Brief Introduction to Taiwan Social Innovation Policies

Brief Introduction to Taiwan Social Innovation Policies
2021/09/13
1. Introduction
The Millennium Development Goals (MDGs)[1] set forth by the United Nations in 2000 are carried out primarily by nations and international organizations. Subsequently, the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) set forth by the United Nations in 2015 started to delegate the functions to organizations of all levels. Presently, there is a global awareness of the importance of balancing “economic growth”, “social progress”, and “environmental protection” simultaneously during development. In the above context, many similar concepts have arisen worldwide, including social/solidarity economy, social entrepreneurship and social enterprise, and social innovation.
Generally, social innovation aims to alter the interactions between various groups in society through innovative applications of technology or business models, and to find new ways to solve social problems through such alterations. In other words, the goal is to use innovative methods to solve social problems. The difference between social innovation and social enterprise is that social enterprise combines commercial power to achieve its social mission under a specific perspective, while social innovation creates social value through cooperation with and coordination among technology, resources, and communities under a diversified nature.
2. Overview of Taiwan Social Enterprise Policy
To integrate into the global community and assist in the development of domestic social innovation, Taiwan’s Executive Yuan launched the “Social Enterprise Action Plan” in 2014, which is the first policy initiative to support social enterprises (from 2014 to 2016). Under this policy initiative, through consulting with various ministries and applying methods such as “amending regulations”, “building platforms”, and “raising funds”, the initiative set to create an environment with favorable conditions for social innovation and start-ups. At this stage, the initiative was adopted under the principle of “administrative guidance before legislation” in order to encourage private enterprise development without excessive burden, and avoid regulations restricting the development of social enterprises, such as excessive definition of social enterprises. Moreover, for preserving the original types of these enterprises, this Action Plan did not limit the types of social enterprises to companies, non-profit organizations, or other specific types of organizations.
To sustain the purpose of the Social Enterprise Action Plan and to echo and reflect the 17 sustainable development goals proposed in SDGs by the United Nations, the Executive Yuan launched the “Social Innovation Action Plan” (effective from 2018 to 2022) in 2018 to establish a friendly development environment for social innovation and to develop diversified social innovation models through the concept of “openness, gathering, practicality, and sustainability”. In this Action Plan, “social innovation” referred to “social innovation organizations” that solve social problems through technology or innovative business models. The balancing of the three managerial goals of society, environment value, and profitability is the best demonstration of the concept of social innovation.
3. Government’s Relevant Social Enterprise Policy and Resources
The ministries of the Taiwan Government have been promoting relevant policies in accordance with the Social Innovation Action Plan issued by the Executive Yuan in 2018, such as the “Registration System for Social Innovation Enterprises” (counseling of social enterprises), the “Buying Power - Social Innovation Products and Services Procurement”, the “Social Innovation Platform” established by the Ministry of Economic Affairs, the “Social Innovation Manager Training Courses”, the “Promoting Social Innovation and Employment Opportunities” administered by the Ministry of Labor, and the “University Social Responsibility Program” published by the Ministry of Education. Among the above policies stands out the measures adopted by the Ministry of Economic Affairs, and a brief introduction of those policies are as follows:
i. Social Innovation Platform
To connect all resources involved in social issues to promote social innovation development in Taiwan, the Ministry of Economic Affairs established the “Social Innovation Platform”.[2] With visibility through the Social Innovation Platform, it has become more efficient to search for targets in a public and transparent way and to assist with the input of resources originally belonging to different fields in order to expand social influence.
As a digital platform gathering “social innovation issues in Taiwan,” the Social Innovation Platform covers multiple and complete social innovation resources, which include the “SDGs Map” constructed on the Social Innovation Platform, by which we can better understand how county and city governments in Taiwan implement SDGs and Voluntary Local Review Reports, and which allow us to search the Social Innovation Database[3] and the registered organizations, by which citizens, enterprises, organizations, and even local governments concerned with local development can find their partners expediently as possible, establish service lines to proactively assist public or private entities with their needs/resources, and continue to enable the regional revitalization organizations, ministries, and enterprises to identify and put forward their needs for social innovation through the function of “Social Innovation Proposals”, which assist social innovation organizations with visibility while advancing cooperation and expanding social influence.
In addition, the “Event Page” was established on the Social Innovation Platform and offers functions, such as the publishing, searching, and sorting of events in four major dimensions with respect to social innovation organization, governments, enterprises, and citizens; and encourages citizens, social innovation organizations, enterprises, and governments to devote themselves via open participation to continuously expande the influence of the (Civic Technology) Social Innovation Platform. The “Corporate Social Responsibility Report” collects the corporate social responsibility reports, observes the distribution of resources for sustainable development by corporations in Taiwan, offers filtering functions by regions, keyword, popular rankings, and or SDGs types, and provides contact information and a download function for previous years’ reports, in order to effectively assist social innovation organizations to obtain a more precise understanding of the status quo, needs, and trends with respect to their development of respective products and services.
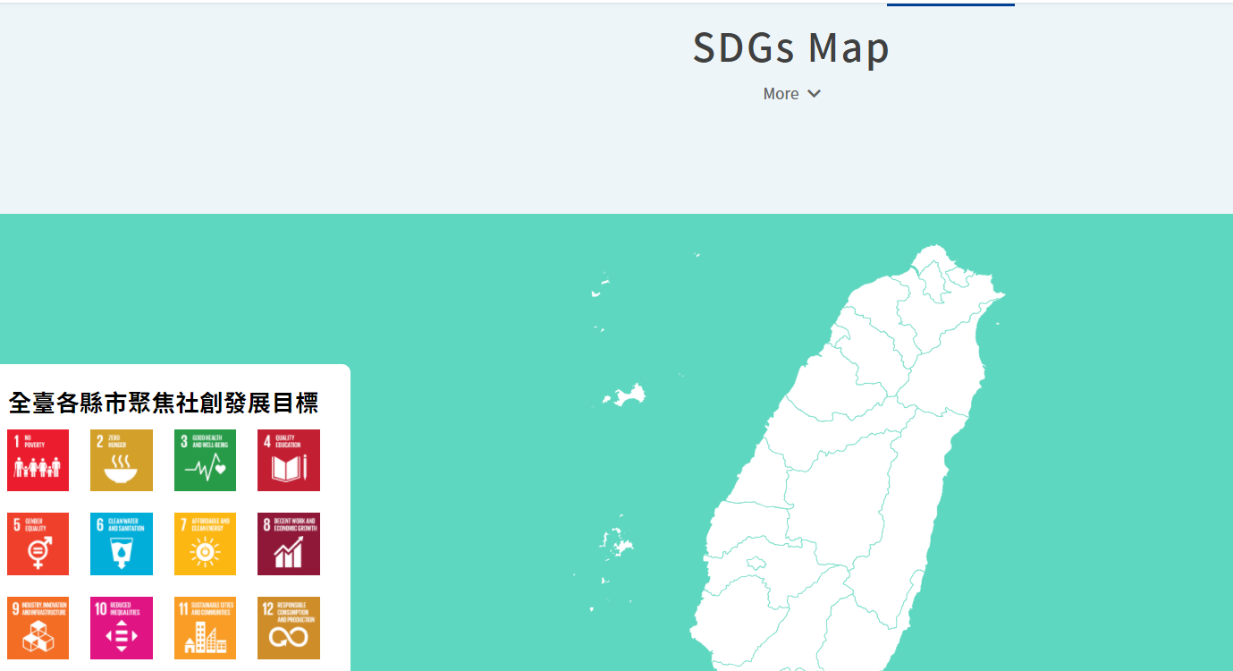
Figure 1: SDGs Map
Reference: Social Innovation Platform (https://si.taiwan.gov.tw/)
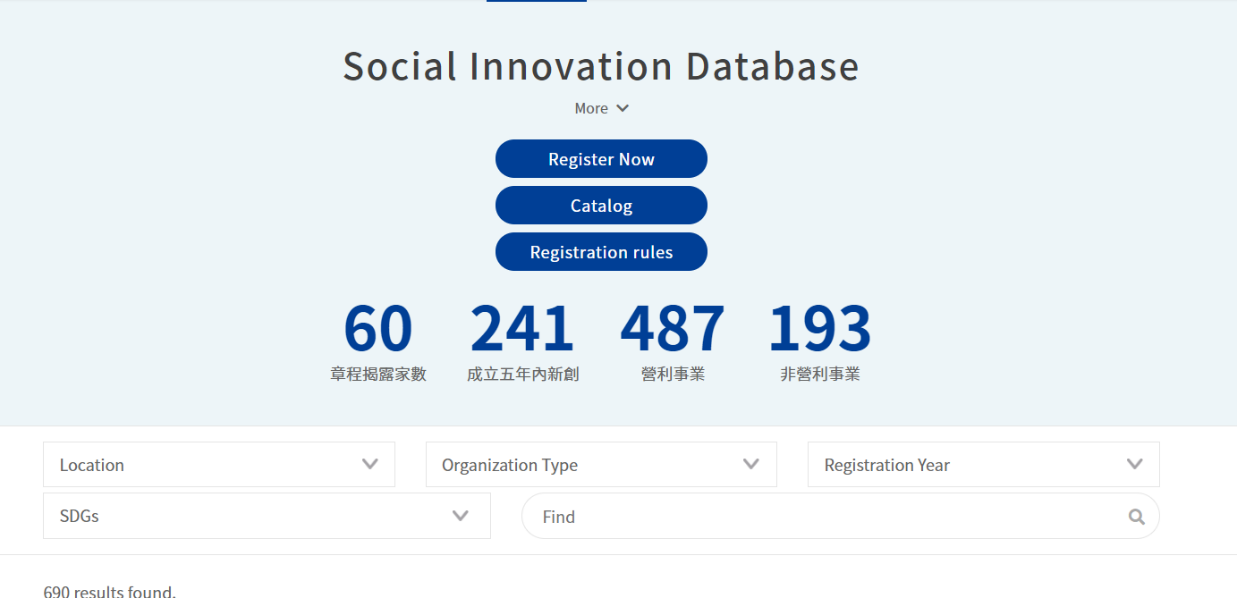
Figure 2: Social Innovation Database
Reference: Social Innovation Platform (https://si.taiwan.gov.tw/)
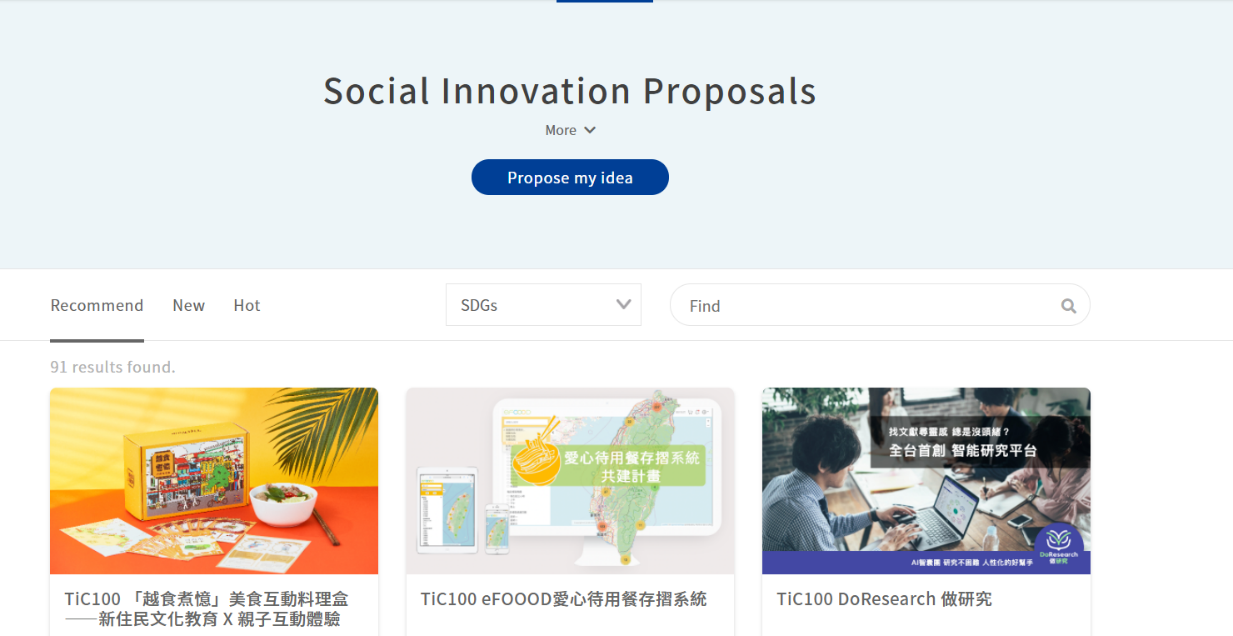
Figure 3: Social Innovation Proposals
Reference: Social Innovation Platform (https://si.taiwan.gov.tw/)
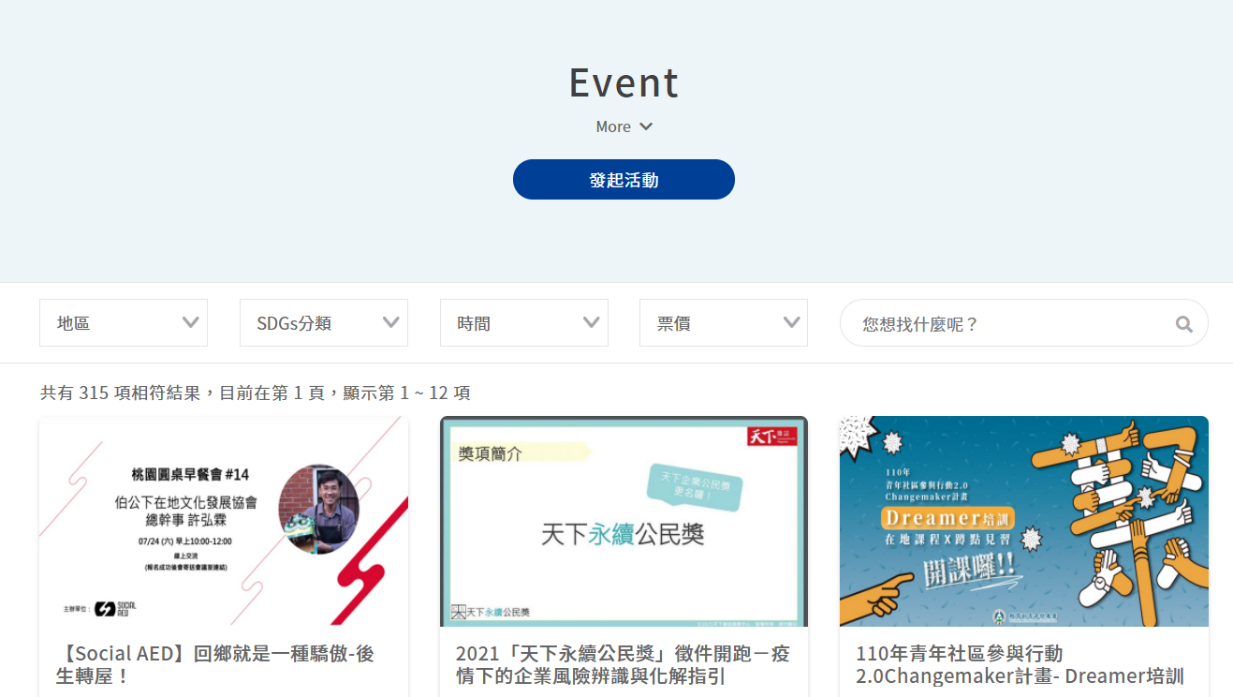
Figure 4: Event Page
Reference: Social Innovation Platform (https://si.taiwan.gov.tw/)

Figure 5: Corporate Social Responsibility Report
Reference: Social Innovation Platform (https://si.taiwan.gov.tw/)
ii. Social Innovation Database
To encourage social innovation organizations to disclose their social missions, products and services, and to guide society to understand the content of social innovation, and to assist the administrative ministries to be able to utilize such information, the Ministry of Economic Affairs issued the “Principles of Registration of Social Innovation Organizations” to establish the “Social Innovation Database”.
Once a social innovation organization discloses the items, such as its social missions, business model, or social influence, it may obtain the relevant promotional assistance resources, including becoming a trade partner with Buying Power (Social Innovation Products and Services Procurement), receiving exclusive consultation and assistance from professionals for social innovation organizations, and becoming qualified to apply to entering into the Social Innovation Lab. Moreover, the Ministry of Economic Affairs is simultaneously consolidating, identifying, and designating the awards and grants offered by the various ministries, policies and measures in respect of investment, and financing and assistance, as resources made available to registered entities.
As of 25 May 2021, there were 658 registered social innovation organizations and 96 Social Innovation Partners (enterprises with CSR or ESG resources that recognize the cooperation with social innovation under the social innovation thinking model may be registered as a “Social Innovation Partner”). The public and enterprises can search for organizations registered in the Social Innovation Database through the above-said Social Innovation Platform, the search ability of which advances the exposure of and the opportunities for cooperation with social innovation organizations.
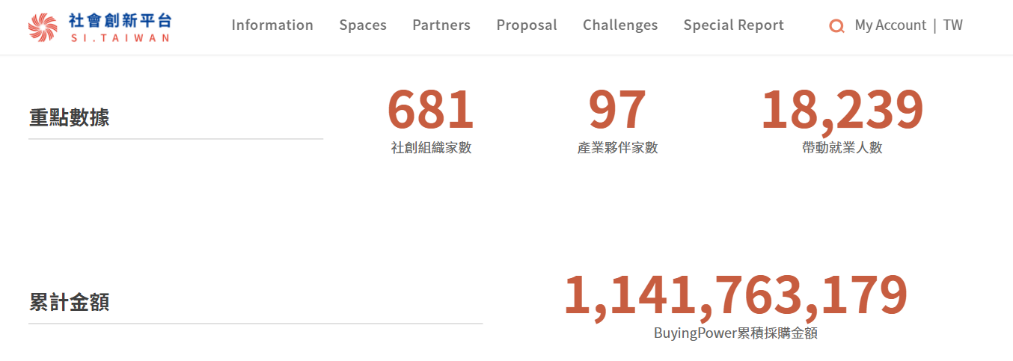
Figure 6: Numbers of registered social innovation organizations and accumulated value of purchases under Buying Power
Reference: Social Innovation Platform(https://si.taiwan.gov.tw/)
iii. Buying Power - Social Innovation Products and Services Procurement
In order to continue increasing the awareness on social innovation organizations and related issues and promote responsible consumption and production in Taiwan, as well as to raise the attention of the commercial sector to the sustainability-driven procurement models, the Ministry of Economic Affairs held the first “Buying Power - Social Innovation Products and Services Procurement” event in 2017. Through the award system under the Buying Power, it continues to encourage the governments, state-owned enterprises, private enterprises, and organizations to take the lead in purchasing products or services from social innovation organizations, to provide the relevant resources so as to assist social innovation organizations to obtain resources and to explore business opportunities in the markets, to practice responsible consumption and production, and to promote innovative cooperation between all industries and commerce and social innovation organizations.
The aim of the implementation of the Buying Power is to encourage the central and local governments, state-owned enterprises, private enterprises, and non-governmental organizations to purchase products or services from organizations registered in the Social Innovation Database, while prizes will be awarded based on the purchase amounts accumulated during the calculation period. The winners can obtain priority in applying for membership in the Social Innovation Partner Group, with corresponding member services, in the future.
Under the Social Innovation Platform, both the amount of purchase awards and the number of applicants for special awards continue to increase. So far, purchases have accumulated to a value of more than NT$1.1 billion (see Figure 6), and more than 300 organizations have proactively participated.
iv. Social Innovation Mark
In order to promote public awareness of social innovation, the Ministry of Economic Affairs has been charged with the commissioned task of promoting the Social Innovation Mark, and issued “ The Small and Medium Enterprise Administration of the Ministry of Economic Affairs Directions for Authorization of the Social Innovation Mark” as the standard for the authorization of the Social Innovation Mark. Social innovation organizations can use the Mark, through obtaining authorization, to hold Social Innovation Summits or other social innovation activities for promoting social innovation concepts.
In order to build the Mark as a conceptual symbol of social innovation, the Ministry of Economic Affairs has been using the Social Innovation Mark in connection with various social innovation activities, such as the Social Innovation Platform, the Buying Power, and the annual Social Innovation Summit. Taking the selection of sponsors of the Social Innovation Summit in 2022 as an example[4], only organizations that have obtained authorization of the Social Innovation Mark can use the Mark to hold the Social Innovation Summit.

Figure 7: The Social Innovation Mark of the Small and Medium Enterprise Administration, Ministry of Economic Affairs
IV. Conclusion
The “Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development” (OECD) regards social innovation as a new strategy for solving future social problems and as an important method for youth entrepreneurship and social enterprise development. Taiwan’s social innovation energy has entered a stage of expansion and development. Through the promotion of the “Social Innovation Action Plan,” the resources from the central and local governments are integrated to establish the Social Innovation Platform, the Social Innovation Database, the Social Innovation Lab, and the Social Innovation Mark. In addition, incentives such as the Buying Power have been created, manifesting the positive influence of Taiwan’s social innovation.
[1] MDGs are put forward by the United Nations in 2000, and are also the goals requiring all the 191 member states and at least 22 international organizations of the United Nations to be committed to on their best endeavors, including: 1. eradicating extreme poverty and hunger, 2. applying universal primary education, 3. promoting gender equality and empowering women, 4. reducing child mortality rates, 5. improving maternal health, 6. combatting HIV/AIDS, malaria, and other diseases, 7. ensuring environmental sustainability, and 8. establishing a global partnership for development.
[2] Please refer to the Social Innovation Platform: https://si.taiwan.gov.tw/.
[3] Please refer to the Social Innovation Database: https://si.taiwan.gov.tw/Home/Org_list.
[4] Please refer to the guidelines for the selection of sponsors of the 2022 Social Innovation Summit: https://www.moeasmea.gov.tw/files/6221/4753E497-B422-4303-A8D4-35AE0B4043A9
With the coming of the Innovation-based economy era, technology research has become the tool of advancing competitive competence for enterprises and academic institutions. Each country not only has begun to develop and strengthen their competitiveness of industrial technology but also has started to establish related mechanism for important technology areas selected or legal analysis. By doing so, they hope to promote collaboration of university-industry research, completely bring out the economic benefits of the R & D. and select the right technology topics. To improve the depth of research cooperation and collect strategic advice, we have to use legislation system, but also social communication mechanism to explore the values and practical recommendations that need to be concerned in policy-making. This article in our research begins with establishing a mechanism for collecting diverse views on the subject, and shaping more efficient dialogue space. Finally, through the process of practicing, this study effectively collects important suggestions of practical experts.
Analyzing the Framwork of the Regulation「Act For The Development of Biotech And New Pharmaceuticals Industry」in TaiwanTaiwan Government passed The「Act for the Development of Biotech and New Pharmaceuticals Industry」for supporting the biopharmaceutical industry. The purpose of the Act is solely for biopharmaceutical industry, and building the leading economic force in Taiwan. To fulfill this goal, the Act has enacted regulations concerning funding, taxation and recruitment especially for the biopharmaceutical industry. The Act has been seen as the recent important law in the arena of upgrading industry regulation on the island. It is also a rare case where single legislation took place for particular industry. After the Act came into force, the government has promulgated further regulations to supplement the Act, including Guidance for MOEA-Approved Biotech and New Pharmaceuticals Company Issuing Stock Certificate, Deductions on Investments in R&D and Personnel Training of Biotech and New Pharmaceuticals Company, Guidance for Deduction Applicable to Shareholders of Profit-Seeking Enterprises -Biotech and New Pharmaceuticals Company etc. The following discussions are going to introduce the Act along with related incentive measures from an integrated standpoint. 1 、 Scope of Application According to Article 3 of the Act, 「Biotech and New Pharmaceuticals Industry」 refers to the industry that deals in New Rugs and High-risk Medical devices used by human beings, animals, and plants; 「Biotech and New Pharmaceuticals Company」 refers to a company in the Biotech and New Pharmaceuticals Industry that is organized and incorporated in accordance with the Company Act and engages in the research, development, and manufacture of new drugs and high-risk medical devices. Thus, the Act applies to company that conducts research and manufacture product in new drug or high-risk medical devices for human and animal use. Furthermore, to become a Biotech and New Pharmaceuticals Company stipulated in the Act, the Company must receive letter of approval to establish as a Biotech and New Pharmaceuticals Company valid for five years. Consequently, company must submit application to the authority for approval by meeting the following requirements: (1) Companies that conduct any R&D activities or clinical trials must receive permission, product registration, or proof of manufacture for such activities from a competent authority. However, for those conducted these activities outside the country will not apply. (2) When applied for funding for the previous year or in the same year, the expense on R&D in the previous year exceeds 5% of the total net revenue within the same year; or the expenses exceeds 10% of the total capital of the company. (3) Hired at least five R&D personnel majored in biotechnology. For New Drug and High-Risk Medical Device are confined in specific areas. New Drug provided in the Act refers to a drug that has a new ingredient, a new therapeutic effect or a new administration method as verified by the central competent authorities. And High-Risk Medical Device refers to a type of Class III medical devices implanted into human bodies as verified by the central competent authorities. Therefore, generic drug, raw materials, unimplanted medical device, and medical device are not qualified as type III, are all not within the scope of the Act and are not the subject matter the Act intends to reward. 2 、 Tax Benefits Article 5, 6 and 7 provided in the Act has followed the footsteps of Article 6 and 8 stipulated of the Statute, amending the rules tailored to the biopharmaceutical industry, and provided tax benefits to various entities as 「Biotech and New Pharmaceuticals Company」, 「Investors of Biotech and New Pharmaceuticals Industry」, 「Professionals and Technology Investors」. (1) Biotech and New Pharmaceuticals Company In an effort to advance the biopharmaceutical industry, alleviate financial burden of the companies and strengthen their R&D capacity. The Act has provided favorable incentive measures in the sector of R&D and personnel training. According to Article 5: 「For the purpose of promoting the Biotech and New Pharmaceuticals Industry, a Biotech and New Pharmaceuticals Company may, for a period of five years from the time it is subject to profit-seeking enterprise income tax payable, enjoy a reduction in its corporate income tax payable, for up to 35% of the total funds invested in research and development (R&D) and personnel training each year.」 Consequently, company could benefit through tax deduction and relieve from the stress of business operation. Moreover, in supporting Biotech and New Pharmaceutical Company to proceed in R&D and personnel training activities, the Act has set out rewards for those participate in ongoing R&D and training activities. As Article 5 provided that」 If the R&D expenditure of a particular year exceeds the average R&D expenditure of the previous two years, or if the personnel training expenditure of a particular year exceeds the average personnel training expenditure of the pervious two years, 50% of the exceed amount in excess of the average may be used to credit against the amount of profit-seeking enterprise income tax payable. 「However, the total amount of investment credited against by the payable corporate income tax in each year shall not exceed 50% of the amount of profit-seeking enterprise income tax payable by a Biotech and New Pharmaceuticals Company in a year, yet this restriction shall not apply to the amount to be offset in the last year of the aforementioned five-year period. Lastly, Article 5 of the Act shall not apply to Biotech and New Pharmaceutical Company that set up headquarters or branches outside of Taiwan. Therefore, to be qualified for tax deduction on R&D and personnel training, the headquarters or branches of the company must be located in Taiwan. (2) Investors of Biotech and New Pharmaceuticals Company To raise funding, expand business development, and attract investor continuing making investments, Article 6 of the Act has stated that 「In order to encourage the establishment or expansion of Biotech and New Pharmaceuticals Companies, a profit-seeking enterprise that subscribes for the stock issued by a Biotech and New Pharmaceuticals Company at the time of the latter's establishment or subsequent expansion; and has been a registered shareholder of the Biotech and New Pharmaceuticals Company for a period of 3 years or more, may, for a period of five years from the time it is subject to corporate income tax, enjoy a reduction in its profit-seeking enterprise income tax payable for up to 20% of the total amount of the price paid for the subscription of shares in such Biotech and New Pharmaceuticals Company.」 Yet 「If the afore-mentioned profit-seeking enterprise is a venture capital company (「VC」), such VC corporate shareholders may, for a period of five years from the fourth anniversary year of the date on which the VC becomes a registered shareholder of the subject Biotech and New Pharmaceuticals Company, enjoy a reduction in their profit-seeking enterprise income tax payable based on the total deductible amount enjoyed by the VC under Paragraph 1 hereof and the shareholders' respective shareholdings in the VC.」 The government enacted this regulation to encourage corporations and VC to invest in biotech and new pharmaceutical company, and thus provide corporate shareholders with 20% of profit-seeking enterprise income tax payable deduction, and provide VC corporate shareholders tax deduction that proportion to its shareholdings in the VC. (3) Top Executives and Technology Investors Top Executives refer to those with biotechnology background, and has experience in serving as officer of chief executive (CEO) or manager; Technology Investors refer to those acquire shares through exchange of technology. As biopharmaceutical industry possesses a unique business model that demands intensive technology, whether top executives and technology investors are willing to participate in a high risk business and satisfy the needs of industry becomes a critical issue. Consequently, Article 7 of the Act stated that 「In order to encourage top executives and technology investors to participate in the operation of Biotech and New Pharmaceuticals Companies and R&D activities, and to share their achievements, new shares issued by a Biotech and New Pharmaceuticals Company to top executives and technology investors (in return of their knowledge and technology) shall be excluded from the amount of their consolidated income or corporate income of the then current year for taxation purposes; provided, however, that if the title to the aforesaid shares is transferred with or without consideration, or distributed as estate, the total purchase price or the market value of the shares at the time of transfer as a gift or distribution as estate shall be deemed income generated in that tax year and such income less the acquisition cost shall be reported in the relevant income tax return.」 Additionally, 「For the title transfer of shares under the preceding paragraph, the Biotech and New Pharmaceuticals Company concerned shall file a report with the local tax authorities within thirty 30 days from the following day of the title transfer.」 Purpose of this regulation is to attract top executives and technology personnel for the company in long-term through defer taxation. Moreover, the Biotech and New Pharmaceutical Company usually caught in a prolong period of losses, and has trouble financing through issuing new shares, as stipulated par value of each share cannot be less than NTD $10.Thus, in order to offer top executive and technology investors incentives and benefits under such circumstances, Article 8 has further provided that」Biotech and New Pharmaceutical Companies may issue subscription warrants to its top executives and technology investors, provided that the proposal for the issuance of the aforesaid subscription warrants shall pass resolution adopted by a majority votes of directors attended by at least two-thirds (2/3) of all the directors of the company; and be approved by the competent authorities. Holders of the subscription warrants may subscribe a specific number of shares at the stipulated price. The amount of stipulated price shall not be subject to the minimum requirement, i.e. par value of the shares, as prescribed under Article 140 of the Company Act. Subscription of the shares by exercising the subscription warrant shall be subject to income tax in accordance with Article 7 hereof. if a Biotech and New Pharmaceutical Company issue new shares pursuant to Article 7 hereof, Article 267 of the Company Act shall not apply. The top executives and technology investors shall not transfer the subscription warrant acquired to pursuant to this Article.」 These three types of tax benefits are detailed incentive measures tailor to the biopharmaceutical industry. However, what is noteworthy is the start date of the benefits provided in the Act. Different from the Statue, the Act allows company to enjoy these benefits when it begins to generate profits, while the Statute provides company tax benefits once the authority approved its application in the current year. Thus, Biotech and New Pharmaceuticals Company enjoys tax benefits as the company starts to make profit. Such approach reflects the actual business operation of the industry, and resolves the issue of tax benefits provided in the Statue is inapplicable to the biopharmaceutical industry. 3 、 Technical Assistance and Capital Investment Due to the R&D capacity and research personnel largely remains in the academic circle, in order to encourage these researchers to convert R&D efforts into commercial practice, the government intends to enhance the collaboration among industrial players, public institutions, and the research and academic sectors, to bolster the development of Biotech and New Pharmaceuticals Company. However, Article 13 of Civil Servants Service Act prohibits officials from engaging in business operation, the Act lifts the restriction on civil servants. According to Article 10 of the Act provided that」For a newly established Biotech and New Pharmaceuticals Company, if the person providing a major technology is a research member of the government research organization, such person may, with the consent of the government research organization, acquired 10% or more of the shares in the Biotech and New Pharmaceuticals Company at the time of its establishment, and act as founder, director, or technical adviser thereof. In such case, Article 13 of the Civil Servants Service Act shall not apply. And the research organization and research member referred to thereof shall be defined and identified by the Executive Yuan, in consultation with the Examination Yuan.」 This regulation was enacted because of the Civil Servants Services Act provided that public officials are not allowed to be corporate shareholders. However, under certain regulations, civil servants are allowed to be corporate shareholders in the sector of agriculture, mining, transportation or publication, as value of the shares cannot exceed 10% of the total value of the company, and the civil servant does not served in the institution. In Taiwan, official and unofficial research institution encompasses most of the biotechnology R&D capacity and research personnel. If a researcher is working for a government research institution, he would be qualified as a public servant and shall be governed by the Civil Servants Service Act. As a result of such restriction, the Act has lifted the restriction and encouraged these researchers to infuse new technologies into the industry. At last, for advancing the development of the industry, Article 11 also provided that 」R&D personnel of the academic and research sectors may, subject to the consent of their employers, served as advisors or consultants for a Biotech and New Pharmaceuticals Company.」 4 、 Other Regulations For introducing and transferring advanced technology in support of the biopharmaceutical industry, Article 9 stated that 「Organization formed with government funds to provide technical assistance shall provide appropriate technical assistance as may be necessary.」 Besides technical assistance, government streamlines the review process taken by various regulatory authorities, in order to achieve an improved product launch process result in faster time-to-market and time-to profit. As Article 12 provided that 「the review and approval of field test, clinical trials, product registration, and others, the central competent authorities shall establish an open and transparent procedure that unifies the review system.」
Impact of Government Organizational Reform to Research Legal System and Response Thereto (2) – Observation of the Swiss Research Innovation System3.Commission of Technology and Innovation (CTI) The CTI is also an institution dedicated to boosting innovation in Switzerland. Established in 1943, it was known as the Commission for the Promotion of Scientific Research[1]. It was initially established for the purpose of boosting economy and raising the employment rate, and renamed after 1996. The CTI and SNSF are two major entities dedicated to funding scientific research in Switzerland, and the difference between both resides in that the CTI is dedicated to funding R&D of the application technology and industrial technology helpful to Switzerland’s economic development. Upon enforcement of the amended RIPA 2011, the CTI was officially independent from the Federal Office for Professional Education and Technology (OEPT) and became an independent entity entitled to making decisions and subordinated to the Federal Department of Economic Affairs (FDEA) directly[2]. The CTI is subject to the council system, consisting of 65 professional members delegated from industrial, academic and research sectors. The members assume the office as a part time job. CTI members are entitled to making decisions on funding, utilization of resources and granting of CTI Start-up Label independently[3]. The CTI primarily carries out the mission including promotion of R&D of industrial technology, enhancement of the market-orientation innovation process and delivery of R&D energy into the market to boost industrial innovation. For innovation, the CTI's core mission is categorized into[4]: (1)Funding technology R&D activities with market potential The CTI invests considerable funds and resources in boosting the R&D of application technology and industrial technology. The CTI R&D Project is intended to fund private enterprises (particularly small-sized and medium-sized enterprises) to engage in R&D of innovation technology or product. The enterprises may propose their innovative ideas freely, and the CTI will decide whether the funds should be granted after assessing whether the ideas are innovative and potentially marketable[5]. CTI’s funding is conditioned on the industrial and academic cooperation. Therefore, the enterprises must work with at least one research institution (including a university, university of science and technology, or ETH) in the R&D. Considering that small-sized and medium-sized enterprises usually do not own enough working funds, technology and human resources to commercialize creative ideas, the CTI R&D Project is intended to resolve the problem about insufficient R&D energy and funds of small- and medium-sized enterprises by delivering the research institutions’ plentiful research energy and granting the private enterprises which work with research institutions (including university, university of science and technology, or ETH) the fund. Notably, CTI’s funding is applicable to R&D expenses only, e.g., research personnel’s salary and expenditure in equipment & materials, and allocated to the research institutions directly. Meanwhile, in order to enhance private enterprises' launch into R&D projects and make them liable for the R&D success or failure, CTI’s funding will be no more than 50% of the total R&D budget and, therefore, the enterprises are entitled to a high degree of control right in the process of R&D. The industrial types which the CTI R&D Project may apply to are not limited. Any innovative ideas with commercial potential may be proposed. For the time being, the key areas funded by CTI include the life science, engineering science, Nano technology and enabling sciences, etc.[6] It intends to keep Switzerland in the lead in these areas. As of 2011, in order to mitigate the impact of drastic CHF revaluation to the industries, the CTI launched its new R&D project, the CTI Voucher[7]. Given this, the CTI is not only an entity dedicated to funding but also plays an intermediary role in the industrial and academic sectors. Enterprises may submit proposals before finding any academic research institution partner. Upon preliminary examination of the proposals, the CTI will introduce competent academic research institutions to work with the enterprises in R&D, subject to the enterprises' R&D needs. After the cooperative partner is confirmed, CTI will grant the fund amounting to no more than CHF3,500,000 per application[8], provided that the funding shall be no more than 50% of the R&D project expenditure. The CTI R&D Project not only boosts innovation but also raises private enterprises’ willingness to participate in the academic and industrial cooperation, thereby narrowing the gap between the supply & demand of innovation R&D in the industrial and academic sectors. Notably, the Project has achieved remarkable effect in driving private enterprises’ investment in technology R&D. According to statistical data, in 2011, the CTI solicited additional investment of CHF1.3 from a private enterprise by investing each CHF1[9]. This is also one of the important reasons why the Swiss innovation system always acts vigorously. Table 1 2005-2011 Passing rate of application for R&D funding Year 2011 2010 2009 2008 2007 2006 2005 Quantity of applications 590 780 637 444 493 407 522 Quantity of funded applications 293 343 319 250 277 227 251 Pass rate 56% 44% 50% 56% 56% 56% 48% Data source: Prepared by the Study (2)Guiding high-tech start-up Switzerland has learnt that high-tech start-ups are critical to the creation of high-quality employment and boosting of economic growth, and start-ups were able to commercialize the R&D results. Therefore, as of 2001, Switzerland successively launched the CTI Entrepreneurship and CTI Startup to promote entrepreneurship and cultivate high-tech start-ups. 1.CTI Entrepreneurship The CTI Entrepreneurship was primarily implemented by the Venture Lab founded by CTI investment. The Venture Lab launched a series of entrepreneurship promotion and training courses, covering day workshops, five-day entrepreneurship intensive courses, and entrepreneurship courses available in universities. Each training course was reviewed by experts, and the experts would provide positive advice to attendants about innovative ideas and business models. Data source: Venture Lab Site Fig. 3 Venture Lab Startup Program 2.CTI Startup The CTI is dedicated to driving the economy by virtue of innovation as its priority mission. In order to cultivate the domestic start-ups with high growth potential in Switzerland, the CTI Startup project was launched in 1996[10] in order to provide entrepreneurs with the relevant guidance services. The project selected young entrepreneurs who provided innovative ideas, and guided them in the process of business start to work their innovative ideas and incorporate competitive start-ups. In order to enable the funding and resources to be utilized effectively, the CTI Startup project enrolled entrepreneurs under very strict procedure, which may be categorized into four stages[11]: Data source: CTI Startup Site Fig. 4 Startup Plan Flow Chart In the first stage, the CTI would preliminarily examine whether the applicant’s idea was innovative and whether it was technologically feasible, and help the applicant register with the CTI Startup project. Upon registration, a more concrete professional examination would be conducted at the second stage. The scope of examination included the technology, market, feasibility and management team’s competence. After that, at the stage of professional guidance, each team would be assigned a professional “entrepreneurship mentor”, who would help the team develop further and optimize the enterprise’s strategy, flow and business model in the process of business start, and provide guidance and advice on the concrete business issues encountered by the start-up. The stage of professional guidance was intended to guide start-ups to acquire the CTI Startup Label, as the CTI Startup Label was granted subject to very strict examination procedure. For example, in 2012, the CTI Startup project accepted 78 applications for entrepreneurship guidance, but finally the CTI Startup Label was granted to 27 applications only[12]. Since 1996, a total of 296 start-ups have acquired the CTI Startup Label, and more than 86% thereof are still operating now[13]. Apparently, the CTI Startup Label represents the certification for innovation and on-going development competence; therefore, it is more favored by investors at the stage of fund raising. Table 2 Execution of start-up plans for the latest three years Quantity of application Quantity of accepted application Quantity of CTI Label granted 2012 177 78 27 2011 160 80 26 2010 141 61 24 Data source: CTI Annual Report, prepared by the Study Meanwhile, the “CTI Invest” platform was established to help start-up raise funds at the very beginning to help commercialize R&D results and cross the valley in the process of R&D innovation. The platform is a private non-business-making organization, a high-tech start-up fund raising platform co-established by CTI and Swiss investors[14]. It is engaged in increasing exposure of the start-ups and contact with investors by organizing activities, in order to help the start-ups acquire investment funds. (3)Facilitating transfer of knowledge and technology between the academic sector and industrial sector KTT Support (Knowledge & Technology Transfer (KTT Support) is identified as another policy instrument dedicated to boosting innovation by the CTI. It is intended to facilitate the exchange of knowledge and technology between academic research institutions and private enterprises, in order to transfer and expand the innovation energy. As of 2013, the CTI has launched a brand new KTT Support project targeting at small-sized and medium-sized enterprises. The new KTT Support project consisted of three factors, including National Thematic Networks (NTNs), Innovation Mentors, and Physical and web-based platforms. Upon the CTI’s strict evaluation and consideration, a total of 8 cooperative innovation subjects were identified in 2012, namely, carbon fiber composite materials, design idea innovation, surface innovation, food study, Swiss biotechnology, wood innovation, photonics and logistics network, etc.[15] One NTN would be established per subject. The CTI would fund these NTNs to support the establishment of liaison channels and cooperative relations between academic research institutions and industries and provide small- and medium-sized enterprises in Switzerland with more rapid and easy channel to access technologies to promote the exchange of knowledge and technology between both parties. Innovation Mentors were professionals retained by the CTI, primarily responsible for evaluating the small-sized and medium-sized enterprises’ need and chance for innovation R&D and helping the enterprises solicit competent academic research partners to engage in the transfer of technology. The third factor of KTT Support, Physical and web-based platforms, is intended to help academic research institutions and private enterprises establish physical liaison channels through organization of activities and installation of network communication platforms, to enable the information about knowledge and technology transfer to be more transparent and communicable widely. In conclusion, the CTI has been dedicated to enhancing the link between scientific research and the industries and urging the industrial sector to involve and boost the R&D projects with market potential. The CTI’s business lines are all equipped with corresponding policy instruments to achieve the industrial-academic cooperation target and mitigate the gap between the industry and academic sectors in the innovation chain. The various CTI policy instruments may be applied in the following manner as identified in the following figure. Data source: CTI Annual Report 2011 Fig. 5 Application of CTI Policy Instrument to Innovation Chain III. Swiss Technology R&D Budget Management and Allocation The Swiss Federal Government has invested considerable expenditures in technology R&D. According to statistic data provided by Swiss Federal Statistical Office (FSO) and OECD, the Swiss research expenditures accounted for 2.37% of the Federal Government’s total expenditures, following the U.S.A. and South Korea (see Fig. 6). Meanwhile, the research expenditures of the Swiss Government grew from CHF2.777 billion in 2000 to CHF4.639 billion in 2010, an average yearly growth rate of 5.9% (see Fig. 7). It is clear that Switzerland highly values its technology R&D. Data source: FSO and OECD Fig. 6 Percentage of Research Expenditures in Various Country Governments’ Total Expenditures (2008) Data source: FSO and OECD Fig. 7 Swiss Government Research Expenditures 2000-2010 1.Management of Swiss Technology R&D Budget Swiss research expenditures are primarily allocated to the education, R&D and innovation areas, and play an important role in the Swiss innovation system. Therefore, a large part of the Swiss research expenditures are allocated to institutions of higher education, including ETH, universities, and UASs. The Swiss research expenditures are utilized by three hierarchies[16] (see Fig. 8): Government R&D funding agencies: The Swiss research budget is primarily executed by three agencies, including SERI, Federal Department of Economic Affairs, Education and Research, and Swiss Agency for Development and Cooperation (SDC). Intermediary R&D funding agencies: Including SNSC and CTI. Funding of R&D performing institutions: Including private enterprises, institutions of higher education and private non-profit-making business, et al. Therefore, the Swiss Government research expenditures may be utilized by the Federal Government directly, or assigned to intermediary agencies, which will allocate the same to the R&D performing institutions. SERI will allocate the research expenditures to institutions of higher education and also hand a lot of the expenditures over to SNSF for consolidated funding to the basic science of R&D. Data source: FSO Fig. 8 Swiss Research Fund Utilization Mechanism ~to be continued~ [1] ORGANIZATION FOR ECONNOMIC CO-OPERATION AND DEVELOPMENT [OECD], OECD Reviews of Innovation Policy: Switzerland 27 (2006). [2] As of January 1, 2013, the Federal Ministry of Economic Affairs was reorganized, and renamed into Federal Department of Economic Affairs, Education and Research (EAER). [3] The Commission for Technology and Innovation CTI, THE COMMISSION FOR TECHOLOGY AND INNOVATION CTI, http://www.kti.admin.ch/org/00079/index.html?lang=en (last visited Jun. 3, 2013). [4] Id. [5] CTI INVEST, Swiss Venture Guide 2012 (2012), at 44, http://www.cti-invest.ch/getattachment/7f901c03-0fe6-43b5-be47-6d05b6b84133/Full-Version.aspx (last visited Jun. 4, 2013). [6] CTI, CTI Activity Report 2012 14 (2013), available at http://www.kti.admin.ch/dokumentation/00077/index.html?lang=en&download=NHzLpZeg7t,lnp6I0NTU042l2Z6ln1ad1IZn4Z2qZpnO2Yuq2Z6gpJCDen16fmym162epYbg2c_JjKbNoKSn6A-- (last visited Jun. 3, 2013). [7] CTI Voucher, THE COMMISSION FOR TECHOLOGY AND INNOVATION CTI, http://www.kti.admin.ch/projektfoerderung/00025/00135/index.html?lang=en (last visited Jun. 3, 2013). [8] Id. [9] CTI, CTI Activity Report 2011 20 (2012), available at http://www.kti.admin.ch/dokumentation/00077/index.html?lang=en&download=NHzLpZeg7t,lnp6I0NTU042l2Z6ln1ad1IZn4Z2qZpnO2Yuq2Z6gpJCDeYR,gWym162epYbg2c_JjKbNoKSn6A--(last visited Jun. 3, 2013). [10] CTI Start-up Brings Science to Market, THE COMMISSION FOR TECHOLOGY AND INNOVATION CTI, http://www.ctistartup.ch/en/about/cti-start-/cti-start-up/ (last visited Jun. 5, 2013). [11] Id. [12] Supra note 8, at 45. [13] Id. [14] CTI Invest, http://www.cti-invest.ch/About/CTI-Invest.aspx (last visited Jun. 5, 2013). [15] KTT Support, CTI, http://www.kti.admin.ch/netzwerke/index.html?lang=en (last visited Jun.5, 2013). [16] Swiss Federal Statistics Office (SFO), Public Funding of Research in Switzerland 2000–2010 (2012), available at http://www.bfs.admin.ch/bfs/portal/en/index/themen/04/22/publ.Document.163273.pdf (last visited Jun. 20, 2013).
Executive Yuan roll-out The Policy of “The Free Economic Pilot Zones”Executive Yuan roll-out The Policy of “The Free Economic Pilot Zones”1.Executive Yuan approved a Bill titled “The Free Economic Pilot Zones Special Act”The “Free Economic Demonstration Zones” (hereinafter as FEDZs) is a critical part to improve the liberalization and internationalization of the economy of Republic of China (R.O.C). By deregulation, FEDZs was conceived as trial zones. Once the results of the program were promising, it would be expanded to the entire country. In order to engage in the regional economic and trade integration, the Executive Yuan approved a Bill titled “The Free Economic Pilot Zones Special Act” (hereinafter as Bill) on April 26th, 2013.On Mar 6th, 2014, the Joint Economic, Internal Administration , and Finance Committee of the Legislation Yuan (the Congress) discussed the Bill for reports and questions. By the end of the March, 2014, the Congress will hold five public hearings. Not until the discussion of the Bill item by item and the passage in the Congress, the second stage of the FEDZ program would not be initiated. There are five main points, including the treatments on foreigners and people from mainland China, tax incentives for Taiwanese businessman, foreign professionals and foreign companies, regulations on untaxed goods and labor, regulations on industrial development, such as the agriculture and the medical, and certain new items on education and professional services.For the reason that the government considered the need of human resources to sustain the operation of the industries, the Executive Yuan is trying to promote innovative education in FEPZs. Since the education requirements for both of public and private universities are unified in local, colleges and universities were restrained and missed some great opportunities to discover their own niches in education. Hence, innovative education in FEPZs is trying to help higher education system to introduce foreign education resources and foresight concepts, and to attract more international students. The innovative educational projects within FEPZs will also facilitate the cooperations among domestic and foreign universities, and set up experimental branch campuses, colleges, degree programs or professional courses. Besides, the financial service sector is also included. Since FEDZs is an important pusher for R.O.C to move forward in regional economic integration, accordingly, the most significant liberate item for the financial industry in the FEPZs is to allow offshore banking units and offshore security units to provide financial products and service (e.g. OSU and OBU). Meanwhile, the financial industry is predicted to receive an NTD$140 billion or more in revenues over the next five year.In summary, FEPZs is regarded as a engine propelling liberalization and internationalization. To gain the international competitiveness, the government will continue to promote policies and measures. By establishing the free economic demonstration zone, it is expected to create innovative effects into the education system and to create more job opportunities.2.Legislation Yuan has reviewd “The Free Ecomonic Pilot Zones Special Act”The Republic of China (R.O.C) have been carried out “free economic” recent years, by promoting “Free Economic Pilot Zone” (hereinafter as FEPZs) to encourage every industrial and foreign investment. Besides, FEPZs will not only keep talents and technologies in R.O.C but also liberalize and internationalize our economic.The Executive Yuan had approved a Bill titled “The Free Economic Pilot Zones Special Act” (hereinafter as the Bill) on Dec. 26th, 2013. At the end of May, the Joint Economic, Internal Administration, and Finance Committee of the Legislation Yuan (the Congress) have taken five public hearings for the Bill, and amended the Bill according to the advices proposed by specialists. Not until the deliberation of the Bill item by item and its passage in the Congress, the second stage of the FEDZ program would not be initiated. There are five main points, including the treatments on foreigners, tax incentives for R.O.C businessman, foreign professionals and foreign companies, regulations on untaxed goods and labor, regulations on industrial development, such as the agriculture and the medical service, and certain new items on education and professional services.The government considers that there have to be enough human resource to sustain the opened industries, so Executive Yuan is trying to promote innovative education in FEPZs. The core concept of FEPZs is foresight, liberalization and internationalization, the premier said, and the higher education systems belong to high-end service and have much more marketability and variability compared to other education systems. Through innovative and efficient way to manage the school could let University being much more liberalized. Furthermore, the higher education systems in R.O.C. have to connect with international education to avoid being marginalized. Our first stage of education innovation will promote to set up “degree programs” and “professional courses”. The first phase for the Ministry of Education is going to found “degree programs” or “professional courses” through collaboration way. The Ministry of Education will also draw up related regulations or guidance on standards for school cooperation, co-regulation, setup conditions, supervision, enrolling new student, and recruiting staff.? Once the Bills pass, The Ministry of Education plans to establish “branch school” and “independence campus” helping R.O.C. higher education goes internationalized.On the other hand, Our medical service also has strong international competitiveness. R.O.C is engage in developing international medical and health industry. The premier said, the Ministry of Health and Welfare have proposed some measures, such as limitation to the number of medical centre, medical personnel working hours, and NHI is not allow to use in the zones.The premier added, on the extemporaneous sittings, “The Free Economic Pilot Zones Special Act” will be the priority bills and be deliberated in the end of June By establishing the free economic demonstration zone, it is expected to propel R.O.C take part in Trans-Pacific Partnership (TPP) and the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP).3.Executive Yuan’s rapid roll-out of “The Free Economic Pilot Zones”, and has published a report concerning the legal and economic implications of its the BillThe “Free Economic Pilot Zones” (hereinafter as FEPZs) plays a pivotal role in promoting market liberalization, especially at an international level. Premier of the Executive Yuan, Mr. Jiang Yi-Hua has stated that the “market economy” and “innovation economy” allows for tremendous economic prosperity to be embraced by the Republic of China (hereinafter as R.O.C). The seizing of such opportunity has been the goal of government efforts, which can be attested by the recent proposal of the “The Free Economic Pilot Zones Special Act” (hereinafter as the Bill), currently undergoing review and consultation proceedings. The Premier further stressed that the national economy should not be left excluded from international commerce, on the other hand, it is imperative that closer economic bonds with other nations are forged, therefore allowing itself open up to wider scope of opportunities for growth. The key in rendering this possible is through the enactment of laws. At a time, when Trans-Pacific nations, including the United States of America, Japan and countries from Southeast Asia, are working towards regional economic cooperation, if R.O.C. is to be left out, it is feared that its position in the global market would further be marginalized.The core innovative strengths of the FEPZs include “Smart Logistics”, “International healthcare services”, “Value added agriculture”, “Financial Services”, “Education Innovation”, all of which are implemented by employing R.O.C.’s finest workforce, knowledge, information and communications technology (ICT), geographical position and cross-strait relationship advantages, leading way for an advantageous basis for pioneering economic development. The first stage of development will be based on 6 locations proximal to the sea (including Keelung Port, Taipei Port, Kaohsiung Port, Suao Harbor, Anping Port, Taichung Port) and Taoyuan Aerotropolis and Pingtung Agricultural Biotech Park. The second stage of development would only commence after the Bill have been approved by the legislative Yuan, which would attract much capital investment, hence boosting high employment rates. Presently, besides the aforementioned regions opened up for the FEPZs, other cities and industrial sites (including those from offshore islands), are striving to gain membership of the FEPZs, or applying for empirical research of the FEPZs.The Executive Yuan has published a report concerning the legal and economic implications of its the Bill on May 2014. The report largely consists of assessments made by varying governing bodies, such as Ministry of Home Affairs, Financial Supervisory Commission etc., on the implications of the draft concerning real estate, employment, fiscal income, logistics, conditions for medical care, agriculture, higher education, social environment and social wealth redistribution etc.Furthermore, international attention has been closely centered on the progress of FEPZs. During the “The third review of the trade policies and practices of Chinese Taipei” after R.O.C accession to the World Trade Organization (WTO) held on the 17th of September 2014 in Geneva, each member state has demonstrated expectations arising out of the direction and planning undertaken for the FEPZs. National economic and international commercial reforms are under way and have seen much progress in further promoting the overall strength of the economic system, in an effort to respond to the rapid global political and economic developments, for example, through the signing of Economic Cooperation Framework Agreement (ECFA), and the implementation of FEPZs policies. In the future, it will be expected that R.O.C. will strive for a more integral international commercial system, allowing much capital investment inflows as well as the cultivating of high-caliber human resources.To promote more liberal and internationalized development of Taiwan economy, government of Republic of China (R.O.C) approved the “Free Economic Pilot Zone (FEPZ) Plan,” which the Bill is currently censored in Legislation Yuan and the measures would be implemented in two phases. The first phase of FEPZs would be initiated within six free trade ports, Taoyuan airport free trade zone, and Pingtung Agricultural Biotechnology Park; other industries that match up with the idea of liberalization, internationalization and foresight can all be incorporated into FEPZ through continuing examination under Execution Yuan. After this special legislation is passed, the set-ups of demonstration zones can be applied by authorities either of central or of local government and the related promotion works of the second phase will be unfolded immediately.Heading to the target of becoming Kin-Xiao (Kinmen and Xiaomen) Free Trade Zone, Kinmen government planned to apply to be one of the FEPZs and thus cooperated with Taiwan Institute of Economic Research (TIER) on December 11, for a commissioned research (which was later released on the conference of accelerating Kin-Xia FTZ on December 19) on evaluating if Kinmen is qualified for an application of FEPZs. Kinmen’s critical location and the featured industries have composed a perfect environment complying with the ideas such as value-added agriculture, international healthcare and innovative education for FEPZ. For instance, the white liquor industry in Kinmen represents the international management and promotion of agricultural products, and is the best example for value-added agriculture. “Long-term Healthcare Village in Kinmen,” which is currently developing in Kinmen, would also be a drive for international healthcare industry. Based on the Taiwan-featured culture, “International Education City” could be developed with a liberal and innovative atmosphere, which would attract famous schools in world to set up their branch school in Kinmen. Above all, Kinmen County vice Mayor, Wu Yo-Chin, indicated that Kinmen would be the first choice for FEPZ and would hold the key to open a new gate for the Cross-Strait. The vice Mayor emphasized that Kinmen government has well budgeting and financial management, which needn’t the extra aids from central government, yet Kinmen was excluded in the first phase of FEPZs. Although Kinmen would apply to be a FEPZ in the second phase after the special legislation passed, Kinmen still strived for taking part in the first phase of FEPZs due to the uncertain schedule for implementation of regulations on FEPZs.National Development Council (NDC), however, gave an opinion on issue of Kinmen applying to be in the first phase of FEPZs, which declared again the original plan for the first phase only included six free trade ports, Taoyuan airport free trade zone, and Pingtung Agricultural Biotechnology Park. NDC also suggested Kinmen could still follow after the first phase and apply to be a FEPZ in the second phase.
- Impact of Government Organizational Reform to Scientific Research Legal System and Response Thereto (1) – For Example, The Finnish Innovation Fund (“SITRA”)
- The Demand of Intellectual Property Management for Taiwanese Enterprises
- Blockchain in Intellectual Property Protection
- Impact of Government Organizational Reform to Research Legal System and Response Thereto (2) – Observation of the Swiss Research Innovation System
- Recent Federal Decisions and Emerging Trends in U.S. Defend Trade Secrets Act Litigation
- The effective and innovative way to use the spectrum: focus on the development of the "interleaved/white space"
- Copyright Ownership for Outputs by Artificial Intelligence
- Impact of Government Organizational Reform to Research Legal System and Response Thereto (2) – Observation of the Swiss Research Innovation System

