connecting with the world, to develop the mentioned vision and objectives. Especially, the way to execute the strategy of connecting with the local industries consists of integrating the capabilities of industry, research organization and the government. At the meantime, the government will encourage the applications of smart vehicles and unmanned aerial vehicles and train the talents as well. The thinking of connecting with the future lies in the goal of deepening the technologies, establishing systematic solutions, and providing a testing areas, which focus on the related applications such as aerospace, advanced semiconductor, smart transportation, green vehicles, energy industry, whole solutions between factories, intelligent man-machine coordination, and robots of machine vision combined with intelligent machinery applications. The government would strengthen the cross-cutting cooperation to develop machines for aerospace and integrate the system of industrial division to form a cluster in order to create Taiwanese IoT technology. Eventually, Taiwan will be able to connect with the world, enhance international cooperation, expand export trade and push industry moving toward the age of information and digital economy and break the edge of industry technology to make the industry feel the goodwill of the government. 4. Green energy innovations The government’s “five plus two” innovative industries program includes a green energy industrial innovation plan passed October 27, 2016 that will focus on Taiwan’s green needs, spur extensive investments from within and outside the country, and increase quality employment opportunities while supporting the growth of green energy technologies and businesses. The government is developing the Shalun Green Energy Science City. The hub’s core in Shalun will house a green energy technology research center as well as a demo site, providing facilities to develop research and development (R&D) capabilities and conduct the requisite certification and demonstration procedures. The joint research center for green energy technologies will integrate the efforts of domestic academic institutions, research institutes, state-run enterprises and industry to develop green energy technologies, focusing on four major functions: creating, conserving and storing energy, as well as system integration. Development strategies include systems integration and finding better ways to conserve, generate and store energy by promoting green energy infrastructure, expanding renewable energy capabilities and cooperating with large international firms. The emergence of the green economy has prompted the government to build infrastructure that will lay the foundation for Taiwan’s green energy sector, transform the nation into a nuclear-free society, and spur industrial innovation. For innovative technology industries, green energy industries can drive domestic economic development by attracting more venture capital and creating more employment opportunities. 5. Biomedical Industry Innovation Program To facilitate development of Taiwan’s biomedical industry, the government proposed a “biomedical industrial innovation promotion program” on November 10, 2016 to serve as the nation’s new blueprint for innovative biomedical research and development (R&D). To facilitate development of the biomedical industry, the government proposed a “biomedical industrial innovation promotion program”. The program centered on the theme of “local, global and future links,” “the biomedical industrial innovation promotion program” includes four action plans: (1) Build a comprehensive ecosystem To address a rapidly ageing global population, Taiwan will enhance the biomedical industry’s capacity for innovation by focusing on talent, capital, topic selection, intellectual property, laws and regulations, and resources. (2) Integrate innovative business clusters Established by the Ministry of Science and Technology and based in Hsinchu Biomedical Science Park, the center will serve as a government think tank on related issues. It is also tasked with initiating and advancing exchanges among local and foreign experts, overseeing project implementation, promoting investment and recruiting talents. Equally important, it will play a central role in integrating resources from other biomedical industry clusters around the country, including Nangang Software Park in Taipei City, Central Taiwan Science Park in Taichung City and Southern Science Park in Tainan City. (3) Connect global market resources Building on Taiwan’s advantages, promote M&A and strategic alliances, and employ buyout funds and syndicated loans to purchase high-potential small and medium-sized international pharmaceutical companies, medical supply companies, distributors and service providers. Use modern mosquito-borne disease control strategies as the foundation of diplomatic cooperation, and promote the development of Taiwan’s public health care and medical services in Southeast Asian countries. (4) Promote specialized key industries Promote niche precision medical services, foster clusters of world-class specialty clinics, and develop industries in the health and wellness sectors. 6. DIGITAL NATION AND INNOVATIVE ECONOMIC DEVELOPMENT PLAN On November 24, 2016, the Executive Yuan promote the Digital Nation and Innovative Economic Development Plan (2017-2025) (DIGI+ program), the plan’s main goals for 2025 are to grow R.O.C.’s digital economy to NT $ 6.5 trillion (US$205.9 billion), increase the digital lifestyle services penetration rate to 80 percent, speed up broadband connections to 2 Gbps, ensure citizens’ basic rights to have 25 Mbps broadband access, and put R.O.C. among the top 10 information technology nations worldwide. In addition to the industrial economy, the program can jump off bottlenecks in the past industrial development, and promote the current Internet of things, intelligent machinery, green energy, medical care and other key national industries, but also attaches great importance to strengthening the digital infrastructure construction, the development of equal active, as well as the creation of a service-oriented digital government. It is also hoped that through the construction of a sustainable and intelligent urban and rural area, the quality of life will be improved and the people will enjoy a wealthy and healthy life. Over the next 8 years, the government will spend more than NT $ 150 billion. The plan contains several important development strategies: DIGI+Infrastructure: Build infrastructure conducive to digital innovation. DIGI+Talent: Cultivate digital innovation talent. DIGI+Industry: Support cross-industry transformation through digital innovation. DIGI+Rights: Make R.O.C. an advanced society that respects digital rights and supports open online communities. DIGI+Cities: Build smart cities through cooperation among central and local governments and the industrial, academic and research sectors. DIGI+Globalization: Boost R.O.C.’s standing in the global digital service economy. The program aims to build a favorable environment for digital innovation and to create a friendly legal environment to complete the draft amendments to the Digital Communications Law and the Telecommunications Act as soon as possible, foster cross-domain digital talents and develop advanced digital technologies, To create a digital economy, digital government, network society, smart urban and rural and other national innovation ecological environment in order to achieve "the development of active network society, promote high value innovation economy, open up rich countries of the policy vision. In order to achieve the overall effectiveness of the DIGI + program, interdisciplinary, inter-ministerial, inter-departmental and inter-departmental efforts will be required to collaborate with the newly launched Digital National Innovation Economy (DIGI +) Promotion Team. 7. “NEW AGRICULTURE” PROMOTION PROJECT At a Cabinet meeting On December 08, 2016, Premier Lin Chuan underscored the importance of a new agricultural paradigm for Taiwan’s economic development, adding that new agriculture is an integral part of the “five plus two” industrial innovation projects proposed by President Tsai Ing-wen. The “new agriculture” promotion project uses innovation technology to bring value to agricultural, and build new agricultural paradigm, agricultural safety systems and promote agricultural marketing. This project also takes resources recycling and environmental sustainability into consideration to promote agricultural transformation, and build a robust new agricultural system. This agricultural project is expected to increase food self-sufficiency rate to 40%, level up agricultural industry value by NT$43.4 billion, create 370,000 jobs and increase portion of total agricultural exports to new overseas markets to 57% by 2020. This project contains three aspects: First is “building new agricultural paradigm”: to protect farmers, agricultural development and ensure sustainability of the environment. Second is “building agricultural safety systems”: Ensuring product safety and quality, and building a certification system which can be trust by the consumers and is consistent with international standards. Last but not least is “leveling up agricultural marketing and promotions”: enhancing promotion, making the agricultural industry become profitable and sustainable. Council of Agriculture’s initiatives also proposed 10 policies to leverage agricultural industry, not only just use the passive subsidies measure of the past. These policies including promoting environmentally friendly farming practices; giving farmers that are beneficial(green) to the land payments; stabilizing farmers’ incomes; increasing the competitiveness of the livestock and poultry industries; using agricultural resources sustainably; ensuring the safety of agricultural products; developing technological innovation; leveling up food security; increasing diversification of domestic and external marketing channels; and increasing agriculture industry added value. In this statutes report, Council of Agriculture said this project will accelerate reforms, create new agricultural models and safety systems, but also build a new sustainable paradigm of agricultural. Premier Lin Chuan also backed this “five plus two innovative industries” program and “new agriculture” project, and asked Council of Agriculture to reviewing the possible legal changes or amendment that may help to enhance the transformation of agricultural sector.
The Research on ownership of cell therapy productsThe Research on ownership of cell therapy products 1. Issues concerning ownership of cell therapy products Regarding the issue of ownership interests, American Medical Association(AMA)has pointed out in 2016 that using human tissues to develop commercially available products raises question about who holds property rights in human biological materials[1]. In United States, there have been several disputes concern the issue of the whether the donor of the cell therapy can claim ownership of the product, including Moore v. Regents of University of California(1990)[2], Greenberg v. Miami Children's Hospital Research Institute(2003)[3], and Washington University v. Catalona(2007)[4]. The courts tend to hold that since cells and tissues were donated voluntarily, the donors had already lost their property rights of their cells and tissues at the time of the donation. In Moore case, even if the researchers used Moore’s cells to obtain commercial benefits in an involuntary situation, the court still held that the property rights of removed cells were not suitable to be claimed by their donor, so as to avoid the burden for researcher to clarify whether the use of cells violates the wishes of the donors and therefore decrease the legal risk for R&D activities. United Kingdom Medical Research Council(MRC)also noted in 2019 that the donated human material is usually described as ‘gifts’, and donors of samples are not usually regarded as having ownership or property rights in these[5]. Accordingly, both USA and UK tends to believe that it is not suitable for cell donors to claim ownership. 2. The ownership of cell therapy products in the lens of Taiwan’s Civil Code In Taiwan, Article 766 of Civil Code stipulated: “Unless otherwise provided by the Act, the component parts of a thing and the natural profits thereof, belong, even after their separation from the thing, to the owner of the thing.” Accordingly, many scholars believe that the ownership of separated body parts of the human body belong to the person whom the parts were separated from. Therefore, it should be considered that the ownership of the cells obtained from the donor still belongs to the donor. In addition, since it is stipulated in Article 406 of Civil Code that “A gift is a contract whereby the parties agree that one of the parties delivers his property gratuitously to another party and the latter agrees to accept it.”, if the act of donation can be considered as a gift relationship, then the ownership of the cells has been delivered from donor to other party who accept it accordingly. However, in the different versions of Regenerative Medicine Biologics Regulation (draft) proposed by Taiwan legislators, some of which replace the term “donor” with “provider”. Therefore, for cell providers, instead of cell donors, after providing cells, whether they can claim ownership of cell therapy product still needs further discussion. According to Article 69 of the Civil Code, it is stipulated that “Natural profits are products of the earth, animals, and other products which are produced from another thing without diminution of its substance.” In addition, Article 766 of the Civil Code stipulated that “Unless otherwise provided by the Act, the component parts of a thing and the natural profits thereof, belong, even after their separation from the thing, to the owner of the thing.” Thus, many scholars believe that when the product is organic, original substance and the natural profits thereof are all belong to the owner of the original substance. For example, when proteins are produced from isolated cells, the proteins can be deemed as natural profits and the ownership of proteins and isolated cells all belong to the owner of the cells[6]. Nevertheless, according to Article 814 of the Civil Code, it is stipulated that “When a person has contributed work to a personal property belonging to another, the ownership of the personal property upon which the work is done belongs to the owner of the material thereof. However, if the value of the contributing work obviously exceeds the value of the material, the ownership of the personal property upon which the work is done belongs to the contributing person.” Thus, scholar believes that since regenerative medical technology, which induces cell differentiation, involves quite complex biotechnology technology, and should be deemed as contributing work. Therefore, the ownership of cell products after contributing work should belongs to the contributing person[7]. Thus, if the provider provides the cells to the researcher, after complex biotechnology contributing work, the original ownership of the cells should be deemed to have been eliminated, and there is no basis for providers to claim ownership. However, since the development of cell therapy products involves a series of R&D activities, it still need to be clarified that who is entitled to the ownership of the final cell therapy products. According to Taiwan’s Civil Code, the ownership of product after contributing work should belongs to the contributing person. However, when there are numerous contributing persons, which person should the ownership belong to, might be determined on a case-by-case basis. 3. Conclusion The biggest difference between cell therapy products and all other small molecule drugs or biologics is that original cell materials are provided by donors or providers, and the whole development process involves numerous contributing persons. Hence, ownership disputes are prone to arise. In addition to the above-discussed disputes, United Kingdom Co-ordinating Committee on Cancer Research(UKCCCR)also noted that there is a long list of people and organizations who might lay claim to the ownership of specimens and their derivatives, including the donor and relatives, the surgeon and pathologist, the hospital authority where the sample was taken, the scientists engaged in the research, the institution where the research work was carried out, the funding organization supporting the research and any collaborating commercial company. Thus, the ultimate control of subsequent ownership and patent rights will need to be negotiated[8]. Since the same issues might also occur in Taiwan, while developing cell therapy products, carefully clarifying the ownership between stakeholders is necessary for avoiding possible dispute. [1]American Medical Association [AMA], Commercial Use of Human Biological Materials, Code of Medical Ethics Opinion 7.3.9, Nov. 14, 2016, https://www.ama-assn.org/delivering-care/ethics/commercial-use-human-biological-materials (last visited Jan. 3, 2021). [2]Moore v. Regents of University of California, 793 P.2d 479 (Cal. 1990) [3]Greenberg v. Miami Children's Hospital Research Institute, 264 F. Suppl. 2d, 1064 (SD Fl. 2003) [4]Washington University v. Catalona, 490 F 3d 667 (8th Cir. 2007) [5]Medical Research Council [MRC], Human Tissue and Biological Samples for Use in Research: Operational and Ethical Guidelines, 2019, https://mrc.ukri.org/publications/browse/human-tissue-and-biological-samples-for-use-in-research/ (last visited Jan. 3, 2021). [6]Wen-Hui Chiu, The legal entitlement of human body, tissue and derivatives in civil law, Angle Publishing, 2016, at 327. [7]id, at 341. [8]Okano, M., Takebayashi, S., Okumura, K., Li, E., Gaudray, P., Carle, G. F., & Bliek, J. UKCCCR guidelines for the use of cell lines in cancer research.Cytogenetic and Genome Research,86(3-4), 1999, https://europepmc.org/backend/ptpmcrender.fcgi?accid=PMC2363383&blobtype=pdf (last visited Jan. 3, 2021).
The Key Elements for Data Intermediaries to Deliver Their PromiseThe Key Elements for Data Intermediaries to Deliver Their Promise 2022/12/13 As human history enters the era of data economy, data has become the new oil. It feeds artificial intelligence algorithms that are disrupting how advertising, healthcare, transportation, insurance, and many other industries work. The excitement of having data as a key production input lies in the fact that it is a non-rivalrous good that does not diminish by consumption.[1] However, the fact that people are reluctant in sharing data due to privacy and trade secrets considerations has been preventing countries to realize the full value of data. [2] To release more data, policymakers and researchers have been exploring ways to overcome the trust dilemma. Of all the discussions, data intermediaries have become a major solution that governments are turning to. This article gives an overview of relevant policy developments concerning data intermediaries and a preliminary analysis of the key elements that policymakers should consider for data intermediaries to function well. I. Policy and Legal developments concerning data intermediaries In order to unlock data’s full value, many countries have started to focus on data intermediaries. For example, in 2021, the UK’s Department for Digital, Culture, Media and Sport (DCMS) commissioned the Centre for Data Ethics and Innovation (CDEI) to publish a report on data intermediaries[3] , in response to the 2020 National Data Strategy.[4] In 2020, the European Commission published its draft Data Governance Act (DGA)[5] , which aims to build up trust in data intermediaries and data altruism organizations, in response to the 2020 European Strategy for Data.[6] The act was adopted and approved in mid-2022 by the Parliament and Council; and will apply from 24 September 2023.[7] The Japanese government has also promoted the establishment of data intermediaries since 2019, publishing guidance to establish regulations on data trust and data banks.[8] II. Key considerations for designing effective data intermediary policy 1.Evaluate which type of data intermediary works best in the targeted country From CDEI’s report on data intermediaries and the confusion in DGA’s various versions of data intermediary’s definition, one could tell that there are many forms of data intermediaries. In fact, there are at least eight types of data intermediaries, including personal information management systems (PIMS), data custodians, data exchanges, industrial data platforms, data collaboratives, trusted third parties, data cooperatives, and data trusts.[9] Each type of data intermediary was designed to combat data-sharing issues in specific countries, cultures, and scenarios. Hence, policymakers need to evaluate which type of data intermediary is more suitable for their society and market culture, before investing more resources to promote them. For example, data trust came from the concept of trust—a trustee managing a trustor’s property rights on behalf of his interest. This practice emerged in the middle ages in England and has since developed into case law.[10] Thus, the idea of data trust is easily understood and trusted by the British people and companies. As a result, British people are more willing to believe that data trusts will manage their data on their behalf in their best interest and share their valuable data, compared to countries without a strong legal history of trusts. With more people sharing their data, trusts would have more bargaining power to negotiate contract terms that are more beneficial to data subjects than what individual data owners could have achieved. However, this model would not necessarily work for other countries without a strong foundation of trust law. 2.Quality signals required to build trust: A government certificate system can help overcome the lemon market problem The basis of trust in data intermediaries depends largely on whether the service provider is really neutral in its actions and does not reuse or sell off other parties’ data in secret. However, without a suitable way to signal their service quality, the market would end up with less high-quality service, as consumers would be reluctant to pay for higher-priced service that is more secure and trustworthy when they have no means to verify the exact quality.[11] This lemon market problem could only be solved by a certificate system established by actors that consumers trust, which in most cases is the government. The EU government clearly grasped this issue as a major obstacle to the encouragement of trust in data intermediaries and thus tackles it with a government register and verification system. According to the Data Government Act, data intermediation services providers who intend to provide services are required to notify the competent authority with information on their legal status, form, ownership structure, relevant subsidiaries, address, public website, contact details, the type of service they intend to provide, the estimated start date of activities…etc. This information would be provided on a website for consumers to review. In addition, they can request the competent authority to confirm their legal compliance status, which would in turn verify them as reliable entities that can use the ‘data intermediation services provider recognised in the Union’ label. 3.Overcoming trust issues with technology that self-enforces privacy: privacy-enhancing technologies (PETs) Even if there are verified data intermediation services available, businesses and consumers might still be reluctant to trust human organizations. A way to boost trust is to adopt technologies that self-enforces privacy. A real-world example is OpenSAFELY, a data intermediary implementing privacy-enhancing technologies (PETs) to provide health data sharing in a secure environment. Through a federated analytics system, researchers are able to conduct research with large volumes of healthcare data, without the ability to observe any data directly. Under such protection, UK NHS is willing to share its data for research purposes. The accuracy and timeliness of such research have provided key insights to inform the UK government in decision-making during the COVID-19 pandemic. With the benefits it can bring, unsurprisingly, PETs-related policies have become quite popular around the globe. In June 2022, Singapore launched its Digital Trust Centre (DTC) for accelerating PETs development and also signed a Memorandum of Understanding with the International Centre of Expertise of Montreal for the Advancement of Artificial Intelligence (CEIMIA) to collaborate on PETs.[12] On September 7th, 2022, the UK Information Commissioners’ Office (ICO) published draft guidance on PETs.[13] Moreover, the U.K. and U.S. governments are collaborating on PETs prize challenges, announcing the first phase winners on November 10th, 2022.[14] We could reasonably predict that more PETs-related policies would emerge in the coming year. Reference: [1] Yan Carrière-Swallow and Vikram Haksar, The Economics of Data, IMFBlog (Sept. 23, 2019), https://blogs.imf.org/2019/09/23/the-economics-of-data/#:~:text=Data%20has%20become%20a%20key,including%20oil%2C%20in%20important%20ways (last visited July 22, 2022). [2] Frontier Economics, Increasing access to data across the economy: Report prepared for the Department for Digital, Culture, Media, and Sport (2021), https://assets.publishing.service.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploads/attachment_data/file/974532/Frontier-access_to_data_report-26-03-2021.pdf (last visited July 22, 2022). [3] The Centre for Data Ethics and Innovation (CDEI), Unlocking the value of data: Exploring the role of data intermediaries (2021), https://assets.publishing.service.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploads/attachment_data/file/1004925/Data_intermediaries_-_accessible_version.pdf (last visited June 17, 2022). [4] Please refer to the guidelines for the selection of sponsors of the 2022 Social Innovation Summit: https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/uk-national-data-strategy/national-data-strategy(last visited June 17, 2022). [5] Regulation of the European Parliament and of the Council on European data governance and amending Regulation (EU) 2018/1724 (Data Governance Act), 2020/0340 (COD) final (May 4, 2022). [6] Communication from the Commission to the European Parliament, the Council, the European Economic and Social Committee and The Committee of the Regions— A European strategy for data, COM/2020/66 final (Feb 19, 2020). [7] Proposal for a Regulation on European Data Governance, European Parliament Legislative Train Schedule, https://www.europarl.europa.eu/legislative-train/theme-a-europe-fit-for-the-digital-age/file-data-governance-act(last visited Aug 17, 2022). [8] 周晨蕙,〈日本資訊信託功能認定指引第二版〉,科技法律研究所,https://stli.iii.org.tw/article-detail.aspx?no=67&tp=5&d=8422(最後瀏覽日期︰2022/05/30)。 [9] CDEI, supra note 3. [10] Ada Lovelace Institute, Exploring legal mechanisms for data stewardship (2021), 30~31,https://www.adalovelaceinstitute.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/03/Legal-mechanisms-for-data-stewardship_report_Ada_AI-Council-2.pdf (last visited Aug 17, 2022). [11] George A. Akerlof, The Market for "Lemons": Quality Uncertainty and the Market Mechanism, THE QUARTERLY JOURNAL OF ECONOMICS, 84(3), 488-500 (1970). [12] IMDA, MOU Signing Between IMDA and CEIMIA is a Step Forward in Cross-border Collaboration on Privacy Enhancing Technology (PET) (2022),https://www.imda.gov.sg/-/media/Imda/Files/News-and-Events/Media-Room/Media-Releases/2022/06/MOU-bet-IMDA-and-CEIMIA---ATxSG-1-Jun-2022.pdf (last visited Nov. 28, 2022). [13] ICO publishes guidance on privacy enhancing technologies, ICO, https://ico.org.uk/about-the-ico/media-centre/news-and-blogs/2022/09/ico-publishes-guidance-on-privacy-enhancing-technologies/ (last visited Nov. 27, 2022). [14] U.K. and U.S. governments collaborate on prize challenges to accelerate development and adoption of privacy-enhancing technologies, GOV.UK, https://www.gov.uk/government/news/uk-and-us-governments-collaborate-on-prize-challenges-to-accelerate-development-and-adoption-of-privacy-enhancing-technologies (last visited Nov. 28, 2022); Winners Announced in First Phase of UK-US Privacy-Enhancing Technologies Prize Challenges, NIST, https://www.nist.gov/news-events/news/2022/11/winners-announced-first-phase-uk-us-privacy-enhancing-technologies-prize (last visited Nov. 28, 2022).
- Impact of Government Organizational Reform to Scientific Research Legal System and Response Thereto (1) – For Example, The Finnish Innovation Fund (“SITRA”)
- The Demand of Intellectual Property Management for Taiwanese Enterprises
- Blockchain in Intellectual Property Protection
- Impact of Government Organizational Reform to Research Legal System and Response Thereto (2) – Observation of the Swiss Research Innovation System
- Recent Federal Decisions and Emerging Trends in U.S. Defend Trade Secrets Act Litigation
- The effective and innovative way to use the spectrum: focus on the development of the "interleaved/white space"
- Copyright Ownership for Outputs by Artificial Intelligence
- Impact of Government Organizational Reform to Research Legal System and Response Thereto (2) – Observation of the Swiss Research Innovation System

