Experiences about opening data in private sector

Experiences about opening data in private sector
Ⅰ. Introduction
Open data is the idea that data should be available freely for everyone to use and republish without restrictions from copyright, patents or other mechanisms of control. The concept of open data is not new; but a formalized definition is relatively new, and The Open Definition gives full details on the requirements for open data and content as follows:
Availability and access: the data must be available as a whole with no more than a reasonable reproduction cost, preferably by downloading over the internet. The data must also be available in a convenient and modifiable form.
Reuse and redistribution: the data must be provided under terms that permit reuse and redistribution including the intermixing with other datasets. The data shall be machine-readable.
Universal participation: everyone must be able to use, reuse and redistribute the data— which by means there should be no discrimination against fields of endeavor or against persons or groups. For example, “non-commercial” restrictions that would prevent “commercial” use, or restrictions of use for certain purposes are not allowed.
In order to be in tune with international developmental trends, Taiwan passed an executive resolution in favor of promoting Open Government Data in November 2012. Through the release of government data, open data has grown significantly in Taiwan and Taiwan has come out on top among 122 countries and areas in the 2015 and 2016 Global Open Data Index[1].
The result represented a major leap for Taiwan, however, progress is still to be made as most of the data are from the Government, and data from other territories, especially from private sector can rarely be seen. It is a pity that data from private sector has not being properly utilized and true value of such data still need to be revealed. The following research will place emphasis to enhance the value of private data and the strategies of boosting private sector to open their own data.
Ⅱ. Why open private data
With the trend of Open Government Data recent years, countries are now starting to realize that Open Government Data is improving transparency, creating opportunities for social and commercial innovation, and opening the door to better engagement with citizens. But open data is not limited to Open Government Data. In fact, the private sector not only interacts with government data, but also produces a massive amount of data, much of which in need of utilized.
According to the G20 open data policy agenda made in 2014, the potential economic value of open data for Australia is up to AUD 64 billion per annum, and the potential value of open data from private sector is around AUD 34 billion per annum.
Figure 1 Value of open data for Australia (AUD billion per annum)
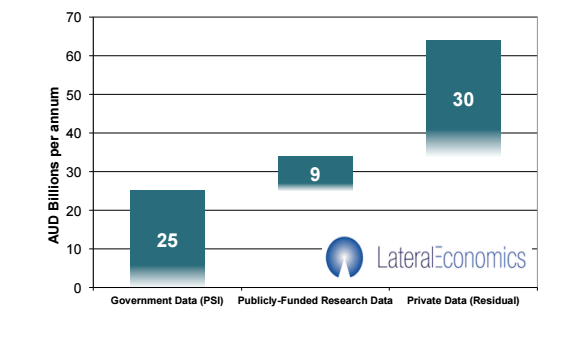.png)
Source: McKinsey Global Institute
The purpose for opening data held by private entities and corporations is rooted in a broad recognition that private data has the potential to foster much public good. Openness of data for companies can translate into more efficient internal governance frameworks, enhanced feedback from workers and employees, improved traceability of supply chains, accountability to end consumers, and with better service and product delivery. Open Private Data is thus a true win-win for all with benefiting not only the governance but environmental and social gains.
At the same time, a variety of constraints, notably privacy and security, but also proprietary interests and data protectionism on the part of some companies—hold back this potential.
Ⅲ. The cases of Open Private Data
Syngenta AG, a global Swiss agribusiness that produces agrochemicals and seeds, has established a solid foundation for reporting on progress that relies on independent data collection and validation, assurance by 3rd party assurance providers, and endorsement from its implementing partners. Through the website, Syngenta AG has shared their datasets for agricultural with efficiency indicators for 3600 farms for selected agro-ecological zones and market segments in 42 countries in Europe, Africa, Latin America, North America and Asia. Such datasets are precious but Syngenta AG share them for free only with a Non-Commercial license which means users may copy and redistribute the material in any medium or format freely but may not use the material for commercial purposes.
Figure 2 Description and License for Open data of Syngenta AG
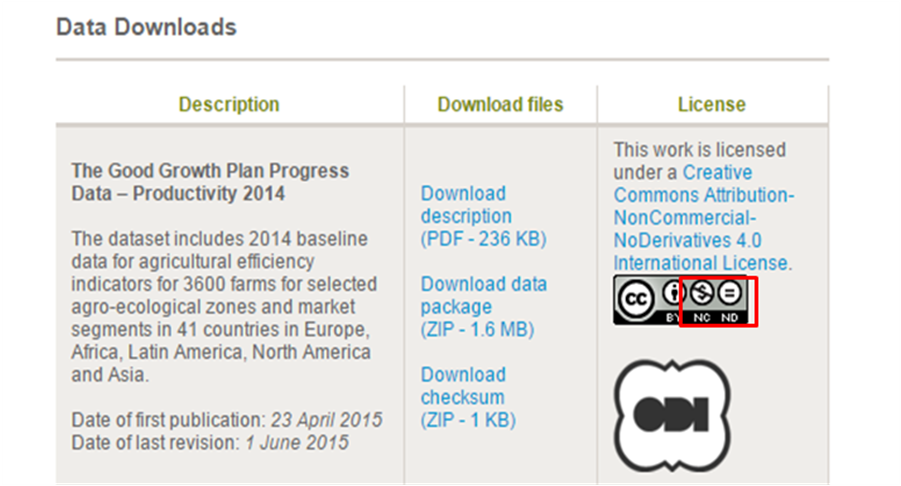
Source: http://www.syngenta.com
Tokyo Metro is a rapid transit system in Tokyo, Japan has released information such as train location and delay times for all lines as open data. The company held an Open Data Utilization Competition from 12 September to 17 November, 2014 to promote development of an app using this data and continues to provide the data even after the competition ended. However, many restrictions such as non-commercial use, or app can only be used for Tokyo Metro lines has weakened the efficiency of open data, it is still valued as an initial step of open private data.
Figure 3 DM of Tokyo Metro Open data Contest

Source: https://developer.tokyometroapp.jp/
Ⅳ. How to enhance Open Private Data
Open Private Data is totally different from Open Government Data since “motivation” is vital for private institutions to release their own data. Unlike the government data can be disclosed and free to use via administrative order or legislation, all of the data controlled by private institutions can only be opened under their own will. The initiative for open data therefore shall focus on how to motivate private sectors releasing their own data-by ensuring profit and minimizing risks.
Originally, open data shall be available freely for everyone to use without any restrictions, and data owners may profit indirectly as users utilizing their data creating apps, etc. but not profit from open data itself. The income is unsteady and data owners therefore lose their interest to open data. As a countermeasure, it is suggested to make data chargeable though this may contradict to the definition of open data. When data owners can charge by usage or by time, the motivation of open data would arise when open data is directly profitable.
Data owners may also worry about many legal issues when releasing their own data. They may not care about whether profitable or not but afraid of being involved into litigation disputes such as intellectual property infringement, unfair competition, etc. It is very important for data owners to have a well protected authorization agreement when releasing data, but not all of them is able to afford the cost of making agreement for each data sharing. Therefore, a standard sample of contract that can be widely adopted plays a very important role for open private data.
A data sharing platform would be a solution to help data owners sharing their own data. It can not only provide a convenient way to collect profit from data sharing but help data owners avoiding legal risks with the platform’s standard agreement. All the data owners have to do is just to transfer their own data to the platform without concern since the platform would handle other affairs.
Ⅴ. Conclusion
Actively engaging the private sector in the open data value-chain is considered an innovation imperative as it is highly related to the development of information economy. Although many works still need to be done such as identifying mechanisms for catalyzing private sector engagement, these works can be done by organizations such as the World Bank and the Centre for Open Data Enterprise. Private-public collaboration is also important when it comes to strengthening the global data infrastructure, and the benefits of open data are diverse and range from improved efficiency of public administrations to economic growth in the private sector. However, open private data is not the goal but merely a start for open data revolution. It is to add variation for other organizations and individuals to analyze to create innovations while individuals, private sectors, or government will benefit from that innovation and being encouraged to release much more data to strengthen this data circulation.
[1] Global Open Data Index, https://index.okfn.org/place/(Last visited: May 15, 2017)
Introduction to Tax Incentive Regime for SMEs I. Introduction The developments of SMEs (small-and-medium enterprises) plays an important pillar of development of industries and creation of jobs in Taiwan. In 2017, the total number of SMEs in Taiwan was 1,437,616. They offer 8,904,000 jobs, accounting for 78.44% of the workforce[1]. However, SMEs have difficulties in entering international supply chains because of their weakness in finance. Therefore, how to enhance the global competitiveness of SMEs is an important issue for the concerned authority. Chapter 4 of the Act for Development of Small and Medium Enterprises prescribes the tax incentive regime based on the financial capability of SMEs and characteristics of industries in order to facilitate the development of SMEs, especially the globalization of SMEs. This paper will review the importance of tax incentives to SMEs and introduces the tax incentive regime under the Act for Development of Small and Medium Enterprises In order to help SMES have an understanding of such regime. II. SME Tax Incentives Scheme As the gatekeeper of the market, the government may intervene the market with various policies or tools to reallocate and improve the soundness of the market environment when the market competitions is impaired due to information asymmetry or externalities. At this juncture, preferential tax rates or tax deductions can be offered to specific taxpayers through legal institution. This allows these taxpayers to retain higher post-tax earnings so that they are incentified to invest more resources in the legally defined economic activities. Tax incentives targeting at risky or spillover investments to create benefits to specific economic activities will help the development of industries and markets. Whilst Article 10 of the Statute for Industrial Innovation has provided tax cuts for R&D expenditures, these incentives are not focus on SMEs and hence not supportive to their research and innovations. This was the reason for the 2016 amendment of the Act for Development of Small and Medium Enterprises added Article 35 to offer tax incentives in order to encourage R&D and innovative efforts and Article 35-1 to activate intellectual properties via licensing. These articles aim to accelerate the momentum of innovations and transformations which promoting investments for SMEs. OthersTo assist SMEs to cope with change of the business environment, the Article 36-2 added the tax incentives for salary or headcount increases, to contribute to the sustainability of SMEs and stabilize the labour market and industrial structures. Following is an explanation of the applicability of these schemes and the requirements to qualify such incentives. III. Tax Incentives to Promote Investments (I) Tax deductions for R&D expenditures Governments around the world seek to encourage corporate R&D activities, that Tax incentives are put in place to reduce R&D costs and foster a healthy environment of investment for more R&D initiatives. Neighboring countries such as Japan, Korea and Singapore are frequently practicing belowing tax burdens to encourage R&D efforts. Article 35 of the Act for Development of Small and Medium Enterprises in Taiwan allows accelerated depreciation and offers tax cuts[2] to stimulate R&D and innovations and create an investment friendly environment for SMEs. 1. Taxpaying Entities and Requirements (1) Qualifications for SMEs Article 35 of the Act is applicable to qualified SMEs and individual taxpayers, which are (1) from manufacturing, construction & engineering, mining and quarrying industries, with paid-in capital below or equal to NT$80 million or with the number of full-time employees less than 200 people; (2) from other industries with the sales of the previous year below or equal to NT$100 million or with the number of full-time employees less than 100 people. Thus, the qualifications of Small and Medium Enterprises are based on either paid-in capital/sales or number of employees under the Act[3].Meanwhile, SMEs may not have an independent R&D department due to the limit of size or operating cost.Therefore, if the taxpayers hiring full-time R&D personnel that can provide records of job descriptions and work logs to R&D activities, the SMEs can access the tax incentives provided that the R&D functions. The recognized by government agencies is increasingly flexibility for SMEs seeking policy support. 2. Taxpayers and requirements (1) A certain degree of innovativeness As the tax incentive regime strives to promote innovations, the R&D expenses should be used to fund innovative developments. According to the official letters from the Small and Medium Enterprise Administration, Ministry of Economic Affairs, there is no high bar as forward-looking, risky and innovative as usually” required for other incentives previously, which is considering the size of SMEs and their industry characteristics. The “certain degree” of innovativeness shall be based on industry environments and SME businesses as determined by competent authorities in a flexible manner. (2) Flexibility in the utilization of business income tax reductions To encourage regular R&D activities, The case that SMEs may not have R&D undertakings each year due to funding constraints, or start-up company may have incurred R&D expenditures but are not yet profitable and hence have no tax liabilities during the year, Corporate taxpayers were able to choose beside deduct the payable taxes during a single year, and reduce the payable taxes during the current year over three years starting from the year when tax incentives are applicable. 3. Tax incentive effects As previously mentioned, Article 35 of the Act for Development of Small and Medium Enterprises accommodates the characteristics of SMEs by allowing reductions of corporate business taxes for up to 15% R&D expenditures during the current year, or spreading the tax reductions by spreading up to 10% of the R&D expenditures over three years from the first year when the incentives are applicable. It is worth noting that the tax deductions shall not exceed 30% of the payable business income taxes during a single year. If the instruments and equipment for R&D, experiments or quality inspections have a lifetime over two years or longer, it is possible to accelerate the depreciation within half of the years of service prescribed by the income tax codes for fixed assets. However, the final year less than 12 months over the shortened service years shall not be counted. Accelerated depreciation brings in tax benefits for fixed asset investments during the initial stage, that meets the requirements for new technologies and risk management by frontloading the equipment depreciation and creates a buffer for capital utilization. (II) Deferred taxations on licensing/capitalization of intellectual properties The deferral of tax payments under the Act for Development of Small and Medium Enterprises is meant to avoid any adverse effect on the application of technological R&Ds by SMEs. As the equity stakes via capitalization of intellectual properties by inventors or creators are not cashed out yet and the subsequent gains may not be at the same valuation as determined at the time of capitalization, the immediate taxation may hinder the willingness to transfer intellectual properties. Therefore, assisting SMEs to release intellectual properties with potential economic value, the licensing and capitalization of intellectual properties is strongly encouraged. The tax expenses shall be deferred within SME or an individual acquires stakes on a non-publicly-listed company by transferring their intellectual properties. This is to stimulate the applications and sharing of relevant manufacturing technologies. When an SME or an individual acquires stakes on a non-publicly-listed company by transferring their intellectual properties, their tax expenses shall be deferred. 1. Taxpayers and requirements (1) Qualifications for individuals or SMEs Article 35-1 of the Act for Development of Small and Medium Enterprises is applicable to SMEs and individual taxpayers. This is to foster the growth of SMEs and enhancement of industry competitiveness by encouraging R&D and innovations from individuals and start-ups. To promote the commercialize of intellectual properties in different ways, the Act for Development of Small and Medium Enterprises provides income tax incentives to individuals and SMEs transferring intellectual properties. The purpose is to encourage different paths to industry upgrades. (2) Ownership of intellectual properties To ensure that the proceeds of intellectual property is linked to the activity of intellectual properties which perform by individuals or SMEs. Only the owners of the intellectual properties capitalized and transferred can enjoy the tax benefits. Intellectual properties referred to in the Act for Development of Small and Medium Enterprises are the properties with value created with human activities and hence conferred with legal rights. These include but are not limited to copyrights, patent rights, trademarks, trade secrets, integrated circuit layouts, plant variety rights and any other intellectual properties protected by laws[4]. (3) Acquisition of stock options The abovementioned tax incentives are offered to the individuals or SMEs who transfer intellectual properties to non-listed companies in exchange of their new shares. The income taxes on the owners of intellectual properties are deferred until acquisition of shares. These shares are not registered with the book-entry system yet. Before the transferrers of intellectual properties dispose or offload these shares, immediate taxations will impose economic burdens and funding challenges given the unknown prices of the eventual cash-out. Therefore, this legislation is only applicable to taxpayers who obtain options for new shares. 2. Taxpayers and requirements (1) Transfer of intellectual properties According to Article 36 of the Copyright Act as interpreted by official letters issued by the Ministry of Finance, the transfer of intellectual properties is the conferring of intellectual properties to others, and the transferees access these intellectual properties within the scope of the transfer. In terms “transfer” of the first and second paragraphs of Article 36 does not include licensing[5], but such as granting, licensing and inheritance. (2) Timing of income tax payments In general, the particular time that calculation of taxes payable is based on when the taxpayers acquire the incomes, less relevant expenses or costs. The taxes payable timing should be depending on when the taxpayers obtain the newly issued shares by transferring intellectual properties. However, the levy of income taxes at the time of intellectual property transfers and new share acquisitions may cause a sudden jump in taxes payable in the progressive system and thus a burden on the economics of SMEs and individuals concerned. Thus, to avoid disruptions to company operations or personal finance planning, Article 36 makes the exception for the incomes earned by subscribing to new shares as a result of transferring intellectual properties. Such incomes are not subject to taxes during the year when the shares are acquired, in order to mitigate the tax barriers concerned. In sum, the taxes shall be paid when such shares are transferred, gifted or distributed. 3. Tax incentive effects Article 35-1 of the Act for Development of Small and Medium Enterprises provides tax incentives to stimulate the mobilization of intellectual properties by smoothing out the impact of income taxes payable. This is applicable to (1) SMEs who can postpone the business income taxes payable from the year when they acquire new shares of non-listed companies by transferring the intellectual properties they own; (2) individuals who can postpone the individual income taxes payable from the year when they acquire new shares of non-listed companies by transferring the intellectual properties they own. IV. Tax incentives aiming to improve the business environment (I) Tax reductions for wages to additional headcounts SMEs are vital to the Taiwan, making uo 90% of the companies accounting in Taiwan, who employ more than 6.5 million people or 72.8% of the total workforce. Any economic recession may make it difficult for SMEs to maintain their labor costs given their smaller funding size and external challenges. This will cause higher unemployment rates and hurt the economy, which may cause impairment of the capacity or create a labor gap for SMEs, eventually shrink the industry scale. To lower the burden of operational and investment costs and learn from the legislatives in Japan and the U.S.[6], tax incentives are put in place as a buffer for adverse effects of external environments. The first paragraph of Article 36-2 of the Act for Development of Small and Medium Enterprises provide tax incentives for employee salaries of new headcounts based on the assessment on the economy over a time period. This is intended to encourage domestic investments and avoid the pitfall of direct government subsidies distorting salary structures. It is hoped that investments from SMEs can stimulate the momentum of economic growth. 1. Taxpayers The tax incentives under Article 36-2 of the Act for Development of Small and Medium Enterprises aim to assist SMEs through difficult times in an economic downturn. The threshold of the period time is based on the unemployment rate has been below the economic indicator predetermined for six consecutive months, which calculated by the Directorate General of Budget, Accounting and Statistics, Executive Yuan. In number of the unemployment rate has been below the economic indicator predetermined for six consecutive months, it is deemed that the business environment is not friendly to SMEs. In this instance, the Regulations for the Tax Preferences Provided to Small and Medium-sized Enterprises on Additional Wage Payment will trigger the tax incentives. The abovementioned economic indicator shall be published by the competent authorities once every two years. Moreover, to qualify for the tax incentives for new employees, SMEs should investing new ventures or instill new capital by at least $500,000[7] or hiring workforce at least two full-time headcounts compared with the previous fiscal year, that constitute at the Article 36-2 of the Act for Development of Small and Medium Enterprises, which aims to encourage SMEs investments. 2. Taxpayers (1) Qualifications of additional headcounts As the dispatched human resource services typically meet temporary or short-term requirements and contractors do not enjoy employment security, this is not consistent with the spirit of the legislation to create jobs and reduce unemployment. Therefore, to avoid the one-time increase of headcounts from accessing the tax reductions during the year and the deterioration of labor relations in Taiwan. Tax incentive is not offered to the additional recruitment of part-time or contracted workers. Meanwhile, the tax incentives are only applicable to the additional employment of Taiwanese nationals, above or below 24 years old. A tax deduction of 50% based on annual wages is provided for the hiring of people below 24 years old. The extra tax deduction will stimulate young employment. (2) Definition of additional employment The number of additional headcounts is based on permanent hires and calculated as the difference between the average number of Taiwanese employees covered by labor insurance per month throughout a single fiscal year or before and after the incremental increase of workforce. The conversion of regular contracts to indefinite employment in writing or signing up for indefinite R&D headcounts under the military service scheme can also be deemed as additional employment. It is worth noting, however, the new headcounts resulted from M&A activities or transfer between affiliated companies are excluded in this legislation. (3) Calculation of wages Companies are also required to increase employment as well as the Comparable Wages. The comparable wages are estimated with the summation of 30% of the wages for the year before and after additional employment that based on the aggregate of the new hires comparable wages compared to the prior year. In other words, if the aggregate wages paid out are higher than comparable wages during the year, the companies concerned have indeed incurred higher personnel expenses. Tax incentives are thus granted because it improves the business environment and it is the purpose of this legislation. 3. Tax incentive effects The first paragraph of Article 36-2 of the Act for Development of Small and Medium Enterprises provides deductions of business income taxes during the year to qualified SMEs at an amount equivalent to 130% of the incremental wages paid to new headcounts who are Taiwanese nationals. The deductible amount is equivalent to 150% of the incremental wages if new headcounts are Taiwanese nationals below 24 years old. (II) Tax incentives for companies that increase salaries Companies are subject to the effect of changes in the external factors such as global supply and demand on the international market, as well as the domestic business environment as a result of risk aversion from investors and expectation from customers. These uncertainties associated with investments and the rising prices for consumers will suppress the wage levels in Taiwan. This the reason why the second paragraph of Article 36-2 of the Act for Development of Small and Medium Enterprises grants tax deductions for the companies who increase salaries, to encourage companies share earnings with employees and enhance private-sector consumption. SMEs may deduct their business income taxes payable during the year up to 30% of salary increase for existing entry-level employees who are Taiwanese nationals, not as a result of statutory requirement for basic wage adjustments. 1. Taxpayers The tax incentives are applicable to SMEs as defined by the Regulations for the Tax Preferences Provided to Small and Medium-sized Enterprises on Additional Wage Payment and based on the same economic indicators previously mentioned. 2. Qualification for tax incentives (1) Definition of entry-level employees The object of taxation under this act is the enterprise's average wage payment to the entry-level employees. The entry-level employees referred to in this act are authorized by the "Small and medium-sized enterprise employee salary increase, salary deduction act " that refers to employees of local nationality with an average monthly recurring salary below nt $50,000[8] whose were entered into indefinite employment contracts with SMEs. Through such conditions, the effect of tax concessions will be concentrated on promoting the salary level of grassroots staff and helping enterprises to cope with changes in the industrial environment. (2) Average salaries The salaries to entry-level employees refer to the basic salaries, fixed allowances and bonuses paid on a monthly basis. Payment-in-kind shall be discounted based on the actual prices and included into the regular salaries. Meanwhile, regular salaries should be calculated with annualized averages, as this legislation seeks to boost salary levels. The regular salaries to entry-level employees during the year are estimated with the monthly number of entry-level employees during the same year. Only when the average basis salaries during the year are higher than those in the prior year can the tax incentives be applicable. 3. Tax incentive effects Applying this article, SMEs can deduct their business income taxes each year up to 130% of salary increase for existing entry-level employees who are Taiwanese nationals, which are not as a result of statutory requirement for basic wage adjustments. However, it is not allowed to double count the increased personnel expenses for new headcounts applicable to the first and second paragraphs of the same article. V. Conclusions The funding scales and relatively weak financial structures are the factors that led SMEs be susceptible influenced by supply change dynamics and business cycles. To the extent that is suppressing the flexible in capital utilization for SMEs, also influencing on the sustainability of SMEs. Differ from government subsidies require budgeting, reviewing and implementations, there are complications regarding the allocation of administrative resources. Therefore, it is important to plan for tax incentives in order to stimulate R&D, innovation and job creation by SMEs and ultimately make SMEs more competitive. The tax incentives to SMEs amended in 2016 by the Small and Medium Enterprise Administration are known for the following: (I) The lowering of thresholds for tax reductions of R&D expenses in order to encourage SMEs to invest in R&D activities with a “certain degree” of innovativeness and enhance the momentum for SMEs to upgrade and transform themselves; (II) Deferral the income taxations on the transfer of intellectual properties for equity, in order to encourage application and utilization of such intellectual properties, provide incentives for R&D programs or innovations by individuals and SMEs. This also creates a catalyst for industry upgrade; (III) Tax deductions for the employment of new headcounts or the increase of employee wages during the time the economic indicators have reached a certain threshold and based on the health of the investment environment. This is to encourage company investments and capital increases in Taiwan and mitigate the volatility of economic cycles, in order to get ready for business improvement. The above tax incentive programs, i.e. tax deductions for R&D and innovations; deferral of taxations on the transfer of intellectual properties for equity; tax deductions for the hiring of new headcounts and the increase of employee salaries, are meant to boost the investment from SMEs and the competitiveness of SMEs. The Act for Development of Small and Medium Enterprises seeks to reduce tax burdens of SMEs actively investing for their future and competitive advantages. Tax incentives help to mitigate the adverse effect of the economy on the business environment. It is also the fostering of the sources of business income tax revenues for the government. This is the very purpose of the Act for Development of Small and Medium Enterprises. [1]White Paper on Small and Medium Enterprises in Taiwan, 2018, p21 (November 9, 2018) published by the Ministry of Economic Affairs [2]Pursuant to the authorization conferred by Article 35 of the Act for Development of Small and Medium Enterprises, the Ministry of Economic Affairs has announced the Regulations Governing the Reduction of Expenditures for Small and Medium Enterprises Research and Development as Investment. [3]Article 2 on the definition of SMEs. The abovementioned criterion is universally applicable to the Act for Development of Small and Medium Enterprises. It also applies to the eligibility of tax incentives to be introduced in this paper unless otherwise specified. [4]Official Letter Economic-Business No. 10304605790, Ministry of Economic Affairs [5]Official Letter Taiwan-Finance No. 10300207480, Ministry of Finance [6]“Assessment of the Taxations under Article 35, Article 35-1, the first paragraph and the second paragraph of Article 36-2, the Act for Development of Small and Medium Enterprises” published by the Small and Medium Enterprise Administration, Ministry of Economic Affairs, pages 15-17, https://www.moeasmea.gov.tw/files/2670/93B9AF54-84E2-4293-A5CA-EA7DD9FAA05A(most recently browsed date September 9, 2019). [7]Order of Interpretation Economics-Business No. 104004602510 from the Ministry of Economic Affairs: “Second, on the day when the economic indicator has reached the threshold, the paid-in capital of the new business should be at least NT$500,000 and there is no need to instill additional capital during the period when tax incentives are applicable. For existing businesses, there is no limitation on the number of capital increases during the applicable period. So long as the cumulative increase in capital reaches NT$500,000 and new employees are hired during the same fiscal year or during the prior fiscal year.” [8]Paragraph 1, Article 2 of the Regulations for the Tax Preferences Provided to Small and Medium-sized Enterprises on Additional Wage Payment
The Study of Estonian Human Genes DatabaseI. Introduction The human genes database or human genome project, the product under the policy of biotechnology no matter in a developed or developing country, has been paid more attention by a government and an ordinary people gradually. The construction of human genes database or human genome project, which is not only related to a country’s innovation on biotechnology, but also concerns the promotion of a country’s medical quality, the construction of medical care system, and the advantages brought by the usage of bio-information stored in human genes database or from human genome project. However, even though every country has a high interest in setting up human genes database or performing human genome project, the issues concerning the purposes of related biotechnology policies, the distribution of advantages and risks and the management of bio-information, since each country has different recognition upon human genes database or human genome project and has varied standards of protecting human basic rights, there would be a totally difference upon planning biotechnology policies or forming the related systems. Right now, the countries that vigorously discuss human genes database or practice human genome project include England, Iceland, Norway, Sweden, Latvia and Estonia. Estonia, which is the country around the Baltic Sea, has planned to set up its own human genes database in order to draw attention from other advanced countries, to attract intelligent international researchers or research groups, and to be in the lead in the area of biotechnology. To sum up, the purpose of constructing Estonian human genes database was to collect the genes and health information of nearly 70% Estonia’s population and to encourage bio-research and promote medical quality. II. The Origin of Estonian Human Genes Database The construction of Estonian human genes database started from Estonian Genome Project (EGP). This project was advocated by the professor of biotechnology Andres Metspalu at Tartu University in Estonia, and he proposed the idea of setting up Estonian human genes database in 1999. The purposes of EGP not only tried to make the economy of Estonia shift from low-cost manufacturing and heavy industry to an advanced technological economy, but also attempted to draw other countries’ attention and to increase the opportunity of making international bio-researches, and then promoted the development of biotechnology and assisted in building the system of medical care in Estonia. EGP started from the agreement made between Estonian government and Eesti Geenikeskus (Estonian Genome Foundation) in March, 1999. Estonian Genome Foundation was a non-profit organization formed by Estonian scientists, doctors and politicians, and its original purposes were to support genes researches, assist in proceeding any project of biotechnology and to set up EGP. The original goals of constructing EGP were “(a) reaching a new level in health care, reduction of costs, and more effective health care, (b) improving knowledge of individuals, genotype-based risk assessment and preventive medicine, and helping the next generation, (c) increasing competitiveness of Estonia – developing infrastructure, investments into high-technology, well-paid jobs, and science intensive products and services, (d) [constructing] better management of health databases (phenotype/genotype database), (e) … [supporting]… economic development through improving gene technology that opens cooperation possibilities and creates synergy between different fields (e.g., gene technology, IT, agriculture, health care)”1. III. The Way of Constructing Estonian Human Genes Database In order to ensure that Estonian human genes database could be operated properly and reasonably in the perspectives of law, ethics and society in Estonia, the Estonian parliament followed the step of Iceland to enact “Human Genes Research Act” (HGRA) via a special legislative process to regulate its human genes database in 2000. HGRA not only authorizes the chief processor to manage Estonian human genes database, but also regulates the issues with regard to the procedure of donation, the maintenance and building of human genes database, the organization of making researches, the confidential identity of donator or patient, the discrimination of genes, and so on. Since the construction of Estonian human genes database might bring the conflicts of different points of view upon the database in Estonia, in order to “avoid fragmentation of societal solidarity and ensure public acceptability and respectability”2 , HGRA adopted international standards regulating a genes research to be a norm of maintaining and building the database. Those standards include UNESCO Universal Declaration on the Human Genome and Human Rights (1997) and the Council of Europe’s Convention on Human Rights and Biomedicine (1997). The purpose of enacting HGRA is mainly to encourage and promote genes researches in Estonia via building Estonian human genes database. By means of utilizing the bio-information stored in the database, it can generate “more exact and efficient drug development, new diagnostic tests, improved individualized treatment and determination of risks of the development of a disease in the future”3 . In order to achieve the above objectives, HGRA primarily puts emphasis on several aspects. Those aspects include providing stronger protection on confidential identity of donators or patients, caring for their privacy, ensuring their autonomy to make donations, and avoiding any possibility that discrimination may happen because of the disclosure of donators’ or patients’ genes information. 1.HERBERT GOTTWEIS & ALAN PETERSEN, BIOBANKS – GOVERNANCE IN COMPARATIVE PERSPECTIVE 59 (2008). 2.Andres Rannamae, Populations and Genetics – Legal and Socio-Ethical Perspectives, in Estonian Genome Porject – Large Scale Health Status Description and DNA Collection 18, 21 (Bartha Maria Knoppers et al. eds., 2003. 3.REMIGIUS N. NWABUEZE, BIOTECHNOLOGY AND THE CHALLENGE OF PROPERTY – PROPERTY RIGHTS IN DEAD BODIES, BODY PARTS, AND GENETIC INFORMATION, 163 (2007).
Taiwan Planed Major Promoting Program for Biotechnology and Pharmaceutical IndustryTaiwan Government Lauched the “Biotechnology Action Plan” The Taiwan Government has planned to boost the support and develop local industries across the following six major sectors: biotechnology, tourism, health care, green energy, innovative culture and post-modern agriculture. As the biotechnology industry has reached its maturity by the promulgation of "Biotech and New Pharmaceutical Development Act" in July, 2007, it will be the first to take the lead among the above sectors. Thus, the Executive Yuan has launched the Biotechnology Action Plan as the first project in building the leading industry sectors, to upgrade local industries and stimulate future economic growth. Taiwan Government Planed to Promote the Biotechnology and Other newly Industries by Investing Two Hundred Billion To expand every industrial scale, enhance industrial value, increase the value around the main industrial field, and to encourage the industrial development by government investments for creating the civil working opportunities to reach the goal of continuous economic development, the Executive Yuan Economic Establishment commission has expressed that, the government has selected six newly industrials including "Biotechnology", "Green Energy", "Refined Agriculture", "Tourism", "Medicare", and "Culture Originality" on November 19, 2009 to promote our national economic growth. The government will invest two hundred billion NT dollars to support the industrial development aggressively and to enhance the social investments from year 2009 to 2012. According to a Chung-Hua Institution for Economic Research report, the future growth rate will reach 8.16% after the evaluation, Hence, the future of the industries seems to be quite bright. Currently, the government plans to put money into six newly industries through the existing ways for investment. For instance, firstly, in accordance with the "Act For The Development Of Biotech And New Pharmaceuticals Industry" article 5 provision 1 ",for the purpose of promoting the Biotech and New Pharmaceuticals Industry, a Biotech and New Pharmaceuticals Company may, for a period of five years from the time it is subject to corporate income tax, enjoy a reduction in its corporate income tax payable for up to thirty-five percent (35%) of the total funds invested in research and development ("R&D") and personnel training each year; provided, however, that if the R&D expenditure of a particular year exceeds the average R&D expenditure of the previous two years or if the personnel training expenditure of a particular year exceeds the average personnel training expenditure of the previous two years, fifty percent (50%) of the amount in excess of the average may be used to credit against the amount of corporate income tax payable. Secondly, according to same act of the article 6 provision 1 ", in order to encourage the establishment or expansion of Bio tech and New Pharmaceuticals Companies, a profit-seeking enterprise that (i) subscribes for the stock issued by a Biotech and New Pharmaceuticals Company at the time of the latter's establishment or subsequent expansion; and (ii) has been a registered shareholder of the Biotech and New Pharmaceuticals Company for a period of three (3) years or more, may, for a period of five years from the time it is subject to corporate income tax, enjoy a reduction in its corporate income tax payable for up to twenty percent (20%) of the total amount of price paid for the subscription of shares in such Biotech and New Pharmaceuticals Company; provided that such Biotech and New Pharmaceuticals Company has not applied for exemption from corporate income tax or shareholders investment credit based on the subscription price under other applicable laws and regulations. Thirdly, to promote the entire biotechnological industry development, the government has drafted the "Biotechnology Takeoff Package" for subsidizing the startup´s social investment companies which can satisfy the conditions to invest in "Drug discovery", "Medical Device" or other related biotech industries up to 5 billion with the capital invest in domestic industry over 50%, , with operating experience of multinational biotech investment companies with capital over 150 million in related industrial fields, and with the working experiences of doctor accumulated up to 60 years. Additionally, the refined agriculture industry field has not only discovered the gene selected products, but also combined the tourism with farming business for new business model creation. According to the "Guidelines for Preferential Loans for the Upgrading of Tourism Enterprises" point 4 provision 1, the expenditure for spending on machine, instruments, land or repairing can be granted a preferential loan in accordance with the rule of point 6, and government will provide a subsidy of interest for loaning Tourism Enterprises with timely payments. At last, Council for Economic Planning and Development also points out because most of technology industry has been impacted seriously by fluctuation of international prosperity due to conducting the export trade oriented strategy. Furthermore, the aspects of our export trade of technology industry have been impacted by the U.S. financial crisis and the economic decay in EU and US; and the industrial development seems to face the problem caused by over centralization in Taiwan. Hence, the current framework of domestic industry should be rearranged and to make it better by promoting the developmental project of six newly industries. Taiwan Government Had Modifies Rules to Accelerate NDA Process and Facilitate Development of Clinical Studies in Taiwan In July 2007, the "Biotech and New Pharmaceutical Development Act" modified many regulations related to pharmaceutical administration, taxes, and professionals in Taiwan. In addition, in order to facilitate the development of the biotechnology and pharmaceutical industries, the government has attempted to create a friendly environment for research and development by setting up appropriate regulations and application systems. These measures show that the Taiwanese government is keenly aware that these industries have huge potential value. To operate in coordination with the above Act and to better deal with the increasing productivity of pharmaceutical R&D programs in Taiwan, the Executive Yuan simplified the New Drug Application (NDA) process to facilitate the submission that required Certificate of Pharmaceutical Product (CPP) for drugs with new ingredients. The current NDA process requires sponsors to submit documentation as specified by one of the following four options: (1) three CPPs from three of "ten medically-advanced countries," including Germany, the U.S., England, France, Japan, Switzerland, Canada, Australia, Belgium, and Sweden; (2) one CPP from the U.S., Japan, Canada, Australia, or England and one CPP from Germany, France, Switzerland, Sweden, or Belgium; (3) a Free Sale Certificate (FSC) from one of ten medically-advanced countries where the pharmaceuticals are originally produced and one CPP from one of the other nine countries; or (4) a CPP from the European Medicines Agency. Thus, the current NDA process requires sponsors to spend inordinate amounts of time and incur significant costs to acquire two or three FSCs or CPPs from ten medically-advanced countries in order to submit an NDA in Taiwan. According to the new rules, sponsors will not have to submit above CPPs if (1) Phase I clinical studies have been conducted in Taiwan, and Phase III Pivotal Trial clinical studies have been simultaneously conducted both in Taiwan and in another country or (2) Phase II and Phase III Pivotal Trial clinical studies have been simultaneously conducted both in Taiwan and in another country. Besides, the required minimum numbers of patients were evaluated during each above phase. Therefore, sponsors who conduct clinical studies in Taiwan and in another country simultaneously could reduce their costs and shorten the NDA process in Taiwan. The new rules aim to encourage international pharmaceutical companies to conduct clinical studies in Taiwan or to conduct such studies cooperatively with Taiwanese pharmaceutical companies. Such interactions will allow Taiwanese pharmaceutical companies to participate in development and implementation of international clinical studies in addition to benefiting from the shortened NDA process. Therefore, the R&D abilities and the internationalization of the Taiwanese pharmaceutical industry will be improved.
Innovative Practice of Israel's Government ProcurementInnovative Practice of Israel's Government Procurement Government procurement is an important pillar of government services. Because of the huge number of government purchases, government procurement management play an important role in promoting public sector efficiency and building citizenship. Well-designed government procurement systems also help to achieve policy such as environmental protection, innovation, start-ups and the development of small and medium-sized enterprises. Nowadays, countries in the world, especially OECD countries, have been widely practiced with innovative procurement to stimulate innovation and start-ups, and call Innovation procurement can deliver solutions to challenges of public interest and ICTs can play a major role in this. However, in the OECD countries, in addition to the advanced countries that have been developed, many developing countries have also used government procurement to stimulate national R & D and innovation with remarkable results. Israel is one of the world's leading technology innovation centers, one of the most innovative economies in the world, continues to leverage its own strengths, support of technology entrepreneurship and unique environment, an international reputation in the high-tech industry, the spirit of technological innovation and novelty. Government procurement is a core element of the activities of Israeli government, agreement with suppliers and compliance with the Mandatory Tenders Law. The main challenge is how to ensure efficiency and maintain government performance while ensuring an equitable and transparent procurement process. Israel’s Mandatory Tenders Law has shown the central role played by the Israeli Supreme Court in creating and developing this law, even in the absence of any procurement legislation, based instead on general principles of administrative law. Once the project of creating a detailed body of public tendering law had been completed, and the legislator was about to step in, the Supreme Court was prepared to step out and transferring the jurisdiction to lower courts. The Knesset passed the Mandatory Tenders Law, and based on it the Government issued the various tendering regulations. Besides, Israel's various international agreements on government procurement, mainly GPA and other bilateral international agreements such as free trade agreements with Mexico and Colombia and free trade agreements and memoranda of understanding with the United States. The practical significance of these commitments can only be understood on the backdrop of Israel’s domestic preference and offset policies. These policies were therefore discussed and analyzed as they apply when none of the international agreements applies. The Challenge Tenders "How to solve the problem of overcrowding in the emergency department and the internal medicine department?" is the first of a series of "problem solicitations" released by the Israeli Ministry of Health which seeks to find a digital solution to the public health system problem, questions from the government while avoiding preconceived prejudices affect the nature of the solution, allowing multiple innovative ideas from different fields to enter the health system, make fair and transparent judgments about the ideal solution to the problem. In order to ensure transparency and integrity, equality, efficiency and competition in the decision-making process, the tender proposed by the Israeli Ministry of Health defines a two-stage tender process. The Ministry of Health of Israel, in order to improve the quality of medical care, shorten the waiting time for hospitalized patients, protect the dignity of patients and their families with patients as its center, and ensure their rights, while alleviating the burden of hospital staff, so as to pass the targeted treatment areas reduce the gap between various residential areas. The Israeli government deals with these issues through challenging tenders and offers a digital solution combined with innovative ideas. The initiative proposed through the development of public service projects can raise the level of public services in the country and help the government to reduce costs and achieve the purpose of promoting innovation with limited conceptual, technical and financial capabilities. In addition, due to the online operation of the challenging tender process throughout the entire process, fair and transparent procedures can be ensured, while public-private partnerships are encouraged to facilitate the implementation of the implementation plan.
- Impact of Government Organizational Reform to Scientific Research Legal System and Response Thereto (1) – For Example, The Finnish Innovation Fund (“SITRA”)
- The Demand of Intellectual Property Management for Taiwanese Enterprises
- Blockchain in Intellectual Property Protection
- Impact of Government Organizational Reform to Research Legal System and Response Thereto (2) – Observation of the Swiss Research Innovation System
- Recent Federal Decisions and Emerging Trends in U.S. Defend Trade Secrets Act Litigation
- The effective and innovative way to use the spectrum: focus on the development of the "interleaved/white space"
- Copyright Ownership for Outputs by Artificial Intelligence
- Impact of Government Organizational Reform to Research Legal System and Response Thereto (2) – Observation of the Swiss Research Innovation System
