Impact of Government Organizational Reform to Scientific Research Legal System and Response Thereto (1) – For Example, The Finnish Innovation Fund (“SITRA”)

Impact of Government Organizational Reform to Scientific Research Legal System and Response Thereto (1) – For Example, The Finnish Innovation Fund (“SITRA”)
I. Foreword
We hereby aim to analyze and research the role played by The Finnish Innovation Fund (“Sitra”) in boosting the national innovation ability and propose the characteristics of its organization and operation which may afford to facilitate the deliberation on Taiwan’s legal system. Sitra is an independent organization which is used to reporting to the Finnish Parliament directly, dedicated to funding activities to boost sustainable development as its ultimate goal and oriented toward the needs for social change. As of 2004, it promoted the fixed-term program. Until 2012, it, in turn, primarily engaged in 3-year program for ecological sustainable development and enhancement of society in 2012. The former aimed at the sustainable use of natural resources to develop new structures and business models and to boost the development of a bioeconomy and low-carbon society, while the latter aimed to create a more well-being-oriented public administrative environment to upgrade various public sectors’ leadership and decision-making ability to introduce nationals’ opinion to policies and the potential of building new business models and venture capital businesses[1].
II. Standing and Operating Instrument of Sitra
1. Sitra Standing in Boosting of Finnish Innovation Policies
(1) Positive Impact from Support of Innovation R&D Activities by Public Sector
Utilization of public sector’s resources to facilitate and boost industrial innovation R&D ability is commonly applied in various countries in the world. Notwithstanding, the impact of the public sector’s investment of resources produced to the technical R&D and the entire society remains explorable[2]. Most studies still indicate positive impact, primarily as a result of the market failure. Some studies indicate that the impact of the public sector’s investment of resources may be observable at least from several points of view, including: 1. The direct output of the investment per se and the corresponding R&D investment potentially derived from investees; 2. R&D of outputs derived from the R&D investment, e.g., products, services and production methods, etc.; 3. direct impact derived from the R&D scope, e.g., development of a new business, or new business and service models, etc.; 4. impact to national and social economies, e.g., change of industrial structures and improvement of employment environment, etc. Most studies indicate that from the various points of view, the investment by public sector all produced positive impacts and, therefore, such investment is needed definitely[3]. The public sector may invest in R&D in diversified manners. Sitra invests in the “market” as an investor of corporate venture investment market, which plays a role different from the Finnish Funding Agency for Technology and Innovation (“Tekes”), which is more like a governmental subsidizer. Nevertheless, Finland’s characteristics reside in the combination of multiple funding and promotion models. Above all, due to the different behavior model, the role played by the former is also held different from those played by the general public sectors. This is why we choose the former as the subject to be studied herein.
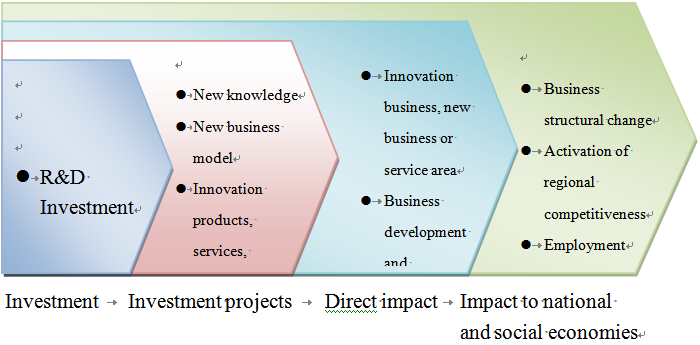
Data source: Jari Hyvärinen & Anna-Maija Rautiainen, Measuring additionality and systemic impacts of public research and development funding – the case of TEKES, FINLAND, RESEARCH EVALUATION, 16(3), 205, 206 (2007).
Fig. 1 Phased Efforts of Resources Invested in R&D by Public Sector
(2) Two Sided f Role Played by Sitra in Boosting of Finnish Innovation Policies
Sitra has a very special position in Finland’s national innovation policies, as it not only helps successful implementation of the innovation policies but also acts an intermediary among the relevant entities. Sitra was founded in 1967 under supervision of the Bank of Finland before 1991, but was transformed into an independent foundation under the direction of the Finnish Parliament[4].
Though Sitra is a public foundation, its operation will not be intervened or restricted by the government. Sitra may initiate any innovation activities for its new organization or system, playing a role dedicated to funding technical R&D or promoting venture capital business. Meanwhile, Sitra also assumes some special function dedicated to decision-makers’ training and organizing decision-maker network to boost structural change. Therefore, Sitra may be identified as a special organization which may act flexibly and possess resources at the same time and, therefore, may initiate various innovation activities rapidly[5].
Sitra is authorized to boost the development of innovation activities in said flexible and characteristic manner in accordance with the Finland Innovation Fund Act (Laki Suomen itsenäisyyden juhlarahastosta). According to the Act, Finland established Sitra in 1967 and Sitra was under supervision of Bank of Finland (Article 1). Sitra was established in order to boost the stable growth of Finland’s economy via the national instrument’s support of R&D and education or other development instruments (Article 2). The policies which Sitra may adopt include loaning or funding, guarantee, marketable securities, participation in cooperative programs, partnership or equity investment (Article 3). If necessary, Sitra may collect the title of real estate or corporate shares (Article 7).
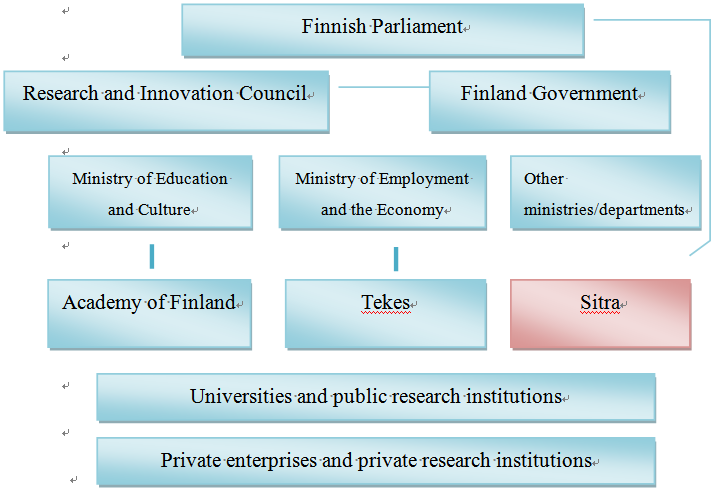
Data source: Finnish innovation system, Research.fi, http://www.research.fi/en/innovationsystem.html (last visited Mar. 15, 2013).
Fig. 2 Finnish Scientific Research Organization Chart
Sitra's innovation role has been evolved through two changes. Specifically, Sitra was primarily dedicated to funding technical R&D among the public sectors in Finland, and the funding model applied by Sitra prior to the changes initiated the technical R&D promotion by Tekes, which was established in 1983. The first change of Sitra took place in 1987. After that, Sitra turned to focus on the business development and venture capital invested in technology business and led the venture capital investment. Meanwhile, it became a partner of private investment funds and thereby boosted the growth of venture capital investments in Finland in 1990. In 2000, the second change of Sitra took place and Sitra’s organization orientation was changed again. It achieved the new goal for structural change step by step by boosting the experimental social innovation activities. Sitra believed that it should play the role contributing to procedural change and reducing systematic obstacles, e.g., various organizational or institutional deadlocks[6].
Among the innovation policies boosted by the Finnish Government, the support of Start-Ups via governmental power has always been the most important one. Therefore, the Finnish Government is used to playing a positive role in the process of developing the venture capital investment market. In 1967, the Government established a venture capital company named Sponsor Oy with the support from Bank of Finland, and Sponsor Oy was privatized after 1983. Finland Government also established Kera Innovation Fund (now known as Finnvera[7]) in 1971, which was dedicated to boosting the booming of Start-Ups in Finland jointly with Finnish Industry Investment Ltd. (“FII”) established by the Government in 1994, and Sitra, so as to make the “innovation” become the main development force of the country[8] .
Sitra plays a very important role in the foundation and development of venture capital market in Finland and is critical to the Finnish Venture Capital Association established in 1990. After Bank of Finland was under supervision of Finnish Parliament in 1991, Sitra became on the most important venture capital investors. Now, a large portion of private venture capital funds are provided by Sitra[9]. Since Sitra launched the new strategic program in 2004, it has turned to apply smaller sized strategic programs when investing young innovation companies, some of which involved venture capital investment. The mapping of young innovation entrepreneurs and angel investors started as of 1996[10].
In addition to being an important innovation R&D promoter in Finland, Sitra is also an excellent organization which is financially self-sufficient and tends to gain profit no less than that to be generated by a private enterprise. As an organization subordinated to the Finnish Parliament immediately, all of Sitra’s decisions are directly reported to the Parliament (public opinion). Chairman of Board, Board of Directors and supervisors of Sitra are all appointed by the Parliament directly[11]. Its working funds are generated from interest accruing from the Fund and investment income from the Fund, not tax revenue or budget prepared by the Government any longer. The total fund initially founded by Bank of Finland amounted to DEM100,000,000 (approximately EUR17,000,000), and was accumulated to DEM500,000,000 (approximately EUR84,000,000) from 1972 to 1992. After that, following the increase in market value, its nominal capital amounted to DEM1,400,000,000 (approximately EUR235,000,000) from 1993 to 2001. Obviously, Sitra generated high investment income. Until 2010, it has generated the investment income amounting to EUR697,000,000 .
In fact, Sitra’s concern about venture capital investment is identified as one of the important changes in Finland's national technical R&D polices after 1990[13]. Sitra is used to funding businesses in three manners, i.e., direct investment in domestic stock, investment in Finnish venture capital funds, and investment in international venture capital funds, primarily in four industries, technology, life science, regional cooperation and small-sized & medium-sized starts-up. Meanwhile, it also invests in venture capital funds for high-tech industries actively. In addition to innovation technology companies, technical service providers are also its invested subjects[14].
2. “Investment” Instrument Applied by Sitra to Boost Innovation Business
The Starts-Up funding activity conducted by Sitra is named PreSeed Program, including INTRO investors’ mapping platform dedicated to mapping 450 angel investment funds and entrepreneurs, LIKSA engaged in working with Tekes to funding new companies no more than EUR40,000 for purchase of consultation services (a half thereof funded by Tekes, and the other half funded by Sitra in the form of loan convertible to shares), DIILI service[15] dedicated to providing entrepreneurs with professional sale consultation resources to integrate the innovation activity (product thereof) and the market to remedy the deficit in the new company’s ability to sell[16].
The investment subjects are stated as following. Sitra has three investment subjects, namely, corporate investments, fund investments and project funding.
(1) Corporate investment
Sitra will not “fund” enterprises directly or provide the enterprises with services without consideration (small-sized and medium-sized enterprises are aided by other competent authorities), but invest in the businesses which are held able to develop positive effects to the society, e.g., health promotion, social problem solutions, utilization of energy and effective utilization of natural resources. Notwithstanding, in order to seek fair rate of return, Sitra is dedicated to making the investment (in various enterprises) by its professional management and technology, products or competitiveness of services, and ranging from EUR300,000 to EUR1,000,000 to acquire 10-30% of the ownership of the enterprises, namely equity investment or convertible funding. Sitra requires its investees to value corporate social responsibility and actively participate in social activities. It usually holds the shares from 4 years to 10 years, during which period it will participate the corporate operation actively (e.g., appointment of directors)[17].
(2) Fund investments
For fund investments[18], Sitra invests in more than 50 venture capital funds[19]. It invests in domestic venture capital fund market to promote the development of the market and help starts-up seek funding and create new business models, such as public-private partnerships. It invests in international venture capital funds to enhance the networking and solicit international funding, which may help Finnish enterprises access international trend information and adapt to the international market.
(3) Project funding
For project funding, Sitra provides the on-site information survey (supply of information and view critical to the program), analysis of business activities (analysis of future challenges and opportunities) and research & drafting of strategies (collection and integration of professional information and talents to help decision making), and commissioning of the program (to test new operating model by commissioning to deal with the challenge from social changes). Notwithstanding, please note that Sitra does not invest in academic study programs, research papers or business R&D programs[20].
(4) DIILI Investment Model Integrated With Investment Absorption
A Start-Up usually will not lack technologies (usually, it starts business by virtue of some advanced technology) or foresighted philosophy when it is founded initially, while it often lacks the key to success, the marketing ability. Sitra DIILI is dedicated to providing the professional international marketing service to help starts-up gain profit successfully. Owing to the fact that starts-up are usually founded by R&D personnel or research-oriented technicians, who are not specialized in marketing and usually retains no sufficient fund to employ marketing professionals, DILLI is engaged in providing dedicated marketing talents. Now, it employs about 85 marketing professionals and seeks to become a start-up partner by investing technical services.
Notwithstanding, in light of the characteristics of Sitra’s operation and profitability, some people indicate that it is more similar to a developer of an innovation system, rather than a neutral operator. Therefore, it is not unlikely to hinder some work development which might be less profitable (e.g., establishment of platform). Further, Sitra is used to developing some new investment projects or areas and then founding spin-off companies after developing the projects successfully. The way in which it operates seems to be non-compatible with the development of some industries which require permanent support from the public sector. The other issues, such as INTRO lacking transparency and Sitra's control over investment objectives likely to result in adverse choice, all arise from Sitra’s consideration to its own investment opportunities and profit at the same time of mapping. Therefore, some people consider that it should be necessary to move forward toward a more transparent structure or a non-income-oriented funding structure[21] . Given this, the influence of Sitra’s own income over upgrading of the national innovation ability when Sitra boosts starts-up to engage in innovation activities is always a concern remaining disputable in the Finnish innovation system.
3. Boosting of Balance in Regional Development and R&D Activities
In order to fulfill the objectives under Lisbon Treaty and to enable EU to become the most competitive region in the world, European Commission claims technical R&D as one of its main policies. Among other things, under the circumstance that the entire R&D competitiveness upgrading policy is always progressing sluggishly, Finland, a country with a population of 5,300,000, accounting for 1.1% of the population of 27 EU member states, was identified as the country with the No. 1 innovation R&D ability in the world by World Economic Forum in 2005. Therefore, the way in which it promotes innovation R&D policies catches the public eyes. Some studies also found that the close relationship between R&D and regional development policies of Finland resulted in the integration of regional policies and innovation policies, which were separated from each other initially, after 1990[22]. Finland has clearly defined the plan to exploit the domestic natural resources and human resources in a balanced and effective manner after World War II. At the very beginning, it expanded the balance of human resources to low-developed regions, in consideration of the geographical politics, but in turn, it achieved national balanced development by meeting the needs for a welfare society and mitigation of the rural-urban divide as time went by. The Finnish innovation policies which may resort to technical policies retroactively initially drove the R&D in the manners including upgrading of education degree, founding of Science and Technology Policy Council and Sitra, establishment of Academy of Finland (1970) and establishment of the technical policy scheme, et al.. Among other things, people saw the role played by Sitra in Finland’s knowledge-intensive society policy again. From 1991 to 1995, the Finnish Government officially included the regional competitiveness into the important policies. The National Industrial Policy for Finland in 1993 adopted the strategy focusing on the development based on competitive strength in the regional industrial communities[23].
Also, some studies indicated that in consideration of Finland’s poor financial and natural resources, its national innovation system should concentrate the resources on the R&D objectives which meet the requirements about scale and essence. Therefore, the “Social Innovation, Social and Economic Energy Re-building Learning Society” program boosted by Sitra as the primary promoter in 2002 defined the social innovation as “the reform and action plan to enhance the regulations of social functions (law and administration), politics and organizational structure”, namely reform of the mentality and cultural ability via social structural changes that results in social economic changes ultimately. Notwithstanding, the productivity innovation activity still relies on the interaction between the enterprises and society. Irrelevant with the Finnish Government’s powerful direction in technical R&D activities, in fact, more than two-thirds (69.1%) of the R&D investment was launched by private enterprises and even one-thirds launched by a single enterprise (i.e., Nokia) in Finland. At the very beginning of 2000, due to the impact of globalization to Finland’s innovation and regional policies, a lot of R&D activities were emigrated to the territories outside Finland[24]. Multiple disadvantageous factors initiated the launch of national resources to R&D again. The most successful example about the integration of regional and innovation policies in Finland is the Centres of Expertise Programme (CEP) boosted by it as of 1990. Until 1994, there have been 22 centres of expertise distributed throughout Finland. The centres were dedicated to integrating local universities, research institutions and enterprise for co-growth. The program to be implemented from 2007 to 2013 planned 21 centres of expertise (13 groups), aiming to promote the corporate sectors’ cooperation and innovation activities. CEP integrated local, regional and national resources and then focused on the businesses designated to be developed[25].
[1] Sitra, http://www.sitra.fi/en (last visited Mar. 10, 2013).
[2] Jari Hyvärinen & Anna-Maija Rautiainen, Measuring additionality and systemic impacts of public research and development funding – the case of TEKES, FINLAND, RESEARCH EVALUATION, 16(3), 205, 208 (2007).
[3] id. at 206-214.
[4] Charles Edquist, Tterttu Luukkonen & Markku Sotarauta, Broad-Based Innovation Policy, in EVALUATION OF THE FINNISH NATIONAL INNOVATION SYSTEM – FULL REPORT 11, 25 (Reinhilde Veugelers st al. eds., 2009).
[5] id.
[6] id.
[7] Finnvera is a company specialized in funding Start-Ups, and its business lines include loaning, guarantee, venture capital investment and export credit guarantee, etc. It is a state-run enterprise and Export Credit Agency (ECA) in Finland. Finnvera, http://annualreport2012.finnvera.fi/en/about-finnvera/finnvera-in-brief/ (last visited Mar. 10, 2013).
[8] Markku Maula, Gordon Murray & Mikko Jääskeläinen, MINISTRY OF TRADE AND INDUSTRY, Public Financing of Young Innovation Companies in Finland 32 (2006).
[9] id. at 33.
[10] id. at 41.
[11] Sitra, http://www.sitra.fi/en (last visited Mar. 10, 2013).
[12] Sitra, http://www.sitra.fi/en (last visited Mar. 10, 2013).
[13] The other two were engaged in boosting the regional R&D center and industrial-academy cooperative center programs. Please see Gabriela von Blankenfeld-Enkvist, Malin Brännback, Riitta Söderlund & Marin Petrov, ORGANISATION FOR ECONOMIC CO-OPERATION AND DEVELOPMENT [OECD],OECD Case Study on Innovation: The Finnish Biotechnology Innovation System 15 (2004).
[14] id. at20.
[15] DIILI service provides sales expertise for SMEs, Sitra, http://www.sitra.fi/en/articles/2005/diili-service-provides-sales-expertise-smes-0 (last visited Mar. 10, 2013).
[16] Maula, Murray & Jääskeläinen, supra note 8 at 41-42.
[17] Corporate investments, Sitra, http://www.sitra.fi/en/corporate-investments (last visited Mar. 10, 2013).
[18] Fund investments, Sitra, http://www.sitra.fi/en/fund-investments (last visited Mar. 10, 2013).
[19] The venture capital funds referred to herein mean the pooled investment made by the owners of venture capital, while whether it exists in the form of fund or others is not discussed herein.
[20] Project funding, Sitra, http://www.sitra.fi/en/project-funding (last visited Mar. 10, 2013).
[21] Maula, Murray & Jääskeläinen, supra note 8 at 42.
[22] Jussi S. Jauhiainen, Regional and Innovation Policies in Finland – Towards Convergence and/or Mismatch? REGIONAL STUDIES, 42(7), 1031, 1032-1033 (2008).
[23] id. at 1036.
[24] id. at 1038.
[25] id. at 1038-1039.
Over the past twenty years, the Government has sought to cultivate the biopharmaceutical industry as one of the future major industry in Taiwan. Back in 1982, the Government has begun to regard biotechnology as a key technology in Technology Development Program, demonstrated that biotechnology is a vital technology in pursuit of future economic growth. Subsequently, the Government initiated national programs that incorporated biotechnology as a blueprint for future industrial development. In order to enhance our competitiveness and building an initial framework for the industry, The Executive Yuan has passed the Biotechnology Industry Promotion Plan. As the Government seeks to create future engines of growth by building an environment conducive for enterprise development, the Plan has been amended four times, and implemented measures focused on the following six areas: related law and regulations, R&D and applications, technology transfer and commercialization, personnel training, investment promotion and coordination, marketing information and marketing service. In 2002, the Executive Yuan approved the Challenge 2008, a six-year national development plan, pointing out biotechnology industry as one of the Two Trillion, Twin Stars industries. The Government planned for future economic growth by benefiting through the attributes of the biotechnology: high-tech, high-reward and less pollution. Thus, since 1997 the Strategic Review Board (SRB) under the Executive Yuan Science and Technology Advisory Panel has taken action in coordinating government policies with industry comments to form a sound policy for the biotechnology industry. Additionally, a well-established legal system for sufficient protection of intellectual property rights is the perquisite for building the industry, as the Government recognized the significance through amending and executing related laws and regulations. By stipulating data exclusivity and experimental use exception in the Pharmaceutical Affair Act, tax benefits provided in Statute for Upgrading Industries , Incentives for Production and R&D of Rare Disease Medicine, Incentives for Medical Technology Research and Development, provide funding measures in the Guidance of Reviewing Programs for Promoting Biotechnology Investment. Clearly, the government has great expectation for the industry through establishing a favorable environment by carrying out these policies and revising outdated regulations. Thus, the Legislative Yuan has passed the “Act for The Development of Biotechnology and New Pharmaceuticals Industry” in June, 2007, and immediately took effect in July. The relevant laws and regulations became effective as well, driving the industry in conducting researches on new drugs and manufacturing new products, increasing sales and expanding the industry to meet an international level. For a biopharmaceutical industry that requires long-term investment and costly R&D, incentive measures is vital to the industry’s survival before the product launches the market. Accordingly, this article will be introducing the recent important regulation that supports the biopharmaceutical industry in Taiwan, and analyzing the government’s policies. Biotechnology is increasingly gaining global attention for its potential in building future economic growth and generating significant profits. In an effort to support the biotechnology industry in Taiwan, the Government has made a step forward by enacting the “Act for the Development of Biotech and New Pharmaceutical Industry”. The biopharmaceutical industry is characterized as high-risk and high-reward, strong government support and a well-developed legal system plays a vital role from its establishment throughout the long term development. Therefore, the Act was enacted tailor to the Biotech and New Pharmaceutical Industry, primarily focuses on tax benefits, R&D activities, personnel recruitment and investment funding, in support of start-up companies and attracting a strong flow of funding worldwide. To pave the way for promoting the biopharmaceutical industry and the Biotech and New Pharmaceutical Company, here the article will be introducing the incentive measures provided in the Act, and supporting development of the industry, demonstrating the efforts made by the Government to build a “Bio-tech Island”. Reference “Act for Development of Biotech and New Pharmaceutical Industry”, webpage of Law and Regulations Database of the Republic of China. 4 July, 2007. Ministry of Justice, Taiwan. 5 Nov. 2008 http://law.moj.gov.tw/Eng/Fnews/FnewsContent.asp?msgid=3180&msgType=en&keyword=undefined
Innovative Practice of Israel's Government ProcurementInnovative Practice of Israel's Government Procurement Government procurement is an important pillar of government services. Because of the huge number of government purchases, government procurement management play an important role in promoting public sector efficiency and building citizenship. Well-designed government procurement systems also help to achieve policy such as environmental protection, innovation, start-ups and the development of small and medium-sized enterprises. Nowadays, countries in the world, especially OECD countries, have been widely practiced with innovative procurement to stimulate innovation and start-ups, and call Innovation procurement can deliver solutions to challenges of public interest and ICTs can play a major role in this. However, in the OECD countries, in addition to the advanced countries that have been developed, many developing countries have also used government procurement to stimulate national R & D and innovation with remarkable results. Israel is one of the world's leading technology innovation centers, one of the most innovative economies in the world, continues to leverage its own strengths, support of technology entrepreneurship and unique environment, an international reputation in the high-tech industry, the spirit of technological innovation and novelty. Government procurement is a core element of the activities of Israeli government, agreement with suppliers and compliance with the Mandatory Tenders Law. The main challenge is how to ensure efficiency and maintain government performance while ensuring an equitable and transparent procurement process. Israel’s Mandatory Tenders Law has shown the central role played by the Israeli Supreme Court in creating and developing this law, even in the absence of any procurement legislation, based instead on general principles of administrative law. Once the project of creating a detailed body of public tendering law had been completed, and the legislator was about to step in, the Supreme Court was prepared to step out and transferring the jurisdiction to lower courts. The Knesset passed the Mandatory Tenders Law, and based on it the Government issued the various tendering regulations. Besides, Israel's various international agreements on government procurement, mainly GPA and other bilateral international agreements such as free trade agreements with Mexico and Colombia and free trade agreements and memoranda of understanding with the United States. The practical significance of these commitments can only be understood on the backdrop of Israel’s domestic preference and offset policies. These policies were therefore discussed and analyzed as they apply when none of the international agreements applies. The Challenge Tenders "How to solve the problem of overcrowding in the emergency department and the internal medicine department?" is the first of a series of "problem solicitations" released by the Israeli Ministry of Health which seeks to find a digital solution to the public health system problem, questions from the government while avoiding preconceived prejudices affect the nature of the solution, allowing multiple innovative ideas from different fields to enter the health system, make fair and transparent judgments about the ideal solution to the problem. In order to ensure transparency and integrity, equality, efficiency and competition in the decision-making process, the tender proposed by the Israeli Ministry of Health defines a two-stage tender process. The Ministry of Health of Israel, in order to improve the quality of medical care, shorten the waiting time for hospitalized patients, protect the dignity of patients and their families with patients as its center, and ensure their rights, while alleviating the burden of hospital staff, so as to pass the targeted treatment areas reduce the gap between various residential areas. The Israeli government deals with these issues through challenging tenders and offers a digital solution combined with innovative ideas. The initiative proposed through the development of public service projects can raise the level of public services in the country and help the government to reduce costs and achieve the purpose of promoting innovation with limited conceptual, technical and financial capabilities. In addition, due to the online operation of the challenging tender process throughout the entire process, fair and transparent procedures can be ensured, while public-private partnerships are encouraged to facilitate the implementation of the implementation plan.
Brief Introduction to Taiwan Social Innovation PoliciesBrief Introduction to Taiwan Social Innovation Policies 2021/09/13 1. Introduction The Millennium Development Goals (MDGs)[1] set forth by the United Nations in 2000 are carried out primarily by nations and international organizations. Subsequently, the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) set forth by the United Nations in 2015 started to delegate the functions to organizations of all levels. Presently, there is a global awareness of the importance of balancing “economic growth”, “social progress”, and “environmental protection” simultaneously during development. In the above context, many similar concepts have arisen worldwide, including social/solidarity economy, social entrepreneurship and social enterprise, and social innovation. Generally, social innovation aims to alter the interactions between various groups in society through innovative applications of technology or business models, and to find new ways to solve social problems through such alterations. In other words, the goal is to use innovative methods to solve social problems.The difference between social innovation and social enterprise is that social enterprise combines commercial power to achieve its social mission under a specific perspective, while social innovation creates social value through cooperation with and coordination among technology, resources, and communities under a diversified nature. 2. Overview of Taiwan Social Enterprise Policy To integrate into the global community and assist in the development of domestic social innovation, Taiwan’s Executive Yuan launched the “Social Enterprise Action Plan” in 2014, which is the first policy initiative to support social enterprises (from 2014 to 2016).Under this policy initiative, through consulting with various ministries and applying methods such as “amending regulations”, “building platforms”, and “raising funds”, the initiative set to create an environment with favorable conditions for social innovation and start-ups. At this stage, the initiative was adopted under the principle of “administrative guidance before legislation” in order to encourage private enterprise development without excessive burden, and avoid regulations restricting the development of social enterprises, such as excessive definition of social enterprises. Moreover, for preserving the original types of these enterprises, this Action Plan did not limit the types of social enterprises to companies, non-profit organizations, or other specific types of organizations. To sustain the purpose of the Social Enterprise Action Plan and to echo and reflect the 17 sustainable development goals proposed in SDGs by the United Nations, the Executive Yuan launched the “Social Innovation Action Plan” (effective from 2018 to 2022) in 2018 to establish a friendly development environment for social innovation and to develop diversified social innovation models through the concept of “openness, gathering, practicality, and sustainability”.In this Action Plan, “social innovation” referred to “social innovation organizations” that solve social problems through technology or innovative business models. The balancing of the three managerial goals of society, environment value, and profitability is the best demonstration of the concept of social innovation. 3. Government’s Relevant Social Enterprise Policy and Resources The ministries of the Taiwan Government have been promoting relevant policies in accordance with the Social Innovation Action Plan issued by the Executive Yuan in 2018, such as the “Registration System for Social Innovation Enterprises” (counseling of social enterprises), the “Buying Power - Social Innovation Products and Services Procurement”, the “Social Innovation Platform” established by the Ministry of Economic Affairs, the “Social Innovation Manager Training Courses”, the “Promoting Social Innovation and Employment Opportunities” administered by the Ministry of Labor, and the “University Social Responsibility Program” published by the Ministry of Education. Among the above policies stands out the measures adopted by the Ministry of Economic Affairs, and a brief introduction of those policies are as follows: i. Social Innovation Platform To connect all resources involved in social issues to promote social innovation development in Taiwan, the Ministry of Economic Affairs established the “Social Innovation Platform”.[2] With visibility through the Social Innovation Platform, it has become more efficient to search for targets in a public and transparent way and to assist with the input of resources originally belonging to different fields in order to expand social influence. As a digital platform gathering “social innovation issues in Taiwan,” the Social Innovation Platform covers multiple and complete social innovation resources, which include the “SDGs Map” constructed on the Social Innovation Platform, by which we can better understand how county and city governments in Taiwan implement SDGs and Voluntary Local Review Reports, and which allow us to search the Social Innovation Database[3] and the registered organizations, by which citizens, enterprises, organizations, and even local governments concerned with local development can find their partners expediently as possible, establish service lines to proactively assist public or private entities with their needs/resources, and continue to enable the regional revitalization organizations, ministries, and enterprises to identify and put forward their needs for social innovation through the function of “Social Innovation Proposals”, which assist social innovation organizations with visibility while advancing cooperation and expanding social influence. In addition, the “Event Page” was established on the Social Innovation Platform and offers functions, such as the publishing, searching, and sorting of events in four major dimensions with respect to social innovation organization, governments, enterprises, and citizens; and encourages citizens, social innovation organizations, enterprises, and governments to devote themselves via open participation to continuously expande the influence of the (Civic Technology) Social Innovation Platform. The “Corporate Social Responsibility Report” collects the corporate social responsibility reports, observes the distribution of resources for sustainable development by corporations in Taiwan, offers filtering functions by regions, keyword, popular rankings, and or SDGs types, and provides contact information and a download function for previous years’ reports, in order to effectively assist social innovation organizations to obtain a more precise understanding of the status quo, needs, and trends with respect to their development of respective products and services. Figure 1: SDGs Map Reference: Social Innovation Platform (https://si.taiwan.gov.tw/) Figure 2: Social Innovation Database Reference: Social Innovation Platform (https://si.taiwan.gov.tw/) Figure 3: Social Innovation Proposals Reference: Social Innovation Platform (https://si.taiwan.gov.tw/) Figure 4: Event Page Reference: Social Innovation Platform (https://si.taiwan.gov.tw/) Figure 5: Corporate Social Responsibility Report Reference: Social Innovation Platform (https://si.taiwan.gov.tw/) ii. Social Innovation Database To encourage social innovation organizations to disclose their social missions, products and services, and to guide society to understand the content of social innovation, and to assist the administrative ministries to be able to utilize such information, the Ministry of Economic Affairs issued the “Principles of Registration of Social Innovation Organizations” to establish the “Social Innovation Database”. Once a social innovation organization discloses the items, such as its social missions, business model, or social influence, it may obtain the relevant promotional assistance resources, including becoming a trade partner with Buying Power (Social Innovation Products and Services Procurement), receiving exclusive consultation and assistance from professionals for social innovation organizations, and becoming qualified to apply to entering into the Social Innovation Lab.Moreover, the Ministry of Economic Affairs is simultaneously consolidating, identifying, and designating the awards and grants offered by the various ministries, policies and measures in respect of investment, and financing and assistance, as resources made available to registered entities. As of 25 May 2021, there were 658 registered social innovation organizations and 96 Social Innovation Partners (enterprises with CSR or ESG resources that recognize the cooperation with social innovation under the social innovation thinking model may be registered as a “Social Innovation Partner”).The public and enterprises can search for organizations registered in the Social Innovation Database through the above-said Social Innovation Platform, the search ability of which advances the exposure of and the opportunities for cooperation with social innovation organizations. Figure 6: Numbers of registered social innovation organizations and accumulated value of purchases under Buying Power Reference: Social Innovation Platform(https://si.taiwan.gov.tw/) iii. Buying Power - Social Innovation Products and Services Procurement In order to continue increasing the awareness on social innovation organizations and related issues and promote responsible consumption and production in Taiwan, as well as to raise the attention of the commercial sector to the sustainability-driven procurement models, the Ministry of Economic Affairs held the first “Buying Power - Social Innovation Products and Services Procurement” event in 2017. Through the award system under the Buying Power, it continues to encourage the governments, state-owned enterprises, private enterprises, and organizations to take the lead in purchasing products or services from social innovation organizations, to provide the relevant resources so as to assist social innovation organizations to obtain resources and to explore business opportunities in the markets, to practice responsible consumption and production, and to promote innovative cooperation between all industries and commerce and social innovation organizations. The aim of the implementation of the Buying Power is to encourage the central and local governments, state-owned enterprises, private enterprises, and non-governmental organizations to purchase products or services from organizations registered in the Social Innovation Database, while prizes will be awarded based on the purchase amounts accumulated during the calculation period. The winners can obtain priority in applying for membership in the Social Innovation Partner Group, with corresponding member services, in the future. Under the Social Innovation Platform, both the amount of purchase awards and the number of applicants for special awards continue to increase.So far, purchases have accumulated to a value of more than NT$1.1 billion (see Figure 6), and more than 300 organizations have proactively participated. iv. Social Innovation Mark In order to promote public awareness of social innovation, the Ministry of Economic Affairs has been charged with the commissioned task of promoting the Social Innovation Mark, and issued “ The Small and Medium Enterprise Administration of the Ministry of Economic Affairs Directions for Authorization of the Social Innovation Mark” as the standard for the authorization of the Social Innovation Mark. Social innovation organizations can use the Mark, through obtaining authorization, to hold Social Innovation Summits or other social innovation activities for promoting social innovation concepts. In order to build the Mark as a conceptual symbol of social innovation, the Ministry of Economic Affairs has been using the Social Innovation Mark in connection with various social innovation activities, such as the Social Innovation Platform, the Buying Power, and the annual Social Innovation Summit. Taking the selection of sponsors of the Social Innovation Summit in 2022 as an example[4], only organizations that have obtained authorization of the Social Innovation Mark can use the Mark to hold the Social Innovation Summit. Figure 7: The Social Innovation Mark of the Small and Medium Enterprise Administration, Ministry of Economic Affairs IV. Conclusion The “Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development” (OECD) regards social innovation as a new strategy for solving future social problems and as an important method for youth entrepreneurship and social enterprise development.Taiwan’s social innovation energy has entered a stage of expansion and development. Through the promotion of the “Social Innovation Action Plan,” the resources from the central and local governments are integrated to establish the Social Innovation Platform, the Social Innovation Database, the Social Innovation Lab, and the Social Innovation Mark. In addition, incentives such as the Buying Power have been created, manifesting the positive influence of Taiwan’s social innovation. [1] MDGs are put forward by the United Nations in 2000, and are also the goals requiring all the 191 member states and at least 22 international organizations of the United Nations to be committed to on their best endeavors, including: 1. eradicating extreme poverty and hunger, 2. applying universal primary education, 3. promoting gender equality and empowering women, 4. reducing child mortality rates, 5. improving maternal health, 6. combatting HIV/AIDS, malaria, and other diseases, 7. ensuring environmental sustainability, and 8. establishing a global partnership for development. [2] Please refer to the Social Innovation Platform: https://si.taiwan.gov.tw/. [3] Please refer to the Social Innovation Database: https://si.taiwan.gov.tw/Home/Org_list. [4] Please refer to the guidelines for the selection of sponsors of the 2022 Social Innovation Summit: https://www.moeasmea.gov.tw/files/6221/4753E497-B422-4303-A8D4-35AE0B4043A9
The use of automated facial recognition technology and supervision mechanism in UKThe use of automated facial recognition technology and supervision mechanism in UK I. Introduction Automatic facial recognition (AFR) technology has developed rapidly in recent years, and it can identify target people in a short time. The UK Home Office announced the "Biometrics Strategy" on June 28, 2018, saying that AFR technology will be introduced in the law enforcement, and the Home Office will also actively cooperate with other agencies to establish a new oversight and advisory board in order to maintain public trust. AFR technology can improve law enforcement work, but its use will increase the risk of intruding into individual liberty and privacy. This article focuses on the application of AFR technology proposed by the UK Home Office. The first part of this article describes the use of AFR technology by the police. The second part focuses on the supervision mechanism proposed by the Home Office in the Biometrics Strategy. However, because the use of AFR technology is still controversial, this article will sort out the key issues of follow-up development through the opinions of the public and private sectors. The overview of the discussion of AFR technology used by police agencies would be helpful for further policy formulation. II. Overview of the strategy of AFR technology used by the UK police According to the Home Office’s Biometrics Strategy, the AFR technology will be used in law enforcement, passports and immigration and national security to protect the public and make these public services more efficient[1]. Since 2017 the UK police have worked with tech companies in testing the AFR technology, at public events like Notting Hill Carnival or big football matches[2]. In practice, AFR technology is deployed with mobile or fixed camera systems. When a face image is captured through the camera, it is passed to the recognition software for identification in real time. Then, the AFR system will process if there is a ‘match’ and the alarm would solicit an operator’s attention to verify the match and execute the appropriate action[3]. For example, South Wales Police have used AFR system to compare images of people in crowds attending events with pre-determined watch lists of suspected mobile phone thieves[4]. In the future, the police may also compare potential suspects against images from closed-circuit television cameras (CCTV) or mobile phone footage for evidential and investigatory purposes[5]. The AFR system may use as tools of crime prevention, more than as a form of crime detection[6]. However, the uses of AFR technology are seen as dangerous and intrusive by the UK public[7]. For one thing, it could cause serious harm to democracy and human rights if the police agency misuses AFR technology. For another, it could have a chilling effect on civil society and people may keep self-censoring lawful behavior under constant surveillance[8]. III. The supervision mechanism of AFR technology To maintaining public trust, there must be a supervision mechanism to oversight the use of AFR technology in law enforcement. The UK Home Office indicates that the use of AFR technology is governed by a number of codes of practice including Police and Criminal Evidence Act 1984, Surveillance Camera Code of Practice and the Information Commissioner’s Office (ICO)’s Code of Practice for surveillance cameras[9]. (I) Police and Criminal Evidence Act 1984 The Police and Criminal Evidence Act (PACE) 1984 lays down police powers to obtain and use biometric data, such as collecting DNA and fingerprints from people arrested for a recordable offence. The PACE allows law enforcement agencies proceeding identification to find out people related to crime for criminal and national security purposes. Therefore, for the investigation, detection and prevention tasks related to crime and terrorist activities, the police can collect the facial image of the suspect, which can also be interpreted as the scope of authorization of the PACE. (II) Surveillance Camera Code of Practice The use of CCTV in public places has interfered with the rights of the people, so the Protection of Freedoms Act 2012 requires the establishment of an independent Surveillance Camera Commissioner (SCC) for supervision. The Surveillance Camera Code of Practice proposed by the SCC sets out 12 principles for guiding the operation and use of surveillance camera systems. The 12 guiding principles are as follows[10]: A. Use of a surveillance camera system must always be for a specified purpose which is in pursuit of a legitimate aim and necessary to meet an identified pressing need. B. The use of a surveillance camera system must take into account its effect on individuals and their privacy, with regular reviews to ensure its use remains justified. C. There must be as much transparency in the use of a surveillance camera system as possible, including a published contact point for access to information and complaints. D. There must be clear responsibility and accountability for all surveillance camera system activities including images and information collected, held and used. E. Clear rules, policies and procedures must be in place before a surveillance camera system is used, and these must be communicated to all who need to comply with them. F. No more images and information should be stored than that which is strictly required for the stated purpose of a surveillance camera system, and such images and information should be deleted once their purposes have been discharged. G. Access to retained images and information should be restricted and there must be clearly defined rules on who can gain access and for what purpose such access is granted; the disclosure of images and information should only take place when it is necessary for such a purpose or for law enforcement purposes. H. Surveillance camera system operators should consider any approved operational, technical and competency standards relevant to a system and its purpose and work to meet and maintain those standards. I. Surveillance camera system images and information should be subject to appropriate security measures to safeguard against unauthorised access and use. J. There should be effective review and audit mechanisms to ensure legal requirements, policies and standards are complied with in practice, and regular reports should be published. K. When the use of a surveillance camera system is in pursuit of a legitimate aim, and there is a pressing need for its use, it should then be used in the most effective way to support public safety and law enforcement with the aim of processing images and information of evidential value. L. Any information used to support a surveillance camera system which compares against a reference database for matching purposes should be accurate and kept up to date. (III) ICO’s Code of Practice for surveillance cameras It must need to pay attention to the personal data and privacy protection during the use of surveillance camera systems and AFR technology. The ICO issued its Code of Practice for surveillance cameras under the Data Protection Act 1998 to explain the legal requirements operators of surveillance cameras. The key points of ICO’s Code of Practice for surveillance cameras are summarized as follows[11]: A. The use time of the surveillance camera systems should be carefully evaluated and adjusted. It is recommended to regularly evaluate whether it is necessary and proportionate to continue using it. B. A police force should ensure an effective administration of surveillance camera systems deciding who has responsibility for the control of personal information, what is to be recorded, how the information should be used and to whom it may be disclosed. C. Recorded material should be stored in a safe way to ensure that personal information can be used effectively for its intended purpose. In addition, the information may be considered to be encrypted if necessary. D. Disclosure of information from surveillance systems must be controlled and consistent with the purposes for which the system was established. E. Individuals whose information is recoded have a right to be provided with that information or view that information. The ICO recommends that information must be provided promptly and within no longer than 40 calendar days of receiving a request. F. The minimum and maximum retention periods of recoded material is not prescribed in the Data Protection Act 1998, but it should not be kept for longer than is necessary and should be the shortest period necessary to serve the purposes for which the system was established. (IV) A new oversight and advisory board In addition to the aforementioned regulations and guidance, the UK Home Office mentioned that it will work closely with related authorities, including ICO, SCC, Biometrics Commissioner (BC), and Forensic Science Regulator (FSR) to establish a new oversight and advisory board to coordinate consideration of law enforcement’s use of facial images and facial recognition systems[12]. To sum up, it is estimated that the use of AFR technology by law enforcement has been abided by existing regulations and guidance. Firstly, surveillance camera systems must be used on the purposes for which the system was established. Secondly, clear responsibility and accountability mechanisms should be ensured. Thirdly, individuals whose information is recoded have the right to request access to relevant information. In the future, the new oversight and advisory board will be asked to consider issues relating to law enforcement’s use of AFR technology with greater transparency. IV. Follow-up key issues for the use of AFR technology Regarding to the UK Home Office’s Biometrics Strategy, members of independent agencies such as ICO, BC, SCC, as well as civil society, believe that there are still many deficiencies, the relevant discussions are summarized as follows: (I) The necessity of using AFR technology Elizabeth Denham, ICO Commissioner, called for looking at the use of AFR technology carefully, because AFR is an intrusive technology and can increase the risk of intruding into our privacy. Therefore, for the use of AFR technology to be legal, the UK police must have clear evidence to demonstrate that the use of AFR technology in public space is effective in resolving the problem that it aims to address[13]. The Home Office has pledged to undertake Data Protection Impact Assessments (DPIAs) before introducing AFR technology, including the purpose and legal basis, the framework applies to the organization using the biometrics, the necessity and proportionality and so on. (II)The limitations of using facial image data The UK police can collect, process and use personal data based on the need for crime prevention, investigation and prosecution. In order to secure the use of biometric information, the BC was established under the Protection of Freedoms Act 2012. The mission of the BC is to regulate the use of biometric information, provide protection from disproportionate enforcement action, and limit the application of surveillance and counter-terrorism powers. However, the BC’s powers do not presently extend to other forms of biometric information other than DNA or fingerprints[14]. The BC has expressed concern that while the use of biometric data may well be in the public interest for law enforcement purposes and to support other government functions, the public benefit must be balanced against loss of privacy. Hence, legislation should be carried to decide that crucial question, instead of depending on the BC’s case feedback[15]. Because biometric data is especially sensitive and most intrusive of individual privacy, it seems that a governance framework should be required and will make decisions of the use of facial images by the police. (III) Database management and transparency For the application of AFR technology, the scope of biometric database is a dispute issue in the UK. It is worth mentioning that the British people feel distrust of the criminal database held by the police. When someone is arrested and detained by the police, the police will take photos of the suspect’s face. However, unlike fingerprints and DNA, even if the person is not sued, their facial images are not automatically deleted from the police biometric database[16]. South Wales Police have used AFR technology to compare facial images of people in crowds attending major public events with pre-determined watch lists of suspected mobile phone thieves in the AFR field test. Although the watch lists are created for time-limited and specific purposes, the inclusion of suspects who could possibly be innocent people still causes public panic. Elizabeth Denham warned that there should be a transparency system about retaining facial images of those arrested but not charged for certain offences[17]. Therefore, in the future the UK Home Office may need to establish a transparent system of AFR biometric database and related supervision mechanism. (IV) Accuracy and identification errors In addition to worrying about infringing personal privacy, the low accuracy of AFR technology is another reason many people oppose the use of AFR technology by police agencies. Silkie Carlo, director of Big Brother Watch, said the police must immediately stop using the AFR technology and avoid mistaking thousands of innocent citizens as criminals; Paul Wiles, Biometrics Commissioner, also called for legislation to manage AFR technology because of its accuracy is too low and the use of AFR technology should be tested and passed external peer review[18]. In the Home Office’s Biometric Strategy, the scientific quality standards for AFR technology will be established jointly with the FSR, an independent agency under the Home Office. In other words, the Home Office plans to extend the existing forensics science regime to regulate AFR technology. Therefore, the FSR has worked with the SCC to develop standards relevant to digital forensics. The UK government has not yet seen specific standards for regulating the accuracy of AFR technology at the present stage. V. Conclusion From the discussion of the public and private sectors in the UK, we can summarize some rules for the use of AFR technology. Firstly, before the application of AFR technology, it is necessary to complete the pre-assessment to ensure the benefits to the whole society. Secondly, there is the possibility of identifying errors in AFR technology. Therefore, in order to maintain the confidence and trust of the people, the relevant scientific standards should be set up first to test the system accuracy. Thirdly, the AFR system should be regarded as an assisting tool for police enforcement in the initial stage. In other words, the information analyzed by the AFR system should still be judged by law enforcement officials, and the police officers should take the responsibilities. In order to balance the protection of public interest and basic human rights, the use of biometric data in the AFR technology should be regulated by a special law other than the regulations of surveillance camera and data protection. The scope of the identification database is also a key point, and it may need legislators’ approval to collect and store the facial image data of innocent people. Last but not least, the use of the AFR system should be transparent and the victims of human rights violations can seek appeal. [1] UK Home Office, Biometrics Strategy, Jun. 28, 2018, https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/home-office-biometrics-strategy (last visited Aug. 09, 2018), at 7. [2] Big Brother Watch, FACE OFF CAMPAIGN: STOP THE MET POLICE USING AUTHORITARIAN FACIAL RECOGNITION CAMERAS, https://bigbrotherwatch.org.uk/all-campaigns/face-off-campaign/ (last visited Aug. 16, 2018). [3] Lucas Introna & David Wood, Picturing algorithmic surveillance: the politics of facial recognition systems, Surveillance & Society, 2(2/3), 177-198 (2004). [4] Supra note 1, at 12. [5] Id, at 25. [6] Michael Bromby, Computerised Facial Recognition Systems: The Surrounding Legal Problems (Sep. 2006)(LL.M Dissertation Faculty of Law University of Edinburgh), http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.197.7339&rep=rep1&type=pdf , at 3. [7] Owen Bowcott, Police face legal action over use of facial recognition cameras, The Guardian, Jun. 14, 2018, https://www.theguardian.com/technology/2018/jun/14/police-face-legal-action-over-use-of-facial-recognition-cameras (last visited Aug. 09, 2018). [8] Martha Spurrier, Facial recognition is not just useless. In police hands, it is dangerous, The Guardian, May 16, 2018, https://www.theguardian.com/commentisfree/2018/may/16/facial-recognition-useless-police-dangerous-met-inaccurate (last visited Aug. 17, 2018). [9] Supra note 1, at 12. [10] Surveillance Camera Commissioner, Surveillance camera code of practice, Oct. 28, 2014, https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/surveillance-camera-code-of-practice (last visited Aug. 17, 2018). [11] UK Information Commissioner’s Office, In the picture: A data protection code of practice for surveillance cameras and personal information, Jun. 09, 2017, https://ico.org.uk/for-organisations/guide-to-data-protection/encryption/scenarios/cctv/ (last visited Aug. 10, 2018). [12] Supra note 1, at 13. [13] Elizabeth Denham, Blog: facial recognition technology and law enforcement, Information Commissioner's Office, May 14, 2018, https://ico.org.uk/about-the-ico/news-and-events/blog-facial-recognition-technology-and-law-enforcement/ (last visited Aug. 14, 2018). [14] Monique Mann & Marcus Smith, Automated Facial Recognition Technology: Recent Developments and Approaches to Oversight, Automated Facial Recognition Technology, 10(1), 140 (2017). [15] Biometrics Commissioner, Biometrics Commissioner’s response to the Home Office Biometrics Strategy, Jun. 28, 2018, https://www.gov.uk/government/news/biometrics-commissioners-response-to-the-home-office-biometrics-strategy (last visited Aug. 15, 2018). [16] Supra note 2. [17] Supra note 13. [18] Jon Sharman, Metropolitan Police's facial recognition technology 98% inaccurate, figures show, INDEPENDENT, May 13, 2018, https://www.independent.co.uk/news/uk/home-news/met-police-facial-recognition-success-south-wales-trial-home-office-false-positive-a8345036.html (last visited Aug. 09, 2018).
- Impact of Government Organizational Reform to Scientific Research Legal System and Response Thereto (1) – For Example, The Finnish Innovation Fund (“SITRA”)
- The Demand of Intellectual Property Management for Taiwanese Enterprises
- Blockchain in Intellectual Property Protection
- Impact of Government Organizational Reform to Research Legal System and Response Thereto (2) – Observation of the Swiss Research Innovation System
- Recent Federal Decisions and Emerging Trends in U.S. Defend Trade Secrets Act Litigation
- The effective and innovative way to use the spectrum: focus on the development of the "interleaved/white space"
- Copyright Ownership for Outputs by Artificial Intelligence
- Impact of Government Organizational Reform to Research Legal System and Response Thereto (2) – Observation of the Swiss Research Innovation System
