To establish a trusted foundation for sports data compliance, the Sports Data Altruism Service releases the Sports Data Altruism Service Personal Data Assessment Legal Compliance Handbook

To establish a trusted foundation for sports data compliance, the Sports Data Altruism Service releases the Sports Data Altruism Service Personal Data Assessment Legal Compliance Handbook
2024/05/15
I. Introduction
The Sports Data Altruism Service aims to construct a blueprint for the development of sports and technology, to promote practical applications for sports scientific research results, to drive industry development, and to establish a sports data innovation ecosystem. This will be achieved through multi-ministerial/multi-agency value-added applications for sports data, multidisciplinary upgrading and transformation of sports technology, digital empowerment to establish a sports technology ecosystem, and public-private collaboration efforts.
The Sports Data Altruism Service aims to build a legal compliance platform, and to reinforce the trust foundation for legally-compliant sports data operations, all while balancing privacy protection and public interest. In pursuit of these ends, the Sports Data Altruism Service draws upon international data governance practices and trends, as well as current industry practices. It aims to develop guidelines and regulations that consider the value of sports data applications and apply them to data legal compliance operations for sports venues. The Service is also intended to help operators in the sports field maintain personal data protections and reasonable use. Consequently, in August 2023, the Sports Data Altruism Service released the Sports Data Altruism Service Personal Data Assessment Legal Compliance Handbook. For entities seeking to become Sports Data Altruism Service data providers, the Handbook explains the related regulations and provides important things to watch out for.
II. Structure of the Sports Data Altruism Service Personal Data Assessment Legal Compliance Handbook
The Handbook is divided into three sections:
A. Requirements for joining the Sports Data Altruism Service:
Before starting with the Sports Data Altruism Service, users must read and agree to the service’s Privacy Policy, Terms of Service, Notification Regarding Personal Data Collection and Personal Data Provision Agreement, and other important platform information.
The Privacy Policy explains how the platform collects, uses, and protects the information that users provide. If you wish to become a data provider or data user, the Terms of Service will explain what you need to comply with to do so. And if you decide to become a data provider or data user, you must register on this platform and must sign the "Notification and Letter of Consent for Collection, Processing, and Use of Personal Data" to state your agreement to provide your data to the platform.
B. Personal data subject rights protection mechanism for sports venue operators (data providers):
After becoming a Sports Data Altruism Service data provider, to lawfully obtain the personal sports data, the data provider must submit the Points of Note When Connecting to the Sports Data Altruism Service and Personal Sports Data Provision Agreement. This form, submitted in either paper or online format, must include a signature from the person whose personal sports data is to be used.
When a data subject needs to correct their personal data or no longer wishes to provide their data to the Sports Data Altruism Service, the data provider must provide the Exercise of Data Subject Rights Application Form. After the data subject submits the application, the sports venue operator must verify whether the data has been processed to the extent that it cannot be used to identify a specific individual. In accordance with Article 4 of the Points of Note When Connecting to the "Notice of Connection to the Sports Data Altruism Service Platform and Consent Form for Provision of Personal Sports Data", data that can no longer identify specific data subjects is no longer considered personal data, and is not subject to exercising of data subject rights, nor is it subject to deletion of statistical or analytical results based on such data. If the data has not been anonymized, the operator must remove the data subject from the list uploaded to the platform and delete any unprocessed sports data. They must also retain records of the deletion and notify the data subject.
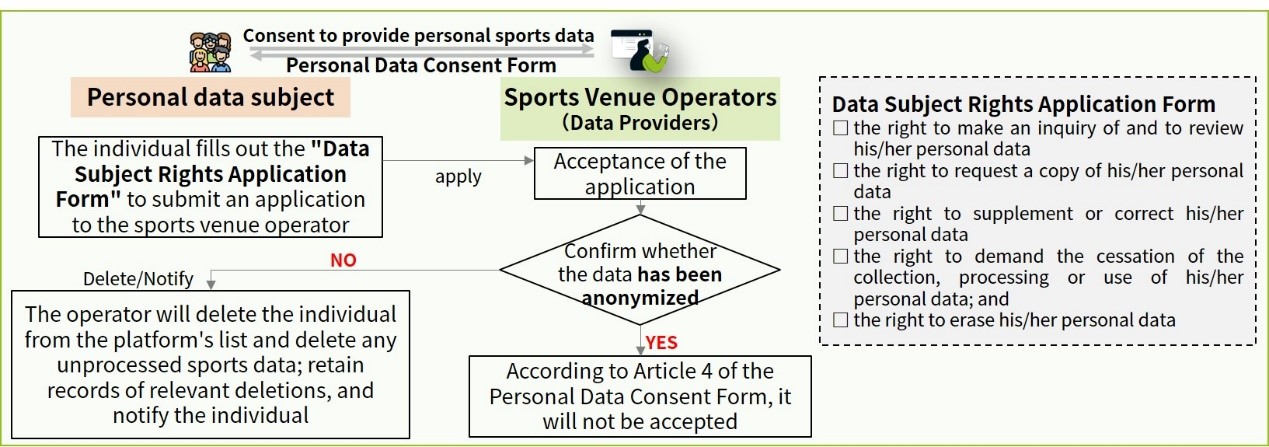
Source: Sports Data Altruism Service Personal Data Assessment Legal Compliance Handbook
Figure 1 Data Subject Rights Exercise Mechanism for Sports Venue Operators
C. Data protection management process for sports venue operators (data providers):
To assist sports venue operators in complying with personal data protection requirements, the Sports Data Altruism Service provides a personal data protection self-assessment tool. After an operator becomes a Sports Data Altruism Service data provider, they must assess their compliance with data protection laws by completing the Self-Assessment Form for Personal Data Protection in Collecting Public Sports Data by Sports Venue Operators (Data Providers). This helps operators understand the importance of personal data protection and establish a robust personal data protection management system, to achieve both data protection and reasonable usage.
The Self-Assessment Form for Personal Data Protection in Collecting Public Sports Data by Sports Venue Operators (Data Providers) is designed in accordance with the regulations of the Personal Data Protection Act and its enforcement rules. It includes 20 assessments in 10 major categories. When filling out the self-assessment form, the operator must provide the name of the self-assessment venue, the name of the person filling out the form, and the date. The form has to be completed based on the personal characteristic data and sports data that is to be uploaded to the Sports Data Altruism Service. However, not every assessment is mandatory. The form requires considering the operator’s actual situation to review the current practices related to personal data protection and management, then conducting the self-assessment based on this.
For more detailed information about the Sports Data Altruism Service Personal Data Assessment Legal Compliance Handbook, please visit the Sports Data Altruism Service website (https://www.data-sports.tw/#/SportData/Landing?redirect=%2FDashboard).
The amendment of the Taiwanese Personal Data Protection Act 2025/05/28 On March 27, 2025, the Executive Yuan released and submitted a draft partial amendment of the Personal Data Protection Act to the Legislative Yuan. The amendment aims to comprehensively enhance personal data protection by constructing the foundation for an independent supervisory agency[1]. Taiwan’s Personal Data Protection Act- legislative progress Taiwan’s Personal Data Protection Act (PDPA) has been amended three times since its release in 1995. In May 2023, the latest amendment to the PDPA introduced Article 1-1, designating the Personal Information Protection Committee as the competent authority under the Act. This legislative development was made in light of the Taiwan Constitutional Court Judgment 111-Hsien-Pan-13 (2022) (Case on the National Health Insurance Research Database)[2], which held that, to ensure the protection of personal information and the constitutional right to privacy under Article 22, the establishment of an independent data protection mechanism is required. In accordance with Taiwan Constitutional Court Judgment 111-Hsien-Pan-13 (2022), the Personal Data Protection Commission (PDPC) must be established by August 2025. To facilitate this, the Preparatory Office of the Personal Data Protection Commission was established in December 2023. This office is mainly responsible for drafting and establishing the regulations and organizational framework required to establish the independent authority, including drafting the Organization Act of the PDPC and the amendments to the PDPA. To develop the regulatory framework for an independent authority, the Preparatory Office of the Personal Data Protection Commission has planned a two-stage amendment process. The first phase seeks to establish the legal foundation of the PDPC, while the second phase will address other substantive issues of personal data protection. For the first stage, the Preparatory Office of the Personal Data Protection Commission drafted the Organization Act of the Personal Information Protection Committee in accordance with Article 1-1 of the PDPA and revised partial provisions of PDPA to reflect the function and duties of the PDPC. The Draft of Partial Amendment to the Personal Data Protection Act The key points of the amendment of PDPA are to empower the commission with essential regulatory functions, to strengthen the regulatory oversight and management of personal data within public sectors, and to set up a transition period to transfer regulatory authority over the private sectors[3]. 1. Empower the commission with essential regulatory functions Due to the lack of a unified agency for receiving incident reports and the efficiency issues caused by the current decentralized legal enforcement, the amendment of PDPA designates the PDPC as the competent authority to receive the incident reports. Centralizing incident reporting under the PDPC facilitates a clearer understanding of the nature and status of related incidents. It also helps regulatory authorities to investigate and handle problems quickly. The rules for reporting data breach incidents are set out in Article 12 of the amended PDPA. According to Article 12 of the amended PDPA, both public sector and private sector entities are required to take appropriate actions and retain the records when a data breach occurs. In addition, public sector entities must report the incident to the PDPC and other relevant government agencies, while private sector entities are required to notify the incident to the PDPC, which will then inform its competent authority[4]. In terms of personal data security maintenance, the amended PDPA states that the competent authority is responsible for formulating regulations concerning security maintenance, governance mechanisms, protective measures, and other relevant matters[5]. Accordingly, PDPC, as the competent authority, will draft the Regulations Governing Security Maintenance and Administration to provide the legal basis for the conducting audits, inspections, and administrative sanctions[6]. 2. Strengthen the regulatory oversight and management of personal data within the public sector The amendment of PDPA designates the PDPC as the independent authority responsible for overseeing the overall personal data protection affairs, including supervision of public sectors. The PDPC is empowered to supervise the public sector entities regarding their compliance with personal data protection regulations. Therefore, the role of the Data Protection Officer (DPO) is introduced in Taiwan for the first time. Article 18 of the amended PDPA states that every public sector entity must appoint a DPO to promote and oversee matters related to personal data protection. This approach reinforces personal data protection from both internal and external perspectives[7]. In considering restructuring and resource allocation associated with introducing this new role, the DPO requirement in PDPA currently applies to the public sector entities. However, both the public and private sectors are required to designate specialists to be responsible for managing personal data protection and security affairs[8]. 3. Set up a transition period to transfer regulatory authority over the private sectors Under the current regulation framework, the supervision of personal data protection in the private sector is decentralized and supervised by different competent authorities. To address this gap, the amendment of PDPA clarifies that the PDPC will serve as the supervisory authority for these entities in the future. In terms of the private sector entities already under the supervision of specific competent authorities, supervisory arrangements will initially remain unchanged. However, to achieve regulatory consistency, the amendment introduced a six-year transitional period during which supervisory responsibility will be transferred to the PDPC. During this transition, the PDPC will collaborate with relevant agencies every 2 years to assess the implementation of the new framework of PDPC and the situation of supervision across the private sector[9]. The draft Organization Act of the Personal Data Protection Committee has also been released To complete the legal basis of PDPC, the draft Organization Act of the Personal Data Protection Committee (hereinafter referred to as the draft of the Organization Act) is released with the PDPA amendment. The draft of the Organization Act aims to formalize the PDPC as the independent central supervisory body. Additionally, it also clarifies the division of responsibilities among agencies on personal data-related matters. Once enacted, the PDPC will serve as Taiwan’s independent authority. According to the draft of the Organization Act, the PDPC is designed as a collegial system with 5-7 committee members, serving a term of 4 years, and members may be reappointed upon completion of their term[10]. As a central third-level agency, the committee members will exercise their powers independently. The draft of the Organization Act states that the PDPC is responsible for making the legislation and policies of personal data protection, the oversight of personal data protection, promoting and researching personal data-related technology, protecting cross-border transfer of personal data and the talent acquisition of personal data protection[11]. The draft of the Organization Act establishes the legal foundation for the PDPC, outlining its organization structure and core responsibilities. Additionally, it grants the PDPC the authority to supervise and enforce compliance with personal data protection regulations. Benefits of the legal reform of the Personal Data Protection Act and the next step The draft partial amendment to the Personal Data Protection Act, along with the draft Organization Act of the Personal Information Protection Committee, have been submitted to the Legislative Yuan for legislative review. This marks the first time that Taiwan has established an independent authority responsible for personal data protection. The PDPA amendment not only formalizes the legal status and authority of the Commission but also enhances the legitimacy and credibility of personal data collection and use. However, amendments to other substantial aspects of data protection will be introduced in the next phase. The Preparatory Office of the Personal Data Protection Commission has already initiated work on the second phase, which will focus on substantial personal data protection issues in the context of the digital era. Reference: [1]The Executive Yuan approved the draft Organizational Act of the Personal Data Protection Commission and the draft of partial amendments to the Personal Data Protection Act, aiming to establish a comprehensive independent supervisory mechanism and enforcement authority, and to build robust data governance for the era of comprehensive AI application., Executive Yuan, https://www.ey.gov.tw/Page/9277F759E41CCD91/747cda78-926f-4205-99b3-1a735fc1b97b (last visited May. 19, 2025). [2]Constitutional Court Judgment 111-Hsien-Pan-13 (2022) (Case on the National Health Insurance Research Database). [3]Establish an independent supervisory authority for personal data protection to strengthen personal data safeguards. The Executive Yuan approved the draft Organization Act of the Personal Data Protection Commission and the draft partial amendments to the Personal Data Protection Act., Preparatory Office of the Personal Data Protection Commission website, https://www.pdpc.gov.tw/News_Content/20/907/ (last visited May. 19, 2025). [4]Partial Amendment Draft to the Personal Data Protection Act, the 8th meeting of the 3rd session of the 11th Legislative Yuan, General Bill No.20, Executive Yuan Proposal No.11010550, Art. 12. [5]Id. Art 18, Art 20-1. [6]Supra note 3. [7]Id. Art.18. [8]Id. Art. 20-1. [9]Id. Art.51-1. [10]Draft of the Organization Act of the Personal Information Protection Committee, the 8th meeting of the 3rd session of the 11th Legislative Yuan, General Bill No.20, Executive Yuan Proposal No. 1101052, Art. 3.Draft of the Organization Act of the Personal Information Protection Committee, the 8th meeting of the 3rd session of the 11th Legislative Yuan, General Bill No.20, Executive Yuan Proposal No. 1101052, Art. 3. [11]Id. at Art. 2.
The Coverage and Policies of Critical Infrastructure Protection in U.S.Regarding the issue of critical infrastructure protection, the emphasis in the past was put on strategic facilities related to the national economy and social security merely based on the concept of national defense and security1. However, since 911 tragedy in New York, terrorist attacks in Madrid in 2004 and several other martial impacts in London in 2005, critical infrastructure protection has become an important issue in the security policy for every nation. With the broad definition, not only confined to national strategies against immediate dangers or to execution of criminal prevention procedure, the concept of "critical infrastructure" should also include facilities that are able to invalidate or incapacitate the progress of information & communication technology. In other words, it is elevated to strengthen measures of security prevention instead. Accordingly, countries around the world have gradually cultivated a notion that critical infrastructure protection is different from prevention against natural calamities and from disaster relief, and includes critical information infrastructure (CII) maintained so that should be implemented by means of information & communication technology into the norm. In what follows, the International CIIP Handbook 2008/2009 is used as a research basis. The Subjects, including the coverage of CIIP, relevant policies promoted in America, are explored in order to provide our nation with some references to strengthen the security development of digital age. 1. Coverage of Important Critical Information Infrastructures Critical infrastructure is mainly defined in "Uniting and Strengthening our country by Providing Appropriate Tools Required to Intercept and Obstruct Terrorism Act of 2001, as known as Patriot Act of the U.S., in section 1016(e)2 . The term ‘critical infrastructure’ refers to "systems and assets, whether physical or virtual, so vital to our country that the incapacity or destruction of such systems and assets would have a debilitating impact on security, national economic security, national public health or safety, or any combination of those matters." In December 2003, the Department of Homeland Security (DHS) promulgated Homeland Security Presidential Directive 7 (HSPD-7)3 to identify 17 Critical Infrastructures and key resources (CI/KR) ,and bleuprinted the responsibility as well as the role for each of CI/KR in the protection task. In this directive, DHS also emphasized that the coverage of CI/KR would depend on the real situations to add or delete sectors to ensure the comprehensiveness of critical infrastructure. In March 2008, DHS added Critical Manufacturing which becomes the 18th critical infrastructure correspondent with 17 other critical infrastructures. The critical infrastructures identified by DHS are: information technology, communications, chemical, commercial facilities, dams, nuclear reactors, materials and waste, government facilities, transportation systems, emergency services, postal and shipping, agriculture and food, healthcare and public health, water, energy (including natural gas, petroleum, and electricity), banking and finance, national monuments and icons, defense industrial Base, and critical manufacturing. 2. Relevant Policies Previously Promoted With Critical Infrastructure Working Group (CIWG) as a basis, the President's Commission on Critical Infrastructure Protection (PCCIP) directly subordinate to the President was established in 1996. It consists of relevant governmental organizations and representatives from private sectors. It is responsible for promoting and drawing up national policies indicating an important critical infrastructure, including natural disasters, negligence and lapses caused by humans, hacker invasion, industrial espionage, criminal organizations, terror campaign, and information & communication war and so on. Although PCCIP no longer exists and its functions were also redefined by HDSP-7, the success of improving cooperation and communication between public and private sectors was viewed as a significant step in the subsequent issues on information security of critical infrastructure of public and private sectors in America. In May 1998, Bill Clinton, the former President of the U.S., amended PCCIP and announced Presidential Decision Directive 62, 63 (PDD-62, PDD-63). Based on these directives, relevant teams were established within the federal government to develop and push the critical infrastructure plans to protect the operations of the government, assist communications between the government and the private sectors, and further develop the plans to secure national critical infrastructure. In addition, concrete policies and plans regarding information security of critical infrastructure would contain the Defence of America's Cyberspace -- National Plan for Information Systems Protection given by President Clinton in January, 2000 based on the issue of critical infrastructure security on the Internet which strengthens the sharing mechanism of internet information security messages between the government and private organizations. After 911, President Bush issued Executive Order 13228 (EO 13228) and Executive Order 13231 to set up organizations to deal with matters regarding critical infrastructure protection. According to EO 13228, the Office of Homeland Security and the Homeland Security Council were established. The duty of the former is mainly assist the U.S. President to integrate all kinds of enforcements related to the protection of the nation and critical infrastructure so as to avoid terrorist attacks, while the latter provides the President with advice on protection of homeland security and assists to solve relevant problems. According to EO 13228, the President's Critical Infrastructure Protection Board directly subordinate to the President was established to be responsible for offering advice on polices regarding information security protection of critical infrastructure and on cooperation plans. In addition, National Infrastructure Advisory Council (NIAC), which consists of owners and managers of national critical infrastructure, was also set up to help promote the cooperation between public and private sectors. Ever since the aforementioned executive order, critical infrastructure protection has been more concrete and specific in definition; for instance, to define critical infrastructure and its coverage through HSPD-7, the National Strategy for Homeland Security issued in 2002, the polices regarding the National Strategy to Secure Cyberspace and the National Strategy for Physical Protection of Critical Infrastructure and Key Assets addressed by the White House in 2003; all of this are based on the National Strategy for Homeland Security. Moreover, the density of critical infrastructure protection which contains virtual internet information security was enhanced for the protection of physical equipment and the protection from destruction caused by humans. Finally, judging from the National Infrastructure Protection Plan (NIPP), Sector-Specific Plans (SPP) supplementing NIPP and offering a detailed list of risk management framework, along with National Strategy for Information-Sharing, the public-private partnership (PPP) and the establishment of information sharing mechanism are highly estimated to ensure that the network of information security protection of critical infrastructure can be delicately interwoven together because plenty of important critical infrastructures in the U.S. still depend on the maintenance and operation of private sectors. 1.Cf. Luiijf, Eric A. M. , Helen H. Burger, and Marieke H. A. Klaver, “Critical Infrastructure Protection in the Netherlands:A Quick-scan”. In:Gattiker, Urs E. , Pia Pedersen, amd Karsten Petersen (eds. ) . EICAR Conference Best Paper Proceedings 2003, http://cip.gmu.edu/archive/2_NetherlandsCIdefpaper_2003.pdf (last accessed at 20. 07. 2009) 2.For each chapter of relevant legal cases, please visit http://academic.udayton.edu/health/syllabi/Bioterrorism/5DiseaseReport/USAPatriotAct.htm. The text regarding the definition of critical infrastructure is cited as "Critical Infrastructure Defined- In this section, the term “critical infrastructure” means systems and assets, whether physical or virtual, so vital to the United States that the incapacity or destruction of such systems and assets would have a debilitating impact on security, national economic security, national public health or safety, or any combination of those matter. " 1.Cf. Luiijf, Eric A. M. , Helen H. Burger, and Marieke H. A. Klaver, “Critical Infrastructure Protection in the Netherlands:A Quick-scan”. In:Gattiker, Urs E. , Pia Pedersen, amd Karsten Petersen (eds. ) . EICAR Conference Best Paper Proceedings 2003, http://cip.gmu.edu/archive/2_NetherlandsCIdefpaper_2003.pdf (last accessed at 20. 07. 2009) 2.For each chapter of relevant legal cases, please visit http://academic.udayton.edu/health/syllabi/Bioterrorism/5DiseaseReport/USAPatriotAct.htm. The text regarding the definition of critical infrastructure is cited as "Critical Infrastructure Defined- In this section, the term “critical infrastructure” means systems and assets, whether physical or virtual, so vital to the United States that the incapacity or destruction of such systems and assets would have a debilitating impact on security, national economic security, national public health or safety, or any combination of those matter. " 3.Introduction of Consumer Protection in Taiwan , Republic of China , Consumer Protection Commission (CPC), Executive Yuan.http://www.fas.org/irp/offdocs/nspd/hspd-7.html ( Last visit 2008/6/27 )
The Organization Framework, the Notification System and the Legal Norms of Critical Infrastructure Protection in the U.S.1. Organization Framework In the organization framework of critical infrastructure protection, there are mainly the public departments and the PPP organizations. The functions and task description of relevant organizations are as follows. (1) Department of Homeland Security After the September 11 attacks in America, the Homeland Security Act was passed in November 2002, and based on this act, 23 federal organizations, plans and offices were integrated to establish the Department of Homeland Security (DHS) to take responsibility for homeland security in America. The tasks include: (1) to analyze intelligence data collected from various departments such as the Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) and the Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) so that any threats to security can be discovered in time, (2) to protect and defend critical infrastructure, (3) to coordinate and lead America to prevent and respond to the attacks from nuclear weapons, biochemical weapons and other and (4) to coordinate the tasks of the federal government, including emergency and rescue. For the task regarding critical infrastructure and critical information infrastructure protection, the main units in charge are the Office of Infrastructure Protection (OIP) and the Office of Cybersecurity and Communications (CS&C) subordinate to National Protection and Programs Directorate (NPPD), Department of Homeland Security (DHS), to reduce the risk in both physical and cyber security to maintain national security1 (2) Congress Relevant units and committees are established both in the Senate and the House of Representatives to be responsible for protection and making policies pertinent to important critical infrastructure and critical information infrastructure. (3) Computer Crime and Intellectual Property Section In 1991, the Department of Justice (DOS) established the Computer Crime and Intellectual Property Section (CCIPS), a section of the Criminal Division, to be responsible for all crime combating computer and intellectual property. Computer crime is referred to cases which include electronic penetrations, data thefts, and cyber attacks to the important critical infrastructure. CCIPS also prevents, investigates, and prosecutes computer crimes by working with other government agencies, the private sector, academic institutions, and foreign counterparts. (4) Other Relevant PPP Organizations 2The Information Sharing and Analysis Center (ISAC) is responsible for the information security message sharing among the industries of each critical infrastructure to ensure the liaison and cooperation among industries. Finally, for the issue on critical information infrastructure, especially cyber crimes, both the National Cyber Security Alliance (NCSA) and the Cross Sector Cyber Security Working Group (CSCSWG) are designated to serve as crucial roles in governmental and non-governmental internet security prevention to be responsible for techniques and education. 2. Notification System (1)Computer Emergency Response Team Coordination Center The Computer Emergency Response Team Coordination Center (CERT/CC) run by Carnegie Mellon University is the oldest and most important early-warning organization for information security in the USA. With its experts studying internet vulnerabilities and risk assessment released regularly, it reminds people of the possible dangers which exist in the information age and the need to improve internet security. (2)US Computer Emergency Readiness Team The US Computer Emergency Readiness Team (US-CERT) was established in 2003. It is responsible for protecting the infrastructure of the internet in America and for coordinating and providing response support and defense against national cyber attacks. It interacts with federal agencies, industry, the research community, state government, and others to disseminate reasoned and actionable cyber security information to the public. (3)Federal Bureau of Investigation The Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI), the first early warning center of critical infrastructure at the national level, is responsible for providing the information pertinent to legal execution presently and also taking responsibility for the investigation of cyber crime. (4)Information Sharing and Analysis Centers Currently, industry in America, including finance, telecommunications, energy, traffic, water resources, together established individual Information Sharing and Analysis Centers (ISACs) based on the policy made in PDD-63. The ISAC of the financial system established in October 1999 being the first established center. These ISACs further work together to form an ISAC Council to integrate the information from each of them and improve their interaction and information sharing. 3. Legal Norms In reference to the laws and regulations of critical infrastructure protection, America has aimed at critical infrastructure protection and computer crime to formulate the following regulations. (1) Federal Advisory Committee Act of 1972 According to the Federal Advisory Committee Act (FACA), the advisory committee can be established in every federal agency to provide the public, along with received open advice, with relevant objectives, and to prevent the public from being inappropriately influenced by the policies made by the government. However, to keep the private institutions which run the critical infrastructures from worrying the inappropriate leak of the sensitive information provided and consulted by them, Critical Infrastructure Partnership Advisory Council was established so that the Secretary of Homeland Security has the right to disregard the regulations of FACA and establish an independent advisory committee. (2) Computer Fraud and Abuse Act of 19863 The Computer Fraud and Abuse Act (CFAA) was enacted and implemented in 1986. It mainly regulates computer fraud and abuse. The Act states that it is against the law for anyone to access a protected computer without authorization. However, it also recognizes the fact that accessing a computer system of electronic and magnetic records does not mean a violation of the law. According to the CFAA, what is needed is one of the following requirements to be the wrongful conduct regulated in the Act: (1) whoever intentionally accesses a computer to obtain specific information inside the government or whoever has influenced the transmission function of the computer system; (2) whoever intentionally accesses a computer to obtain a protected database (including the information contained in a financial record of a financial institution or of a card issuer, or the information contained in a file of a consumer reporting agency on a consumer, or the information from any department of agency of the United States, or the conduct involving an interstate transaction); (3) whoever intentionally accesses any nonpublic computer of a department or agency of the United States, and causes damage. In addition, the Act also prohibits conduct such as transmitting malicious software, and defrauding traffic in any password or similar information. For any person who suffers damage or loss by reason of a violation of the law, he/she may maintain a civil action to obtain compensatory damages and injunctive relief or other equitable relief. However, the Computer Abuse Amendment Act (1994) expands the above Act, planning to include the conduct of transmitting viruses and malicious program into the norms whose regulatory measures were adopted by the USA Patriot Act enacted in October 20014 (3) Homeland Security Act of 20025 The Homeland Security Act provides the legal basis for the establishment of the Department of Homeland Security and integrates relevant federal agencies into it. The Act also puts information analysis and measures of critical infrastructure protection into the norm. And, the norm in which private institutions are encouraged to voluntarily share with DHS the information security message of important critical infrastructure is regulated in the Critical Infrastructure Information Act: Procedures for Handling Critical Infrastructure Information. According to the Act, the DHS should have the obligation to keep the information provided by private institutions confidential, and this information is exempted from disclosure by the Freedom of Information Act. (4) Freedom of Information Act Many critical infrastructures in America are regulated by governmental laws, yet they are run by private institutions. Therefore, they should obey the law and provide the government with the operation report and the sensitive information related with critical infrastructure. However, knowing that people can file a request at will to review relevant data from the government agencies based on the Freedom of Information Act (FOIA), then the security of national critical infrastructure may be exposed to the danger of being attacked. Therefore, the critical infrastructure, especially the information regarding the safety system, early warning, and interdependent units, are all exempted by the Freedom of Information Act. (5) Terrorism Risk Insurance Act of 20026 After the 911 Incident, Congress in America passed the Terrorism Risk Insurance Act to establish the mechanism to underwrite terrorism risk insurance, in which insurance companies are required to provide terrorism attack risk insurance and the federal government will also cover part of loss for severe attacks. 1.http://www.dhs.gov/xabout/structure/editorial_0794. shtm (last accessed at 21. 07. 2009). 2.http://www.thei3p.org/ (last accessed at 21. 07. 2009). 3.http://www.panix.com/~eck/computer-fraud-act. html (last accessed at 21. 07. 2009). 4.Mark G. Milone, Hacktivism:Securing the National Infrastructure, 58 Bus. Law, 389-390, 2002. 5.http://www.dhs.gov/xlibrary/assets/hr_5005_enr.pdf (last accessed at 21. 07. 2009). 6.http://www.ustreas.gov/offices/domestic-finance/financial-institution/terrorism-insurance/pdf/hr3210.pdf (last accessed at 21. 07. 2009).
Implementing Information Security to Protect Individuals' PrivacyThe development of new technology is bound to have both positive and negative effects. However, when a new technology is first introduced, it is common for insufficient attention to be paid to its negative aspects, either because there has not been time to accumulate sufficient experience in using it or because users are blinded by the potential benefits. It is only later, when the technology begins to be abused, that people wake up to the potential dangers. The evolution of computers and the Internet is a classic example of this phenomenon. While the rapid development of information technology has helped to stimulate the flow of information in every corner of society, cyberspace has also become the setting for a wide range of criminal activities. In many cases, countries' existing legal and regulatory frameworks have proved inadequate to cope with the threat posed by the various forms of unauthorized access. A variety of forms of cyber-crime have developed, including denial-of-service attacks, unauthorized accessing of databases, phishing, identity theft and online fraud or intimidation. Cyber-crime may involve making unauthorized use of individuals' personal information, stealing companies' confidential business information or selling state secrets; these new types of crime thus affect every level of society. The effects can be catastrophic, hence the growing importance is now being attached to information security, including both the establishment of effective management mechanisms to prevent cyber-crime from occurring in the first place and the development of the capabilities needed to detect such crime when it occurs. Recognizing the need to plug the gaps in the existing legal and regulatory framework in the face of cyber-crime, countries all over the world are working on the formulation of new legislation, and Taiwan is no exception. The following sections will discuss the key developments in the laws and regulations governing information security in Taiwan in recent years. I. The Convention on Cyber-crime and Chapter 36 of Taiwan’s Criminal Code (offences relating to the abuse of computers) Today, governments throughout the world are formulating measures to combat criminal activity that makes use of the Internet (cyber-crime). In many cases these measures are based on the Convention on Cyber-crime announced by the European Commission on November 23, 2001, and which came into effect on July 1, 2004. This convention is the first international agreement to be established specifically to combat cyber-crime. Its contents include discussion of the various types of cyber-crime, regulations governing the obtaining of electronic evidence, provisions for mutual assistance between nations in judicial matters with respect to cyber-crime and measures to encourage multilateral collaboration. The European Commission asked all signatory nations to revise their own national laws so that they conform to the provisions of the Convention, with the aim of establishing a unified international framework for combating cyber-crime. Responding to the international trend towards the enactment of legislation to fight cyber-crime and to eliminate any loopholes in Taiwanese law that might result in Taiwan becoming a haven for cyber-criminals, on June 25, 2003 the Taiwanese government added a new chapter, Chapter 36 (Offences Relating to the abuse of Computers) to Taiwan's Criminal Code. It contains six articles covering four types of crime: unauthorized access (Article 358), the unauthorized acquisition, deletion or titleeration of electromagnetic records (Article 359), unauthorized use of or interference with a computer system (Article 360) and creating computer programs specifically for the perpetration of a crime (Article 362). Article 361 specifies that more severe punishment should be imposed in the case of violations carried out against the computers or other equipment of a public service organization, and Article 363 states that the provisions of Articles 358–360 shall apply only after prosecution is instituted upon complaint. These new articles provide a clear legal basis for the punishment of common types of cyber-crime such as unauthorized access by hackers, the spreading of computer viruses and the use of Trojan horse programs. In formulating these articles, reference was made to the categorization of cyber-crimes used in the Convention on Cyber-crime and to the suggestions for revision of national laws put forward there. Article 36 is thus in broad conformity with current international practice in this regard and can be expected to achieve significant results in terms of combating cyber-crime. II. The authority of law enforcement to get evidence and ISPs liability In its discussion of the securing of electromagnetic records by law enforcement agencies, the Convention on Cyber-crime notes that such securing of records falls into two broad categories: immediate access and non-immediate access. Immediate access includes the monitoring of communications by law enforcement agencies, non-immediate access relates mainly to the data retention obligations imposed on Internet Service Providers (ISPs). As regards the regulatory framework for the monitoring of communications, Communications Protection and Surveillance Act came into effect in Taiwan on July 16, 1999. According to its provisions, monitoring of communications may only be implemented when it is deemed necessary to protect national security or to maintain social order. Warrants for such surveillance may only be issued if the content of the communications is related to a threat to national security or to the maintenance of social order. Furthermore, the crime in question must be a serious one. In principle, the period for which surveillance is implemented should not exceed 30 days. These restrictions reflect the government’s determination to ensure that citizens' right to privacy is protected. While the Internet is an environment conducive to the maintenance of anonymity, electromagnetic records are easy to erase. Effective investigation of cyber-crime requires automatic recording of communications by the equipment used to transmit the messages, that is to say, it requires the retention of historic data. As regards the extent to which companies are required to collaborate with law enforcement agencies and the conditions applying to the making available of electromagnetic records, these issues relate to the public's right to privacy, and the law in this area needs to be very clear and precise. For the most part, data retention obligations are laid down in Taiwan’s Telecommunications Act. In Taiwan ISPs are classed as "Type II Telecommunications Operators". Article 27 of the Administrative Regulations on Type II Telecommunications Businesses stipulates that Type II telecommunications operators may be required to confirm the existence of, and provide the contents of, customers' communications for the purpose of investigation or collection of evidence upon request in accordance with the requirements of the law. ISPs are required to retain, for a period of between 1 and 6 months, data relating to the account number of subscribers, the times and dates of communications, the times at which subscribers logged on and off, free e-mail accounts, the IP addresses used when applying for Web space and the time and date when such applications were made, the IP address used to make postings on message boards and newsgroups, the time and date when such postings were made and subscribers' e-mail communications records. If a Type II telecommunications operator violates these provisions, he may be fined between NT$200,000 and NT$1 million and be required to remedy the situation within a specified time limit in accordance with Paragraph 2 of Article 64 of the Telecommunications Law. If he fails to remedy the situation within the specified time limit, his license may be revoked. III. The Legal Framework for Personal Data Protection titlehough, as outlined above, some revisions have already been made to the legal framework governing information security, there are still many areas which need to be reviewed. One of the most important is the protection of personal information. Following the explosive growth of the Internet, customer-related information is being processed by computers on a large scale in many different industries. With so many companies collaborating with other firms or adopting new marketing methods, the value and importance of personal information is being reassessed. The dramatic increase in the number of online scams in Taiwan in recent years has made the protection of privacy a focus of attention. The existing Computer-processed Personal Data Protection Law, drawn up to target specific industries, does not really provide adequate protection. A new Personal Data Protection Act, drawn up with reference to the European Union’s Directive (95/46/EC) on the Protection of Individuals with regard to the Processing of Personal Data and on the Free Movement of Such Data and the personal information protection legislation adopted in the USA and Japan, has already been submitted to the Legislative Yuan for deliberation. The key differences between this new Act and the existing Computer-processed Personal Data Protection Law are as follows. Protection is no longer industry-specific, it now applies to both natural and juristic persons and to both public and private agencies. The scope of protection has been expanded to include hard copies of documents containing personal information, and five new types of "sensitive information" – information relating to criminal records, medical examinations, medical records, sexual history and genetic information – have been added. Special restrictions apply to the collection and processing of these types of data. The Personal Data Protection Act also imposes stricter requirements on public and private agencies with regard to the protection of individuals' personal data. For example, agencies must formulate personal data protection plans and measures for dealing with personal data once those data are no longer needed for business purposes. If an agency discovers that an individual's personal data have been stolen, leaked, titleered or violated in any way, they are required to notify by telephone or letter the agency responsible for notifying the individual concerned as soon as possible. If these provisions are violated, the agency's responsible person will be liable for administrative punishment. The new Act also gives regulatory authorities greater powers to undertaking auditing in this area, makes provision for class action suits and increases the amount of compensation to be paid to victims. It is expected that these mechanisms will help boost awareness of the importance of information security in all sectors, thereby helping to ensure better protection for the public's personal information. IV. Management of Unsolicited Commercial E-Mail The widespread utilization of e-mail has created a brand new marketing channel, so that e-mail can fairly be described as one of the most important "killer applications" to which the Internet has given rise. Today, spamming is causing serious problems for both e-mail users and ISPs. E-mail users are concerned about their privacy being violated and about having their e-mail box stuffed full of junk e-mail. Spamming also ties up bandwidth which could be used for other purposes, and Distributed Denial of Service Attacks (DDOS) can make it difficult for ISPs to provide normal service to their customers. Governments throughout the world have begun to consider whether anti-spamming legislation may be necessary. In Taiwan draft legislation of this type has already been submitted to the Legislative Yuan. Taiwan's Anti-SPAM Act was drawn up with reference to the USA's CAN-SPAM Act of 2003, Japan's Law on Regulation of Transmission of Specified Electronic Mail, Australia's SPAM Act and the UK's Privacy and Electronic Communications (EC Directive) Regulations 2003. The draft SPAM Act contains 13 articles, with an emphasis on self-regulation, technology filtering and provision for seeking compensation through civil action. The Act provides for the use of an "opt-out" mechanism to regulate the behavior of e-mail senders, with the following obligations to be imposed on them. (1) The sender must specify in the "Subject" field of the e-mail whether it is a "business communication" or "advertising" to facilitate filtering by ISPs and to make clear to the recipient what type it is. (2) The sender must provide accurate information, including header, information on the sender's identity and the sender's e-mail address. (3) E-mails may not be sent if the sender knows or could be expected to know that the intended recipient has already expressed a wish not to receive e-mail from this source. E-mails may also not be sent if the sender knows or could be expected to know that the information in the "Subject" field is inaccurate or misleading. If the sender continues to send e-mails after the recipient has expressed a clear wish not to receive any more from the sender or if the sender falsifies the "Subject" or header information, then the sender may be required to pay compensation to the recipient at a rate of NT$500–2,000 per person per e-mail. With regard to the widespread practice whereby companies or advertising agencies commission third parties to send junk e-mail on their behalf, in cases where the commissioning party knows or could be expected to know that e-mail is being sent in violation of the above regulations, the commissioning party shall be held jointly liable with the party sending the e-mail. Through the implementation of this new law, the government hopes to establish a first-class Internet environment in Taiwan, putting an end to the current situation whereby large numbers of businesses are engaged in spamming. V. Conclusions Security is the biggest single factor affecting the implementation of e-government initiatives, e-business application adoption and Internet user confidence. Most people associate information security only with the purchasing of security hardware or software and the setting up of firewalls. While these products can indeed help to make the online environment more secure, Internet users should not allow themselves to be lulled into thinking that buying these products will in and of itself be sufficient to ensure security. "Security" is a fluid concept. Over time, the level of security that even a high-end product can provide will deteriorate; the fact that your system is secure now does not guarantee that it will remain secure in the future. Evidence that this is true is provided by the damage that is constantly being caused by viruses, by the need to constantly update security products and by the shift in emphasis away from virus prevention and firewalls towards preventing "backdoor" attacks and towards proactive intrusion detection. Furthermore, the information security risks that companies and organizations have to deal with are not limited to external threats; poor internal management may result in employees selling or leaking customer data or other company data, which can cause serious damage to the organization. Examination of information security theory and practice in Taiwan and overseas suggests that the establishment of effective information security measures embraces four main areas: the detection of cyber-crime, development of new information security technologies and formulation of standards, education and management of computer users and regulatory and policy issues. The most important of these is the education and management of computer users. Detection of cyber-crime is the next most important, while development of new technologies and standard setting and the regulatory and policy aspects play a supporting role. To create a genuinely secure online environment, attention must be paid to all of these. Today governments throughout the world are formulating new legislation to plug the gaps in the regulatory framework governing the online environment. Given the need to let the market mechanism operate freely and to refrain from measures that might retard industrial development, government interference in the Internet, with the exception of crime prevention activity, has generally been viewed as a last resort. Currently the government in Taiwan is still focusing mainly on self-regulation by Internet service providers and other types of business enterprise, and the government's role is still largely confined to formulating standards and assisting with the development of new security products. The area on which both the government and the private sector will need to concentrate in the future is educating and ensuring effective management of computer users.
- Impact of Government Organizational Reform to Scientific Research Legal System and Response Thereto (1) – For Example, The Finnish Innovation Fund (“SITRA”)
- The Demand of Intellectual Property Management for Taiwanese Enterprises
- Blockchain in Intellectual Property Protection
- Impact of Government Organizational Reform to Research Legal System and Response Thereto (2) – Observation of the Swiss Research Innovation System
- Recent Federal Decisions and Emerging Trends in U.S. Defend Trade Secrets Act Litigation
- The effective and innovative way to use the spectrum: focus on the development of the "interleaved/white space"
- Copyright Ownership for Outputs by Artificial Intelligence
- Impact of Government Organizational Reform to Research Legal System and Response Thereto (2) – Observation of the Swiss Research Innovation System

