Impact of Government Organizational Reform to Research Legal System and Response Thereto (2) – Observation of the Swiss Research Innovation System

3.Commission of Technology and Innovation (CTI)
The CTI is also an institution dedicated to boosting innovation in Switzerland. Established in 1943, it was known as the Commission for the Promotion of Scientific Research[1]. It was initially established for the purpose of boosting economy and raising the employment rate, and renamed after 1996. The CTI and SNSF are two major entities dedicated to funding scientific research in Switzerland, and the difference between both resides in that the CTI is dedicated to funding R&D of the application technology and industrial technology helpful to Switzerland’s economic development.
Upon enforcement of the amended RIPA 2011, the CTI was officially independent from the Federal Office for Professional Education and Technology (OEPT) and became an independent entity entitled to making decisions and subordinated to the Federal Department of Economic Affairs (FDEA) directly[2]. The CTI is subject to the council system, consisting of 65 professional members delegated from industrial, academic and research sectors. The members assume the office as a part time job. CTI members are entitled to making decisions on funding, utilization of resources and granting of CTI Start-up Label independently[3].
The CTI primarily carries out the mission including promotion of R&D of industrial technology, enhancement of the market-orientation innovation process and delivery of R&D energy into the market to boost industrial innovation. For innovation, the CTI's core mission is categorized into[4]:
(1)Funding technology R&D activities with market potential
The CTI invests considerable funds and resources in boosting the R&D of application technology and industrial technology. The CTI R&D Project is intended to fund private enterprises (particularly small-sized and medium-sized enterprises) to engage in R&D of innovation technology or product. The enterprises may propose their innovative ideas freely, and the CTI will decide whether the funds should be granted after assessing whether the ideas are innovative and potentially marketable[5].
CTI’s funding is conditioned on the industrial and academic cooperation. Therefore, the enterprises must work with at least one research institution (including a university, university of science and technology, or ETH) in the R&D. Considering that small-sized and medium-sized enterprises usually do not own enough working funds, technology and human resources to commercialize creative ideas, the CTI R&D Project is intended to resolve the problem about insufficient R&D energy and funds of small- and medium-sized enterprises by delivering the research institutions’ plentiful research energy and granting the private enterprises which work with research institutions (including university, university of science and technology, or ETH) the fund. Notably, CTI’s funding is applicable to R&D expenses only, e.g., research personnel’s salary and expenditure in equipment & materials, and allocated to the research institutions directly. Meanwhile, in order to enhance private enterprises' launch into R&D projects and make them liable for the R&D success or failure, CTI’s funding will be no more than 50% of the total R&D budget and, therefore, the enterprises are entitled to a high degree of control right in the process of R&D.
The industrial types which the CTI R&D Project may apply to are not limited. Any innovative ideas with commercial potential may be proposed. For the time being, the key areas funded by CTI include the life science, engineering science, Nano technology and enabling sciences, etc.[6] It intends to keep Switzerland in the lead in these areas. As of 2011, in order to mitigate the impact of drastic CHF revaluation to the industries, the CTI launched its new R&D project, the CTI Voucher[7]. Given this, the CTI is not only an entity dedicated to funding but also plays an intermediary role in the industrial and academic sectors. Enterprises may submit proposals before finding any academic research institution partner. Upon preliminary examination of the proposals, the CTI will introduce competent academic research institutions to work with the enterprises in R&D, subject to the enterprises' R&D needs. After the cooperative partner is confirmed, CTI will grant the fund amounting to no more than CHF3,500,000 per application[8], provided that the funding shall be no more than 50% of the R&D project expenditure.
The CTI R&D Project not only boosts innovation but also raises private enterprises’ willingness to participate in the academic and industrial cooperation, thereby narrowing the gap between the supply & demand of innovation R&D in the industrial and academic sectors. Notably, the Project has achieved remarkable effect in driving private enterprises’ investment in technology R&D. According to statistical data, in 2011, the CTI solicited additional investment of CHF1.3 from a private enterprise by investing each CHF1[9]. This is also one of the important reasons why the Swiss innovation system always acts vigorously.
Table 1 2005-2011 Passing rate of application for R&D funding
|
Year |
2011 |
2010 |
2009 |
2008 |
2007 |
2006 |
2005 |
|
Quantity of applications |
590 |
780 |
637 |
444 |
493 |
407 |
522 |
|
Quantity of funded applications |
293 |
343 |
319 |
250 |
277 |
227 |
251 |
|
Pass rate |
56% |
44% |
50% |
56% |
56% |
56% |
48% |
Data source: Prepared by the Study
(2)Guiding high-tech start-up
Switzerland has learnt that high-tech start-ups are critical to the creation of high-quality employment and boosting of economic growth, and start-ups were able to commercialize the R&D results. Therefore, as of 2001, Switzerland successively launched the CTI Entrepreneurship and CTI Startup to promote entrepreneurship and cultivate high-tech start-ups.
1.CTI Entrepreneurship
The CTI Entrepreneurship was primarily implemented by the Venture Lab founded by CTI investment. The Venture Lab launched a series of entrepreneurship promotion and training courses, covering day workshops, five-day entrepreneurship intensive courses, and entrepreneurship courses available in universities. Each training course was reviewed by experts, and the experts would provide positive advice to attendants about innovative ideas and business models.
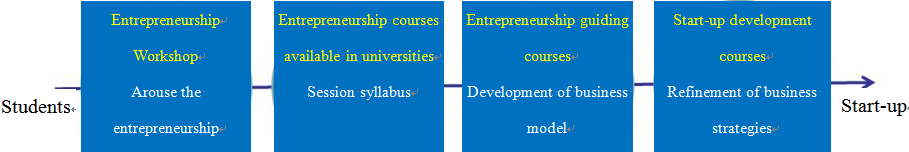
Data source: Venture Lab Site
Fig. 3 Venture Lab Startup Program
2.CTI Startup
The CTI is dedicated to driving the economy by virtue of innovation as its priority mission. In order to cultivate the domestic start-ups with high growth potential in Switzerland, the CTI Startup project was launched in 1996[10] in order to provide entrepreneurs with the relevant guidance services. The project selected young entrepreneurs who provided innovative ideas, and guided them in the process of business start to work their innovative ideas and incorporate competitive start-ups.
In order to enable the funding and resources to be utilized effectively, the CTI Startup project enrolled entrepreneurs under very strict procedure, which may be categorized into four stages[11]:
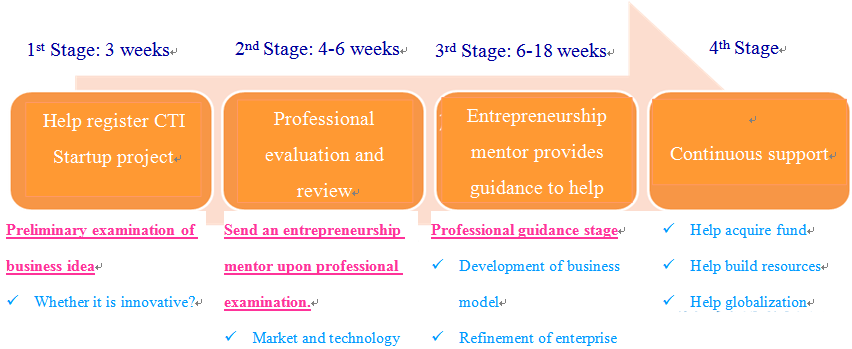
Data source: CTI Startup Site
Fig. 4 Startup Plan Flow Chart
In the first stage, the CTI would preliminarily examine whether the applicant’s idea was innovative and whether it was technologically feasible, and help the applicant register with the CTI Startup project. Upon registration, a more concrete professional examination would be conducted at the second stage. The scope of examination included the technology, market, feasibility and management team’s competence. After that, at the stage of professional guidance, each team would be assigned a professional “entrepreneurship mentor”, who would help the team develop further and optimize the enterprise’s strategy, flow and business model in the process of business start, and provide guidance and advice on the concrete business issues encountered by the start-up. The stage of professional guidance was intended to guide start-ups to acquire the CTI Startup Label, as the CTI Startup Label was granted subject to very strict examination procedure. For example, in 2012, the CTI Startup project accepted 78 applications for entrepreneurship guidance, but finally the CTI Startup Label was granted to 27 applications only[12]. Since 1996, a total of 296 start-ups have acquired the CTI Startup Label, and more than 86% thereof are still operating now[13]. Apparently, the CTI Startup Label represents the certification for innovation and on-going development competence; therefore, it is more favored by investors at the stage of fund raising.
Table 2 Execution of start-up plans for the latest three years
|
|
Quantity of application |
Quantity of accepted application |
Quantity of CTI Label granted |
|
2012 |
177 |
78 |
27 |
|
2011 |
160 |
80 |
26 |
|
2010 |
141 |
61 |
24 |
Data source: CTI Annual Report, prepared by the Study
Meanwhile, the “CTI Invest” platform was established to help start-up raise funds at the very beginning to help commercialize R&D results and cross the valley in the process of R&D innovation. The platform is a private non-business-making organization, a high-tech start-up fund raising platform co-established by CTI and Swiss investors[14]. It is engaged in increasing exposure of the start-ups and contact with investors by organizing activities, in order to help the start-ups acquire investment funds.
(3)Facilitating transfer of knowledge and technology between the academic sector and industrial sector
KTT Support (Knowledge & Technology Transfer (KTT Support) is identified as another policy instrument dedicated to boosting innovation by the CTI. It is intended to facilitate the exchange of knowledge and technology between academic research institutions and private enterprises, in order to transfer and expand the innovation energy.
As of 2013, the CTI has launched a brand new KTT Support project targeting at small-sized and medium-sized enterprises. The new KTT Support project consisted of three factors, including National Thematic Networks (NTNs), Innovation Mentors, and Physical and web-based platforms. Upon the CTI’s strict evaluation and consideration, a total of 8 cooperative innovation subjects were identified in 2012, namely, carbon fiber composite materials, design idea innovation, surface innovation, food study, Swiss biotechnology, wood innovation, photonics and logistics network, etc.[15] One NTN would be established per subject. The CTI would fund these NTNs to support the establishment of liaison channels and cooperative relations between academic research institutions and industries and provide small- and medium-sized enterprises in Switzerland with more rapid and easy channel to access technologies to promote the exchange of knowledge and technology between both parties. Innovation Mentors were professionals retained by the CTI, primarily responsible for evaluating the small-sized and medium-sized enterprises’ need and chance for innovation R&D and helping the enterprises solicit competent academic research partners to engage in the transfer of technology. The third factor of KTT Support, Physical and web-based platforms, is intended to help academic research institutions and private enterprises establish physical liaison channels through organization of activities and installation of network communication platforms, to enable the information about knowledge and technology transfer to be more transparent and communicable widely.
In conclusion, the CTI has been dedicated to enhancing the link between scientific research and the industries and urging the industrial sector to involve and boost the R&D projects with market potential. The CTI’s business lines are all equipped with corresponding policy instruments to achieve the industrial-academic cooperation target and mitigate the gap between the industry and academic sectors in the innovation chain. The various CTI policy instruments may be applied in the following manner as identified in the following figure.
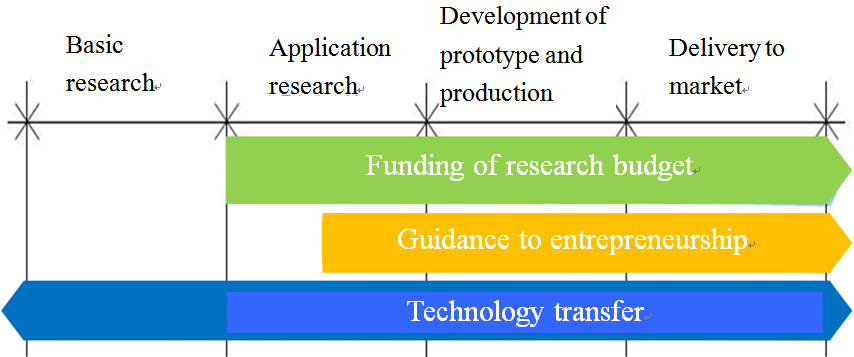
Data source: CTI Annual Report 2011
Fig. 5 Application of CTI Policy Instrument to Innovation Chain
III. Swiss Technology R&D Budget Management and Allocation
The Swiss Federal Government has invested considerable expenditures in technology R&D. According to statistic data provided by Swiss Federal Statistical Office (FSO) and OECD, the Swiss research expenditures accounted for 2.37% of the Federal Government’s total expenditures, following the U.S.A. and South Korea (see Fig. 6). Meanwhile, the research expenditures of the Swiss Government grew from CHF2.777 billion in 2000 to CHF4.639 billion in 2010, an average yearly growth rate of 5.9% (see Fig. 7). It is clear that Switzerland highly values its technology R&D.
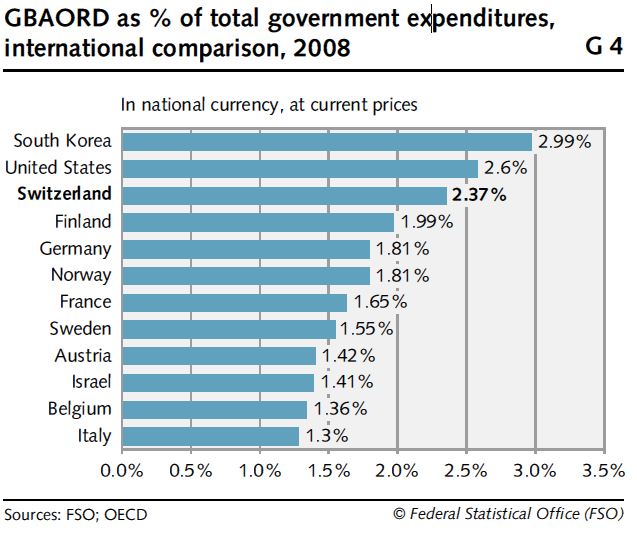.jpg)
Data source: FSO and OECD
Fig. 6 Percentage of Research Expenditures in Various Country Governments’ Total Expenditures (2008)
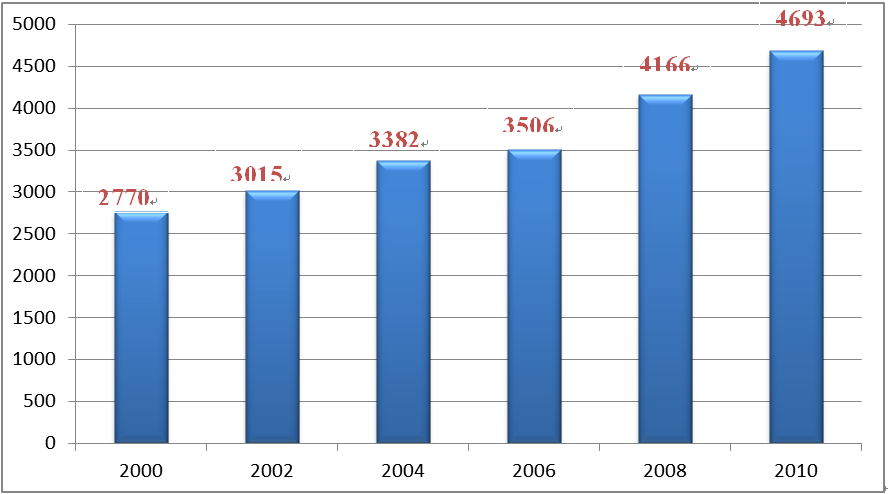
Data source: FSO and OECD
Fig. 7 Swiss Government Research Expenditures 2000-2010
1.Management of Swiss Technology R&D Budget
Swiss research expenditures are primarily allocated to the education, R&D and innovation areas, and play an important role in the Swiss innovation system. Therefore, a large part of the Swiss research expenditures are allocated to institutions of higher education, including ETH, universities, and UASs. The Swiss research expenditures are utilized by three hierarchies[16] (see Fig. 8):
- Government R&D funding agencies: The Swiss research budget is primarily executed by three agencies, including SERI, Federal Department of Economic Affairs, Education and Research, and Swiss Agency for Development and Cooperation (SDC).
- Intermediary R&D funding agencies: Including SNSC and CTI.
- Funding of R&D performing institutions: Including private enterprises, institutions of higher education and private non-profit-making business, et al.
Therefore, the Swiss Government research expenditures may be utilized by the Federal Government directly, or assigned to intermediary agencies, which will allocate the same to the R&D performing institutions. SERI will allocate the research expenditures to institutions of higher education and also hand a lot of the expenditures over to SNSF for consolidated funding to the basic science of R&D.
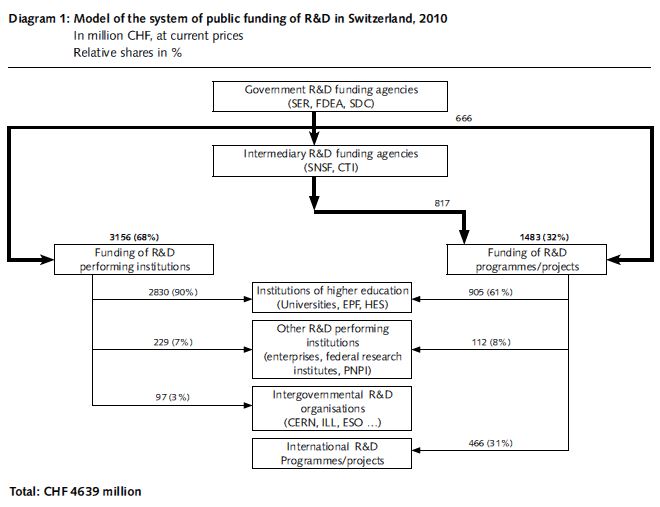
Data source: FSO
Fig. 8 Swiss Research Fund Utilization Mechanism
~to be continued~
[1] ORGANIZATION FOR ECONNOMIC CO-OPERATION AND DEVELOPMENT [OECD], OECD Reviews of Innovation Policy: Switzerland 27 (2006).
[2] As of January 1, 2013, the Federal Ministry of Economic Affairs was reorganized, and renamed into Federal Department of Economic Affairs, Education and Research (EAER).
[3] The Commission for Technology and Innovation CTI, THE COMMISSION FOR TECHOLOGY AND INNOVATION CTI, http://www.kti.admin.ch/org/00079/index.html?lang=en (last visited Jun. 3, 2013).
[4] Id.
[5] CTI INVEST, Swiss Venture Guide 2012 (2012), at 44, http://www.cti-invest.ch/getattachment/7f901c03-0fe6-43b5-be47-6d05b6b84133/Full-Version.aspx (last visited Jun. 4, 2013).
[6] CTI, CTI Activity Report 2012 14 (2013), available at http://www.kti.admin.ch/dokumentation/00077/index.html?lang=en&download=NHzLpZeg7t,lnp6I0NTU042l2Z6ln1ad1IZn4Z2qZpnO2Yuq2Z6gpJCDen16fmym162epYbg2c_JjKbNoKSn6A-- (last visited Jun. 3, 2013).
[7] CTI Voucher, THE COMMISSION FOR TECHOLOGY AND INNOVATION CTI, http://www.kti.admin.ch/projektfoerderung/00025/00135/index.html?lang=en (last visited Jun. 3, 2013).
[8] Id.
[9] CTI, CTI Activity Report 2011 20 (2012), available at http://www.kti.admin.ch/dokumentation/00077/index.html?lang=en&download=NHzLpZeg7t,lnp6I0NTU042l2Z6ln1ad1IZn4Z2qZpnO2Yuq2Z6gpJCDeYR,gWym162epYbg2c_JjKbNoKSn6A--(last visited Jun. 3, 2013).
[10] CTI Start-up Brings Science to Market, THE COMMISSION FOR TECHOLOGY AND INNOVATION CTI, http://www.ctistartup.ch/en/about/cti-start-/cti-start-up/ (last visited Jun. 5, 2013).
[11] Id.
[12] Supra note 8, at 45.
[13] Id.
[14] CTI Invest, http://www.cti-invest.ch/About/CTI-Invest.aspx (last visited Jun. 5, 2013).
[15] KTT Support, CTI, http://www.kti.admin.ch/netzwerke/index.html?lang=en (last visited Jun.5, 2013).
[16] Swiss Federal Statistics Office (SFO), Public Funding of Research in Switzerland 2000–2010 (2012), available at http://www.bfs.admin.ch/bfs/portal/en/index/themen/04/22/publ.Document.163273.pdf (last visited Jun. 20, 2013).
- Fig. 3 Venture Lab Startup Program [ png ]
- Fig. 4 Startup Plan Flow Chart [ png ]
- Fig. 5 Application of CTI Policy Instrument to Innovation Chain [ png ]
- Fig. 6 Percentage of Research Expenditures in Various Country Governments’ Total Expenditures (2008) [ jpg ]
- Fig. 7 Swiss Government Research Expenditures 2000-2010 [ png ]
- Fig. 8 Swiss Research Fund Utilization Mechanism [ jpg ]
The Research on ownership of cell therapy products 1. Issues concerning ownership of cell therapy products Regarding the issue of ownership interests, American Medical Association(AMA)has pointed out in 2016 that using human tissues to develop commercially available products raises question about who holds property rights in human biological materials[1]. In United States, there have been several disputes concern the issue of the whether the donor of the cell therapy can claim ownership of the product, including Moore v. Regents of University of California(1990)[2], Greenberg v. Miami Children's Hospital Research Institute(2003)[3], and Washington University v. Catalona(2007)[4]. The courts tend to hold that since cells and tissues were donated voluntarily, the donors had already lost their property rights of their cells and tissues at the time of the donation. In Moore case, even if the researchers used Moore’s cells to obtain commercial benefits in an involuntary situation, the court still held that the property rights of removed cells were not suitable to be claimed by their donor, so as to avoid the burden for researcher to clarify whether the use of cells violates the wishes of the donors and therefore decrease the legal risk for R&D activities. United Kingdom Medical Research Council(MRC)also noted in 2019 that the donated human material is usually described as ‘gifts’, and donors of samples are not usually regarded as having ownership or property rights in these[5]. Accordingly, both USA and UK tends to believe that it is not suitable for cell donors to claim ownership. 2. The ownership of cell therapy products in the lens of Taiwan’s Civil Code In Taiwan, Article 766 of Civil Code stipulated: “Unless otherwise provided by the Act, the component parts of a thing and the natural profits thereof, belong, even after their separation from the thing, to the owner of the thing.” Accordingly, many scholars believe that the ownership of separated body parts of the human body belong to the person whom the parts were separated from. Therefore, it should be considered that the ownership of the cells obtained from the donor still belongs to the donor. In addition, since it is stipulated in Article 406 of Civil Code that “A gift is a contract whereby the parties agree that one of the parties delivers his property gratuitously to another party and the latter agrees to accept it.”, if the act of donation can be considered as a gift relationship, then the ownership of the cells has been delivered from donor to other party who accept it accordingly. However, in the different versions of Regenerative Medicine Biologics Regulation (draft) proposed by Taiwan legislators, some of which replace the term “donor” with “provider”. Therefore, for cell providers, instead of cell donors, after providing cells, whether they can claim ownership of cell therapy product still needs further discussion. According to Article 69 of the Civil Code, it is stipulated that “Natural profits are products of the earth, animals, and other products which are produced from another thing without diminution of its substance.” In addition, Article 766 of the Civil Code stipulated that “Unless otherwise provided by the Act, the component parts of a thing and the natural profits thereof, belong, even after their separation from the thing, to the owner of the thing.” Thus, many scholars believe that when the product is organic, original substance and the natural profits thereof are all belong to the owner of the original substance. For example, when proteins are produced from isolated cells, the proteins can be deemed as natural profits and the ownership of proteins and isolated cells all belong to the owner of the cells[6]. Nevertheless, according to Article 814 of the Civil Code, it is stipulated that “When a person has contributed work to a personal property belonging to another, the ownership of the personal property upon which the work is done belongs to the owner of the material thereof. However, if the value of the contributing work obviously exceeds the value of the material, the ownership of the personal property upon which the work is done belongs to the contributing person.” Thus, scholar believes that since regenerative medical technology, which induces cell differentiation, involves quite complex biotechnology technology, and should be deemed as contributing work. Therefore, the ownership of cell products after contributing work should belongs to the contributing person[7]. Thus, if the provider provides the cells to the researcher, after complex biotechnology contributing work, the original ownership of the cells should be deemed to have been eliminated, and there is no basis for providers to claim ownership. However, since the development of cell therapy products involves a series of R&D activities, it still need to be clarified that who is entitled to the ownership of the final cell therapy products. According to Taiwan’s Civil Code, the ownership of product after contributing work should belongs to the contributing person. However, when there are numerous contributing persons, which person should the ownership belong to, might be determined on a case-by-case basis. 3. Conclusion The biggest difference between cell therapy products and all other small molecule drugs or biologics is that original cell materials are provided by donors or providers, and the whole development process involves numerous contributing persons. Hence, ownership disputes are prone to arise. In addition to the above-discussed disputes, United Kingdom Co-ordinating Committee on Cancer Research(UKCCCR)also noted that there is a long list of people and organizations who might lay claim to the ownership of specimens and their derivatives, including the donor and relatives, the surgeon and pathologist, the hospital authority where the sample was taken, the scientists engaged in the research, the institution where the research work was carried out, the funding organization supporting the research and any collaborating commercial company. Thus, the ultimate control of subsequent ownership and patent rights will need to be negotiated[8]. Since the same issues might also occur in Taiwan, while developing cell therapy products, carefully clarifying the ownership between stakeholders is necessary for avoiding possible dispute. [1]American Medical Association [AMA], Commercial Use of Human Biological Materials, Code of Medical Ethics Opinion 7.3.9, Nov. 14, 2016, https://www.ama-assn.org/delivering-care/ethics/commercial-use-human-biological-materials (last visited Jan. 3, 2021). [2]Moore v. Regents of University of California, 793 P.2d 479 (Cal. 1990) [3]Greenberg v. Miami Children's Hospital Research Institute, 264 F. Suppl. 2d, 1064 (SD Fl. 2003) [4]Washington University v. Catalona, 490 F 3d 667 (8th Cir. 2007) [5]Medical Research Council [MRC], Human Tissue and Biological Samples for Use in Research: Operational and Ethical Guidelines, 2019, https://mrc.ukri.org/publications/browse/human-tissue-and-biological-samples-for-use-in-research/ (last visited Jan. 3, 2021). [6]Wen-Hui Chiu, The legal entitlement of human body, tissue and derivatives in civil law, Angle Publishing, 2016, at 327. [7]id, at 341. [8]Okano, M., Takebayashi, S., Okumura, K., Li, E., Gaudray, P., Carle, G. F., & Bliek, J. UKCCCR guidelines for the use of cell lines in cancer research.Cytogenetic and Genome Research,86(3-4), 1999, https://europepmc.org/backend/ptpmcrender.fcgi?accid=PMC2363383&blobtype=pdf (last visited Jan. 3, 2021).
Adopting Flexible Mechanism to Promote Public Procurement of Innovation—the Amendment of Article 27 of the Statute for Industrial InnovationAdopting Flexible Mechanism to Promote Public Procurement of Innovation—the Amendment of Article 27 of the Statute for Industrial Innovation I.Introduction To further industrial innovation, improve industrial environment, and enhance industrial competitiveness through a systematic long-term approach, the Statute for Industrial Innovation (hereinafter referred to as the Statute) has been formulated in Taiwan. The central government authority of this Statute is the Ministry of Economic Affairs, and the Industrial Development Bureau of the Ministry of Economic Affairs (henceforth referred to as the IDB) is the administrative body for the formulation of this Statute. Since its formulation and promulgation in 2010, the Statute has undergone four amendments. The latest amendment, passed by the Legislative Yuan on November 3, 2017, on the third reading, is a precipitate of the international industrial development trends. The government is actively encouraging the investment in industrial innovation through a combination of capital, R&D, advanced technologies and human resources to help the promotion of industrial transformation, hence this large scale amendment is conducted. The amendment, promulgated and enacted on November 22, 2017, focuses on eight key points, which include: state-owned businesses partaking in R&D (Article 9-1 of the amended provisions of the Statute), the tax concessions of the limited partnership venture capital businesses (Article 2, Article 10, Article 12-1 and Article 23-1 of the amended provisions of the Statute), the tax concessions of Angel Investors (Article 23-2 of the amended provisions of the Statute), applicable tax deferral of employees' stock compensation (Article 19-1 of the amended provisions of the Statute), tax deferral benefit of stocks given to research institution creators (Article 12-2 of the amended provisions of the Statute), the promotion of flexible mechanism for innovation procurement (Article 27 of the amended provisions of the Statute), the establishment of evaluation mechanism for intangible assets (Article 13 of the amended provisions of the Statute), and forced sale auction of idled land for industrial use (Article 46-1 of the amended provisions of the Statute). This paper focuses on the amendment of Article 27 of the Fourth Revision of the Statute, which is also one of the major focuses of this revision—promoting flexible mechanism for innovation procurement, using the mass-market purchasing power of the government as the energetic force for the development of industrial innovation. II.Explanation of the Amendment of Article 27 of the Statute 1.Purposes and Descriptions of the Amendment of Article 27 of the Statute The original intent of Article 27 (hereinafter referred to as the Article) of the Statute, prior to the latest amendment (content of the original provisions is shown in Table 1), was to encourage government agencies and enterprises to give a priority to using green products through the "priority procurement" provisions of Paragraph 2, which allow government agencies to award contracts to green product producers using special government procurement procedures, so as to increase the opportunities for government agencies to use green products, and thereby promote the sustainable development of the industry. In view of the inherent tasks of promoting the development of industrial innovation, and considering that, using the large-scale government procurement demand to guide industrial innovation activities, has become the policy instrument accepted by most advanced countries, the IDB expects that, with the latest amendment of Article 27, the procurement mechanism policy for software, innovative products and services, in addition to the original green products, may become influential, and that "innovative products and services" may be included in the scope of "Priority Procurement" of this Article namely, make “priority procurement of innovative products and services” as one of the flexible mechanisms for promoting innovation procurement. A comparison of the amended provisions and the original provisions is shown in Table 1, and an explanation of the amendment is described as follows:[1] Table 1 A Comparison of Article 27 Amendment of the Statute for Industrial Innovation Amended Provisions Original Provisions Article 27 (I) Each central government authority in charge of end enterprises of a specific industry shall encourage government organizations (agencies) and enterprises to procure software, innovative and green products or services. (II) To enhance the procurement efficiencies, as effected by supply and demand, the central government authority shall offer assistance and services to the organizations (agencies) that handle these procurements as described in the preceding paragraph; wherein, Inter-entity Supply Contracts that are required for the aforesaid procurements, the common requirements shall be decided, in accordance with policy requirements, upon consultation between the central government authority and each central government authority in charge of end enterprises of a specific industry. (III) Where the software, innovative and green products or services, as described in Paragraph 1, must be tested, audited, accredited and certified, their associated fees and charges may be reduced, exempted, or suspended. (IV) Government organizations (agencies) may specify in the tender document the priority procurement of innovative and green products or services that have been identified to meet the requirements of paragraph 1. However, such a specification shall not violate treaties or agreements that have been ratified by the Republic of China. The measures concerning specifications, categories, and identification procedures of software, innovative and green products or services as prescribed in Paragraph 1; the testing, auditing criteria, accreditation and certification as prescribed in paragraph 3; and the Priority Procurement in paragraph 4 and other relevant items, shall be established by each central government authority in charge of end-enterprises of a specific industry. Article 27 (I) Each central government authority in charge of end enterprises shall encourage government agencies and enterprises to give priority to green products that are energy/resources recyclable/renewable, energy and water saving, non-toxic, less-polluting, or able to reduce the burden on the environment. (II) Agencies may specify in the tender documents that priority is given to green products meeting the requirement set forth in the preceding Paragraph. (III) The regulations governing the specifications, categories, certification procedures, review standards, and other relevant matters relating to the green products as referred to in the preceding Paragraph shall be prescribed by the central government authorities in charge of end enterprises. Source: The Ministry of Economic Affairs (I).Paragraph 1 In order to compel each central government authority in charge of end enterprises of a specific industry to motivate industrial innovation activities and sustainable development on the basis of requirements, and to support the development of the software industry in Taiwan, the provision, that such an authority should encourage government organizations (agencies) and enterprises to procure software and innovative products and services, is added in paragraph 1. (II).Paragraph 2 This procurement, as described in paragraph 1, is different from the property or services procurement of general affairs as handled by various organizations. To enhance procurement efficiencies, as effected by supply and demand, the central government authority, i.e., the Ministry of Economic Affairs, shall provide relevant assistance and services to organizations (agencies) handling these procurements, hence the added provisions in paragraph 2. For purchases using inter-entity supply contracts, which are bound by the requirements of this Article, due to their prospective nature, and that the common demand of each organization is difficult to make an accurate estimate by using a demand survey or other method, the Ministry of Economic Affairs shall discuss the issues with each central government authority in charge of end-enterprises of a specific industry, who consult or promote policies, and are in charge of end enterprises of a specific industry, and then make decisions in accordance with the policy promotion requirements. (III).Paragraph 3 The fee schedule for testing, auditing, accrediting and certifying software, innovative and green products or services is covered by Article 7, Administrative Fees of the Charges And Fees Act. The authorities in charge should determine relevant fee standards.However, considering that the test, audit, accreditation and certification may be conducted during a trial or promotional period, or circumstances dictate that it is necessary to motivate tenderer participation, the fee may be reduced, waived or suspended; hence, paragraph 3 is added. (IV).Paragraph 4 Paragraph 2 of the original provision is moved to paragraph 4 with the revisions made to paragraph 1, accordingly, and the provision for using Priority Procurement to handle innovative products or services is added. However, for organizations covered by The Agreement on Government Procurement (GPA), due to Taiwan's accession to the WTO, ANZTEC, and ASTEP, their procurement of items covered in the aforesaid agreements with a value reaching the legislated threshold, shall be handled in accordance with the regulations stipulated in the aforesaid agreements; hence the stipulation in the proviso that the procurement must not violate the provisions of treaties or agreements ratified by the Taiwan government. (V).Paragraph 5 Paragraph 3 of the original Article is moved to paragraph 5 with the revisions made to paragraph 1, accordingly, and the provision, that authorizes each central government authority in charge of end enterprises of a specific industry to determine appropriate measures concerning the methods of defining software, innovative and green products and services, as well as matters relating to test, accreditation, certification and priority procurement, is added. 2.The Focus of the Amendment of Article 27 of the Statute—Promoting a Flexible Mechanism for Innovation Procurement As previously stated, the amendment of this Article aims to stimulate activities of industrial innovation by taking advantage of the huge demand from government agencies. With the government agencies being the users of the innovative products or services, government's procurement market potential is tapped to support the development of industrial innovation. The original intention of amendment is to incorporate the spirit of Public Procurement of Innovation[2] into this Article, and to try to introduce EU's innovation procurement mechanism[3] into our laws. So that, a procurement procedure, that is more flexible and not subject to the limitation of procurement procedures currently stipulated by the Government Procurement Act, may be adopted to facilitate government sector action in taking the lead on adopting innovative products or services that have just entered their commercial prototype stage, or utilizing the demand for innovation in the government sector to drive industry's innovative ideas or R&D (that can not be satisfied with the existing solutions in the marketplace). However, while it is assessing the relevant laws and regulations of our government procurement system and the practice of implementation, the use of the current government procurement mechanism by organizations in the public sector to achieve the targets of innovation procurement is still in its infancy. It is difficult to achieve the goal, in a short time, of establishing a variety of Public Procurement of Innovation Solutions (PPI Solutions) as disclosed in the EU's Directive 2014/24 / EU, enacted by the EU in 2014, in ways that are not subject to current government procurement legislation. Hence, the next best thing: Instead of setting up an innovative procurement mechanism in such a way that it is "not subject to the restrictions of the current government procurement law", we will focus on utilizing the flexible room available under the current system of government procurement laws and regulations, and promoting the "flexible mechanism for innovation procurement” paradigm. With the provisions now provided in Article 27 of the Statute for Industrial Innovation, the government sector is authorized to adopt the "Priority Procurement" method on innovative products and services, thus increasing the public sector's access to innovative products and services. With this amendment, in addition to the "green products" listed in the original provisions of paragraph 1 of the Statute, "software" and "innovative products or services"[4] are now incorporated into the target procurement scope and each central government authority in charge of end enterprises of a specific industry should now encourage government organizations and enterprises to implement; however, the provisions of this paragraph do not have the specific effect of law, they are declaratory provisions. Two priorities are the1 primary focus of the provisions of paragraph 2 and paragraph 4 of this Article for promoting flexible mechanism for innovation procurement: (I)The procurement of software, innovative and green products or services that uses Inter-entity Supply Contracts may rely on the "policy requirement" to establish the common demand. According to the first half of the provisions of paragraph 2 of this Article, the Ministry of Economic Affairs, being the central government authority of the Statute, may provide assistance and services to organizations dealing with the procurement of software, innovative and green products and services.This is because the procurement subjects, as pertaining to software, products or services that are innovative and green products (or services), usually have the particularities (especially in the software) of the information professions; different qualities (especially in innovative products or services), and are highly profession-specific. They are different from the general affairs goods and services procured by most government agencies. Hence, the Ministry of Economic Affairs may provide assistance and service to these procurement agencies, along with the coordination of relevant organizations, in matters relating to the aforesaid procurement process in order to improve procurement efficiency as relates to supply and demand. Pursuant to the second half of Paragraph 2 of this Article, if the inter-entity supply contract method is used to process the procurement of software, innovative products and services, green products (or services) and other related subjects, there could be "Commonly Required" by two or more organizations concerning the procurement subjects, so in accordance with the stipulations of Article 93 of the Government Procurement Act, and Article 2 of the Regulations for The Implementation of Inter-entity Supply Contracts[5], an investigation of common requirements should be conducted first. However, this type of subject is prospective and profession-specific (innovative products or services in particular), and government organizations are generally not sure whether they have demand or not, which makes it difficult to reliably estimate the demand via the traditional demand survey method[6], resulting in a major obstacle for the procurement process. Therefore, the provisions are now revised to allow the Ministry of Economic Affairs to discuss procurement with each central government authority in charge of end enterprises of a specific industry, who consult or promote policies (such as the National Development Council, or central government authority in charge of end enterprises of a specific industry relevant to the procurement subjects), and then make decisions based on the quantities of goods and services of common requirements in accordance with the demand for promoting the policy. The provisions explicitly stipulate such flexibility in adopting methods other than the "traditional demand survey" method, as is required by laws for the common demand of Inter-entity Supply Contracts. Thus, agencies currently handling procurement of prospective or innovative subjects using inter-entity supply contracts, may reduce the administrative burden typically associated with conducting their own procurement. In addition, with a larger purchase quantity demand, as generated from two or more organizations, the process can more effectively inject momentum into the industry, and achieve a win-win situation for both supply and demand. (II)Government organizations may adopt "Priority Procurement" when handling procurement of innovative and green products or services. Prior to the amendment, the original provision of paragraph 2 of this Article stipulates that organizations may specify in the tender document Priority Procurement of certified green products; Additionally, a provision of paragraph 3 of the original Article stipulates that each central government authority in charge of end enterprises of a specific industry is authorized to establish the specifications, categories and other relevant matters of the green products[7] (according to the interpretation of the original text, it should include "Priority Procurement" in paragraph 3 of the Article).After the amendment of the Article, paragraph 2 of the original Article is moved to paragraph 4. In addition to the original green products, "innovative products or services" are included in the scope of "Priority Procurement" that organizations are permitted to adopt (but, the "software" in paragraph 1 was not included[8]). However, for organizations covered by The Agreement on Government Procurement (GPA), due to Taiwan's accession to the WTO, ANZTEC, and ASTEP, their procurement of items covered by the aforesaid agreements with a value reaching the stated threshold, shall be handled in accordance with the regulations stipulated in the aforesaid agreements; hence the stipulation in the proviso that the procurement must not violate the provisions in treaties or agreements ratified by the Taiwan government. Additionally, paragraph 3 of the original Article is moved to paragraph 5. Each central government authority in charge of end enterprises of a specific industry is authorized to use their own judgment on matters concerning the specifications, categories, certification processes of software, innovative and green products or services and the method for Priority Procurement of paragraph 4. In accordance with the authorization in paragraph 5 of the amended provision of this Article, each central government authority in charge of end enterprises of a specific industry may, depending on the specific policy requirement that promotes innovation development of its supervised industry, establish methods of identification and the processes of Priority Procurement for “Specific categories of innovative products or services", especially on products or services fitting the requirements of the method of using the demands of government organizations to stimulate industrial innovation. The established "Regolations for priority procurement of Specific categories of innovative products or services" is essentially a special regulation of the government procurement legislation, which belongs to the level of regulations, that is, it allows the organizations to apply measures other than the government procurement regulations and its related measures to the procurement process, and adopt "Preferential Contract Awarding" for qualified innovative products or services. Any government agency that has the need to procure a particular category of innovative product or service may, in accordance with the provisions of paragraph 4 of this Article, specify the use of Priority Procurement in the tender document, and administer the procurement, in accordance with the process of this particular category of innovative products, or priority procurement. The agency is now enabled to follow a more flexible procurement process than that of the government procurement regulations to more smoothly award contracts for qualified innovative products or services. Citing two examples of this applied scenario: Example one, "innovative information services": The central government authority in charge of information services is IDB. Thus, IDB may, according to the authorization provided for in paragraph 5 of the Article, establish the identification methods for innovative information services (the purpose of which is to define the categories and specifications of innovative services covered in the scope of priority procurement) and priority procurement processes, pertaining to emerging information services that are more applicable to the requirements of government agencies, such as: cloud computing services, IoT services, and Big Data analysis services.Example two, "Innovative construction or engineering methods": The central government authority in charge of construction affairs is the Construction and Planning Agency of the Ministry of the Interior. Since the agency has already established the "Guidelines for Approval of Applications for New Construction Techniques, Methods, Equipment and Materials", the agency may establish a priority procurement process for new construction techniques, methods or equipment, in accordance with the stipulations in paragraph 5 of the Article. Government agencies may conduct procurement following any of these priority procurement practices, if there is a requirement for innovative information services, or new construction techniques, methods or equipment. In addition to the two aforementioned flexible mechanisms for innovation procurement, where government agencies are granted flexible procedures to handle the procurement of innovative products or services via the use of the flexible procurement mechanism, paragraph 3, concerning the incentive measures of concessionary deductions, is added to the Article to reduce the bidding costs for tenderers participating in the tender. For the Procurement of software, innovative and green products or services encouraged by each central government authority in charge of end-enterprises of a specific industry (not limited to those handled by the authorities themselves, using inter-entity supply contracts or priority procurement methods), if the procurement subjects are still required to be tested, audited, accredited and certified by the government agencies, such a process falls under the scope of administrative fees collection, pursuant to paragraph 1 Article 7 of the Charges And Fees Act. However, considering that the item subject to test, audit, accreditation and certification may be in a trial or promotional period, or that it may be necessary to motivate tenderer participation, the provisions of paragraph 3 are thusly added to the Article to reduce, waive, or suspend the collection of aforementioned fees. Executive authorities in charge of collecting administrative fees shall proceed to reduce, waive, or suspend the collection pursuant to the stipulations of paragraph 3 of the Article and Article 12 subparagraph 7 of the Charges And Fees Act.[9] III.The direction of devising supporting measures of flexible mechanism for innovation procurement The latest amendment of the Statute for Industrial Innovation was promulgated and enacted on November 22, 2017, it is imperative that supporting measures pertaining to Article 27 of the Statute be formulated. As previously stated, the flexible mechanism for innovation procurement, as promoted in this Article, is designed specifically for the products or services that are pertinent to the government procurement requirements and are capable of stimulating industrial innovation, and providing a more flexible government procurement procedure for central authorities in charge of a specific industry as a policy approach in supporting industry innovation. Thus, the premise of devising relevant supporting measures is dependent on whether the specific industry, as overseen by the particular central authority, has a policy in place for promoting the development of industrial innovation, and on whether it is suitable in promoting the flexible mechanism for innovation procurement as described in this Article. The purpose of this Article is to promote the flexible mechanism for innovation procurement. Supporting measures pertaining to this Article will focus on the promotion of devising an "Innovation Identification Method", and of the "Priority Procurement Process" of the innovative products or services of each industry that central government authorities oversee. The former will rely on each central government authority in charge of a specific industry to charter an industry-appropriate and profession-specific planning scheme; while, for the latter, the designing of a priority procurement process, in accordance with the nature of the various types of innovative products or services, does not have to be applicable to all. However, regardless what type of innovative products or services the priority procurement process is designed for, the general direction of consideration should be given to - taking the different qualities of innovative products or services as the core consideration. Additionally, the attribute of the priority procurement procedures focusing specifically on the different qualities of the innovative subjects relates to the special regulation relevant to the government procurement regulations. Thus, the procurement procedures should follow the principle that if no applicable stipulation is found in the special regulation, the provisions of the principal regulation shall apply. The so-called "Priority Procurement" process refers to the "Preferential Contract Awarding" on tenders that meet certain criteria in a government procurement procedure. The existing Government Procurement Act (GPA, for short) and its related laws that have specific stipulations on "Priority Procurement" can be found in the "Regulations for Priority Procurement of Eco-Products" (Regulations for Eco-Products Procurement, for short), and the "Regulations for Obliged Purchasing Units / Institutions to Purchase the Products and Services Provided by Disabled Welfare Institutions, Organizations or Sheltered Workshops" (Regulations for Priority Procurement of Products or Services for Disabled or Shelters, for short). After studying these two measures, the priority procurement procedures applicable to criteria-conformed subjects can be summarized into the following two types: 1.The first type: Giving preferential contract awarding to the tenderer who qualifies with "the lowest tender price”, as proposed in the tender document, and who meets a certain criteria (for example, tenderers of environmental products, disabled welfare institutions, or sheltered workshops). There are two scenarios: When a general tenderer and the criteria-conformed tenderer both submit the lowest tender price, the criteria-conformed tenderer shall obtain the right to be the "preferential winning tender" without having to go through the Price Comparison and Reduction Procedures. Additionally, if the lowest tender price is submitted by a general tenderer, then the criteria-conformed tenderers have the right to a "preferential price reduction” option, that is, the criteria-conformed tenderers can be contacted, in ascending order of the tender submitted, with a one time option to reduce their bidding prices. The first tenderer who reduces their price to the lowest amount shall win the tender. Both the Regulations for Eco-Products Procurement[10] and Regulations for Priority Procurement of Products or Services for Disabilities or Shelters[11] have such relevant stipulations. 2.The second type: It is permitted to give Preferential Contract Awarding to a criteria-conformed tenderer, when the submitted tender is within the rate of price preference. When the lowest tenderer is a general tenderer, and the tender submitted by the criteria-conformed tenderer is higher than the lowest tender price, the law permits that if the tender submitted is "within the rate of price preference ", as set by the procuring entity, the procuring entity may award the contract preferentially to "the tender submitted by the criteria-conformed tenderer." The premise for allowing this method is that the tender submitted by the criteria-conformed tenderer must be within the preferential price ratio. If the submitted tender is higher than the preferential price ratio, then the criteria-conformed tenderer does not have the right to preferential contract awarding. The contract will be awarded to theother criteria-conformed tenderer, or to a general tenderer. This method is covered in the provisions of the Regulations for Eco-Products Procurement[12]. However, the important premise for the above two priority procurement methods is that the nature of the subject matter of the tender is suitable for adopting the awarding principle of the lowest tender (Article 52, Paragraph 1, Subparagraphs 1 and 2 of the Procurement Act), that is, it is difficult to apply these methods to the subjects if they are different qualities. Pursuant to the provisions of Article 66 of the Enforcement Rules of the Government Procurement Act, the so-called "different qualities" refers to the construction work, property or services provided by different suppliers that are different in technology, quality, function, performance, characteristics, commercial terms, etc. Subjects of different qualities are essentially difficult to compare when based on the same specifications. If just looking at pricing alone it is difficult to identify the advantages and disadvantages of the subjects, hence, the awarding principle of the lowest tender is not appropriate. The innovative subjects are essentially subjects of different qualities, and under the same consideration, they are not suitable for applying the awarding principle of the lowest tender. Therefore, it is difficult to adopt the lowest-tender-based priority procurement method for the procurement of innovative subjects. In the case of innovative subjects with different qualities, the principle of the most advantageous tender should be adopted (Article 52 Paragraph 1 Subparagraph 3 of the Procurement Act) to identify the most qualified vender of the subjects through open selection. Therefore, the procedure for the priority procurement of innovative subjects with different qualities should be based on the most advantageous tender principle with focus on the "innovativeness" of the subjects, and consideration on how to give priority to tenderers, who qualify with the criteria of innovation. Pursuant to the provisions of Article 56 Paragraph 4 of the Procurement Act, the Procurement and Public Construction Commission has established the "Regulations for Evaluation of the Most Advantageous Tender". The tendering authorities adopting the most advantageous tender principle should abide by the evaluation method and procedures delineated in the method, and conduct an open selection of a winning tender. According to the Regulations for Evaluation of the Most Advantageous Tender, in addition to pricing, the tenderers' technology, quality, function, management, commercial terms, past performance of contract fulfillment, financial planning, and other matters pertaining to procurement functions or effectiveness, maybe chosen as evaluation criteria and sub-criteria. According to the three evaluation methods delineated in the provisions of Article 11 of the Regulations for Evaluation of the Most Advantageous Tender (overall evaluation score method, price per score point method, and ranking method), pricing could not been included in the scoring. That is, "the prices of the subjects" is not the absolute criterion of evaluation of the most advantageous tender process. The priority procurement procedures designed specifically for innovative subjects with different qualities may adopt an evaluation method that excludes "pricing" as part of the scoring criterion so as to give innovative subject tenderers the opportunity to be more competitive in the bidding evaluation process, and due to the extent of their innovativeness, obtain the right to preferential tenders. If it must be included in the scoring, the percentage of the total score for pricing should be reduced from its usual ratio[13], while stipulating explicitly that "innovation" must be included as part of the evaluation criteria. In addition, its weight distribution should not be less than a ratio that highlights the importance of innovation in the evaluation criteria. Furthermore, when determining how to give preference to tenderers who meet certain innovation criteria in the contract awarding procedures, care should be taken to stay on focus with the degree of innovation of the subject (the higher the degree of innovation, the higher the priority), rather than giving priority to arbitrary standards. In summary, with consideration of priority procurement procedures designed specifically for innovative subjects with different qualities, this paper proposes the following preliminary regulatory directions: 1.Adopt the awarding principle of the most advantageous tender. 2.Explicitly stipulate the inclusion of "innovation" in the evaluation criteria and sub-criteria, and its ratio, one that indicates its importance, should not be less than a certain percentage of the total score (for example 20%). 3.Reduce the distributed ratio of "price" in the scoring criteria in the open selection. 4.After the members of the evaluation committee have concluded the scoring, if more than two tenderers have attained the same highest overall evaluated score or lowest quotient of price divided by overall evaluated score, or more than two tenderers have attained the first ranking, the contract is awarded preferentially to the tenderer who scores the highest in the "innovation" criterion. 5.When multiple awards (according to Article 52 Paragraph 1 Subparagraph 4 of the Procurement Act) are adopted, that is, there is more than one final winning tender, the procuring entity may select the tenderers with higher innovation scores as the price negotiation targets for contract awarding, when there are more than two tenderers with the same ranking. Using the above method to highlight the value of innovative subjects will make these suppliers more competitive, because of their innovativeness ratings in the procurement procedures, and not confine them to the limitation of price-determination. So that, subject suppliers with a high degree of innovation, may attain the right to the preferential contract awarding that they deserve due to their innovativeness, and the procuring entity can purchase suitable innovative products in a more efficient and easy process. It also lowers the threshold for tenderers with innovation energy to enter the government procurement market, thus achieving the goal of supporting industrial innovation and creating a win-win scenario for supply and demand. [1] Cross-reference Table of Amended Provisions of the Statute for Industrial Innovation, The Ministry of Economic Affairs, https://www.moea.gov.tw/MNS/populace/news/wHandNews_File.ashx?file_id=59099 (Last viewed date: 12/08/2017). [2] According to the Guidance for public authorities on Public Procurement of Innovation issued by the Procurement of Innovation Platform in 2015, the so-called innovation procurement in essence refers to that the public sector can obtain innovative products, services, or work by using the government procurement processes, or that the public sector can administer government procurement with a new-and-better process. Either way, the implementation of innovation procurement philosophy is an important link between government procurement, R & D and innovation, which shortens the distance between the foresighted emerging technologies/processes and the public sector/users. [3] The EU's innovative procurement mechanism comprises the "Public Procurement of Innovation Solutions" (PPI Solutions) and "Pre-Commercial Procurement" (PCP). The former is one of the government procurement procedures, explicitly regulated in the new EU Public Procurement Directive (Directive 2014/24 / EU), for procuring solutions that are innovative, near or in preliminary commercial prototype; The latter is a procurement process designed to assist the public sector in obtaining technological innovative solutions that are not yet in commercial prototype, must undergo research and development process, and are not within the scope of EU Public Procurement Directive. [4] The "software, innovative and green products or services", as described in paragraph 1 of Article 27 of the amended Statute for Industrial Innovation, refers to, respectively, "software", "innovative products or services", and "green products or services" in general. There is no co-ordination or subordination relationship between the three; the same applies to "innovative and green products or services" in paragraph 4. [5] Article 93 of the Government Procurement Act stipulates: "An entity may execute an inter-entity supply contract with a supplier for the supply of property or services that are commonly needed by entities." Additionally, Article 2 of the Regulations for The Implementation of Inter-entity Supply Contracts stipulates: "The term 'property or services that are commonly needed by entities' referred to in Article 93 of the Act means property or services which are commonly required by two or more entities. The term 'inter-entity supply contract (hereinafter referred to as the “Contract”)' referred to in Article 93 of the Act means that an entity, on behalf of two or more entities, signs a contract with a supplier for property or services that are commonly needed by entities, so that the entity and other entities to which the Contract applies can utilize the Contract to conduct procurements." Therefore, according to the interpretation made by the Public Construction Commission, the Executive Yuan (PCC, for short), organizations handling inter-entity supply contracts should first conduct a demand investigation. [6] In general, organizations in charge of handling the inter-entity supply contracts will disseminate official documents to applicable organizations with an invitation to furnish information online about their interests and estimated requirement (for budget estimation) at government's e-procurement website. However, in the case of more prospective subjects (such as cloud services of the emerging industry), it may be difficult for an organization to accurately estimate the demand when filling out the survey, resulting in a mismatch of data between the demand survey and actual needs. [7] In accordance with the authorization of paragraph 3 of the Article, the IDB has established "Regulations Governing Examination and Identification of Advanced Recycled Products by Ministry of Economic Affairs" (including an appendix: Identification Specification for Resource Regenerating Green Products), except that the priority procurement process was not stipulated, because the Resource Regenerating Green Products, that meet the requirements of the Ministry of Economic Affairs, are covered by the "Category III Products" in the provisions of Article 6 of the existing "Regulations for Priority Procurement of Eco-Products", set forth by the PPC and The Environmental Protection Administration of the Executive Yuan. Hence, organizations that have the requirement to procure green products, may proceed with priority procurement by following the regulations in the "Regulations for Priority Procurement of Eco-Products". [8] After the amendment of the Article, the "software" in the provisions of paragraph 1 was excluded in paragraph 4, because the objective of paragraph 4 is to promote industry innovation and sustainable development with the use of a more flexible government procurement procedure. Thus, the subjects of the priority procurement mechanism are focused on "innovative" and "green" products or services, which exclude popular "software" that has a common standard in the market. However, if it is an "innovative software", it may be included in the "innovative products or services" in the provisions of paragraph 4. [9] According to the provisions of Article 12 of the Charges And Fees Act: "In any of the following cases, the executive authority in charge of the concerned matters may waive or reduce the amount of the charges and fees, or suspend the collection of the charges and fees: 7. Waiver, reduction, or suspension made under other applicable laws." [10] Refer to Article 12, Paragraph 1, Subparagraphs 1 and Article 13, Paragraph 1 and 2 of Regulations for Priority Procurement of Eco-Products. [11] Refer to Article 4 of Regulations for Obliged Purchasing Units / Institutions to Purchase the Products and Services Provided by Disabled Welfare Institutions, Organizations or Sheltered Workshops. [12] Refer to Article 12, Paragraph 1, Subparagraphs 2 and Article 13, Paragraph 3 of Regulations for Priority Procurement of Eco-Products. [13] The provisions of paragraph 3 Article 16 of the Regulations for Evaluation of the Most Advantageous Tender stipulates: Where price is included in scoring, its proportion of the overall score shall be not less than 20% and not more than 50%.
Introduction to Tax Incentive Regime for SMEsIntroduction to Tax Incentive Regime for SMEs I. Introduction The developments of SMEs (small-and-medium enterprises) plays an important pillar of development of industries and creation of jobs in Taiwan. In 2017, the total number of SMEs in Taiwan was 1,437,616. They offer 8,904,000 jobs, accounting for 78.44% of the workforce[1]. However, SMEs have difficulties in entering international supply chains because of their weakness in finance. Therefore, how to enhance the global competitiveness of SMEs is an important issue for the concerned authority. Chapter 4 of the Act for Development of Small and Medium Enterprises prescribes the tax incentive regime based on the financial capability of SMEs and characteristics of industries in order to facilitate the development of SMEs, especially the globalization of SMEs. This paper will review the importance of tax incentives to SMEs and introduces the tax incentive regime under the Act for Development of Small and Medium Enterprises In order to help SMES have an understanding of such regime. II. SME Tax Incentives Scheme As the gatekeeper of the market, the government may intervene the market with various policies or tools to reallocate and improve the soundness of the market environment when the market competitions is impaired due to information asymmetry or externalities. At this juncture, preferential tax rates or tax deductions can be offered to specific taxpayers through legal institution. This allows these taxpayers to retain higher post-tax earnings so that they are incentified to invest more resources in the legally defined economic activities. Tax incentives targeting at risky or spillover investments to create benefits to specific economic activities will help the development of industries and markets. Whilst Article 10 of the Statute for Industrial Innovation has provided tax cuts for R&D expenditures, these incentives are not focus on SMEs and hence not supportive to their research and innovations. This was the reason for the 2016 amendment of the Act for Development of Small and Medium Enterprises added Article 35 to offer tax incentives in order to encourage R&D and innovative efforts and Article 35-1 to activate intellectual properties via licensing. These articles aim to accelerate the momentum of innovations and transformations which promoting investments for SMEs. OthersTo assist SMEs to cope with change of the business environment, the Article 36-2 added the tax incentives for salary or headcount increases, to contribute to the sustainability of SMEs and stabilize the labour market and industrial structures. Following is an explanation of the applicability of these schemes and the requirements to qualify such incentives. III. Tax Incentives to Promote Investments (I) Tax deductions for R&D expenditures Governments around the world seek to encourage corporate R&D activities, that Tax incentives are put in place to reduce R&D costs and foster a healthy environment of investment for more R&D initiatives. Neighboring countries such as Japan, Korea and Singapore are frequently practicing belowing tax burdens to encourage R&D efforts. Article 35 of the Act for Development of Small and Medium Enterprises in Taiwan allows accelerated depreciation and offers tax cuts[2] to stimulate R&D and innovations and create an investment friendly environment for SMEs. 1. Taxpaying Entities and Requirements (1) Qualifications for SMEs Article 35 of the Act is applicable to qualified SMEs and individual taxpayers, which are (1) from manufacturing, construction & engineering, mining and quarrying industries, with paid-in capital below or equal to NT$80 million or with the number of full-time employees less than 200 people; (2) from other industries with the sales of the previous year below or equal to NT$100 million or with the number of full-time employees less than 100 people. Thus, the qualifications of Small and Medium Enterprises are based on either paid-in capital/sales or number of employees under the Act[3].Meanwhile, SMEs may not have an independent R&D department due to the limit of size or operating cost.Therefore, if the taxpayers hiring full-time R&D personnel that can provide records of job descriptions and work logs to R&D activities, the SMEs can access the tax incentives provided that the R&D functions. The recognized by government agencies is increasingly flexibility for SMEs seeking policy support. 2. Taxpayers and requirements (1) A certain degree of innovativeness As the tax incentive regime strives to promote innovations, the R&D expenses should be used to fund innovative developments. According to the official letters from the Small and Medium Enterprise Administration, Ministry of Economic Affairs, there is no high bar as forward-looking, risky and innovative as usually” required for other incentives previously, which is considering the size of SMEs and their industry characteristics. The “certain degree” of innovativeness shall be based on industry environments and SME businesses as determined by competent authorities in a flexible manner. (2) Flexibility in the utilization of business income tax reductions To encourage regular R&D activities, The case that SMEs may not have R&D undertakings each year due to funding constraints, or start-up company may have incurred R&D expenditures but are not yet profitable and hence have no tax liabilities during the year, Corporate taxpayers were able to choose beside deduct the payable taxes during a single year, and reduce the payable taxes during the current year over three years starting from the year when tax incentives are applicable. 3. Tax incentive effects As previously mentioned, Article 35 of the Act for Development of Small and Medium Enterprises accommodates the characteristics of SMEs by allowing reductions of corporate business taxes for up to 15% R&D expenditures during the current year, or spreading the tax reductions by spreading up to 10% of the R&D expenditures over three years from the first year when the incentives are applicable. It is worth noting that the tax deductions shall not exceed 30% of the payable business income taxes during a single year. If the instruments and equipment for R&D, experiments or quality inspections have a lifetime over two years or longer, it is possible to accelerate the depreciation within half of the years of service prescribed by the income tax codes for fixed assets. However, the final year less than 12 months over the shortened service years shall not be counted. Accelerated depreciation brings in tax benefits for fixed asset investments during the initial stage, that meets the requirements for new technologies and risk management by frontloading the equipment depreciation and creates a buffer for capital utilization. (II) Deferred taxations on licensing/capitalization of intellectual properties The deferral of tax payments under the Act for Development of Small and Medium Enterprises is meant to avoid any adverse effect on the application of technological R&Ds by SMEs. As the equity stakes via capitalization of intellectual properties by inventors or creators are not cashed out yet and the subsequent gains may not be at the same valuation as determined at the time of capitalization, the immediate taxation may hinder the willingness to transfer intellectual properties. Therefore, assisting SMEs to release intellectual properties with potential economic value, the licensing and capitalization of intellectual properties is strongly encouraged. The tax expenses shall be deferred within SME or an individual acquires stakes on a non-publicly-listed company by transferring their intellectual properties. This is to stimulate the applications and sharing of relevant manufacturing technologies. When an SME or an individual acquires stakes on a non-publicly-listed company by transferring their intellectual properties, their tax expenses shall be deferred. 1. Taxpayers and requirements (1) Qualifications for individuals or SMEs Article 35-1 of the Act for Development of Small and Medium Enterprises is applicable to SMEs and individual taxpayers. This is to foster the growth of SMEs and enhancement of industry competitiveness by encouraging R&D and innovations from individuals and start-ups. To promote the commercialize of intellectual properties in different ways, the Act for Development of Small and Medium Enterprises provides income tax incentives to individuals and SMEs transferring intellectual properties. The purpose is to encourage different paths to industry upgrades. (2) Ownership of intellectual properties To ensure that the proceeds of intellectual property is linked to the activity of intellectual properties which perform by individuals or SMEs. Only the owners of the intellectual properties capitalized and transferred can enjoy the tax benefits. Intellectual properties referred to in the Act for Development of Small and Medium Enterprises are the properties with value created with human activities and hence conferred with legal rights. These include but are not limited to copyrights, patent rights, trademarks, trade secrets, integrated circuit layouts, plant variety rights and any other intellectual properties protected by laws[4]. (3) Acquisition of stock options The abovementioned tax incentives are offered to the individuals or SMEs who transfer intellectual properties to non-listed companies in exchange of their new shares. The income taxes on the owners of intellectual properties are deferred until acquisition of shares. These shares are not registered with the book-entry system yet. Before the transferrers of intellectual properties dispose or offload these shares, immediate taxations will impose economic burdens and funding challenges given the unknown prices of the eventual cash-out. Therefore, this legislation is only applicable to taxpayers who obtain options for new shares. 2. Taxpayers and requirements (1) Transfer of intellectual properties According to Article 36 of the Copyright Act as interpreted by official letters issued by the Ministry of Finance, the transfer of intellectual properties is the conferring of intellectual properties to others, and the transferees access these intellectual properties within the scope of the transfer. In terms “transfer” of the first and second paragraphs of Article 36 does not include licensing[5], but such as granting, licensing and inheritance. (2) Timing of income tax payments In general, the particular time that calculation of taxes payable is based on when the taxpayers acquire the incomes, less relevant expenses or costs. The taxes payable timing should be depending on when the taxpayers obtain the newly issued shares by transferring intellectual properties. However, the levy of income taxes at the time of intellectual property transfers and new share acquisitions may cause a sudden jump in taxes payable in the progressive system and thus a burden on the economics of SMEs and individuals concerned. Thus, to avoid disruptions to company operations or personal finance planning, Article 36 makes the exception for the incomes earned by subscribing to new shares as a result of transferring intellectual properties. Such incomes are not subject to taxes during the year when the shares are acquired, in order to mitigate the tax barriers concerned. In sum, the taxes shall be paid when such shares are transferred, gifted or distributed. 3. Tax incentive effects Article 35-1 of the Act for Development of Small and Medium Enterprises provides tax incentives to stimulate the mobilization of intellectual properties by smoothing out the impact of income taxes payable. This is applicable to (1) SMEs who can postpone the business income taxes payable from the year when they acquire new shares of non-listed companies by transferring the intellectual properties they own; (2) individuals who can postpone the individual income taxes payable from the year when they acquire new shares of non-listed companies by transferring the intellectual properties they own. IV. Tax incentives aiming to improve the business environment (I) Tax reductions for wages to additional headcounts SMEs are vital to the Taiwan, making uo 90% of the companies accounting in Taiwan, who employ more than 6.5 million people or 72.8% of the total workforce. Any economic recession may make it difficult for SMEs to maintain their labor costs given their smaller funding size and external challenges. This will cause higher unemployment rates and hurt the economy, which may cause impairment of the capacity or create a labor gap for SMEs, eventually shrink the industry scale. To lower the burden of operational and investment costs and learn from the legislatives in Japan and the U.S.[6], tax incentives are put in place as a buffer for adverse effects of external environments. The first paragraph of Article 36-2 of the Act for Development of Small and Medium Enterprises provide tax incentives for employee salaries of new headcounts based on the assessment on the economy over a time period. This is intended to encourage domestic investments and avoid the pitfall of direct government subsidies distorting salary structures. It is hoped that investments from SMEs can stimulate the momentum of economic growth. 1. Taxpayers The tax incentives under Article 36-2 of the Act for Development of Small and Medium Enterprises aim to assist SMEs through difficult times in an economic downturn. The threshold of the period time is based on the unemployment rate has been below the economic indicator predetermined for six consecutive months, which calculated by the Directorate General of Budget, Accounting and Statistics, Executive Yuan. In number of the unemployment rate has been below the economic indicator predetermined for six consecutive months, it is deemed that the business environment is not friendly to SMEs. In this instance, the Regulations for the Tax Preferences Provided to Small and Medium-sized Enterprises on Additional Wage Payment will trigger the tax incentives. The abovementioned economic indicator shall be published by the competent authorities once every two years. Moreover, to qualify for the tax incentives for new employees, SMEs should investing new ventures or instill new capital by at least $500,000[7] or hiring workforce at least two full-time headcounts compared with the previous fiscal year, that constitute at the Article 36-2 of the Act for Development of Small and Medium Enterprises, which aims to encourage SMEs investments. 2. Taxpayers (1) Qualifications of additional headcounts As the dispatched human resource services typically meet temporary or short-term requirements and contractors do not enjoy employment security, this is not consistent with the spirit of the legislation to create jobs and reduce unemployment. Therefore, to avoid the one-time increase of headcounts from accessing the tax reductions during the year and the deterioration of labor relations in Taiwan. Tax incentive is not offered to the additional recruitment of part-time or contracted workers. Meanwhile, the tax incentives are only applicable to the additional employment of Taiwanese nationals, above or below 24 years old. A tax deduction of 50% based on annual wages is provided for the hiring of people below 24 years old. The extra tax deduction will stimulate young employment. (2) Definition of additional employment The number of additional headcounts is based on permanent hires and calculated as the difference between the average number of Taiwanese employees covered by labor insurance per month throughout a single fiscal year or before and after the incremental increase of workforce. The conversion of regular contracts to indefinite employment in writing or signing up for indefinite R&D headcounts under the military service scheme can also be deemed as additional employment. It is worth noting, however, the new headcounts resulted from M&A activities or transfer between affiliated companies are excluded in this legislation. (3) Calculation of wages Companies are also required to increase employment as well as the Comparable Wages. The comparable wages are estimated with the summation of 30% of the wages for the year before and after additional employment that based on the aggregate of the new hires comparable wages compared to the prior year. In other words, if the aggregate wages paid out are higher than comparable wages during the year, the companies concerned have indeed incurred higher personnel expenses. Tax incentives are thus granted because it improves the business environment and it is the purpose of this legislation. 3. Tax incentive effects The first paragraph of Article 36-2 of the Act for Development of Small and Medium Enterprises provides deductions of business income taxes during the year to qualified SMEs at an amount equivalent to 130% of the incremental wages paid to new headcounts who are Taiwanese nationals. The deductible amount is equivalent to 150% of the incremental wages if new headcounts are Taiwanese nationals below 24 years old. (II) Tax incentives for companies that increase salaries Companies are subject to the effect of changes in the external factors such as global supply and demand on the international market, as well as the domestic business environment as a result of risk aversion from investors and expectation from customers. These uncertainties associated with investments and the rising prices for consumers will suppress the wage levels in Taiwan. This the reason why the second paragraph of Article 36-2 of the Act for Development of Small and Medium Enterprises grants tax deductions for the companies who increase salaries, to encourage companies share earnings with employees and enhance private-sector consumption. SMEs may deduct their business income taxes payable during the year up to 30% of salary increase for existing entry-level employees who are Taiwanese nationals, not as a result of statutory requirement for basic wage adjustments. 1. Taxpayers The tax incentives are applicable to SMEs as defined by the Regulations for the Tax Preferences Provided to Small and Medium-sized Enterprises on Additional Wage Payment and based on the same economic indicators previously mentioned. 2. Qualification for tax incentives (1) Definition of entry-level employees The object of taxation under this act is the enterprise's average wage payment to the entry-level employees. The entry-level employees referred to in this act are authorized by the "Small and medium-sized enterprise employee salary increase, salary deduction act " that refers to employees of local nationality with an average monthly recurring salary below nt $50,000[8] whose were entered into indefinite employment contracts with SMEs. Through such conditions, the effect of tax concessions will be concentrated on promoting the salary level of grassroots staff and helping enterprises to cope with changes in the industrial environment. (2) Average salaries The salaries to entry-level employees refer to the basic salaries, fixed allowances and bonuses paid on a monthly basis. Payment-in-kind shall be discounted based on the actual prices and included into the regular salaries. Meanwhile, regular salaries should be calculated with annualized averages, as this legislation seeks to boost salary levels. The regular salaries to entry-level employees during the year are estimated with the monthly number of entry-level employees during the same year. Only when the average basis salaries during the year are higher than those in the prior year can the tax incentives be applicable. 3. Tax incentive effects Applying this article, SMEs can deduct their business income taxes each year up to 130% of salary increase for existing entry-level employees who are Taiwanese nationals, which are not as a result of statutory requirement for basic wage adjustments. However, it is not allowed to double count the increased personnel expenses for new headcounts applicable to the first and second paragraphs of the same article. V. Conclusions The funding scales and relatively weak financial structures are the factors that led SMEs be susceptible influenced by supply change dynamics and business cycles. To the extent that is suppressing the flexible in capital utilization for SMEs, also influencing on the sustainability of SMEs. Differ from government subsidies require budgeting, reviewing and implementations, there are complications regarding the allocation of administrative resources. Therefore, it is important to plan for tax incentives in order to stimulate R&D, innovation and job creation by SMEs and ultimately make SMEs more competitive. The tax incentives to SMEs amended in 2016 by the Small and Medium Enterprise Administration are known for the following: (I) The lowering of thresholds for tax reductions of R&D expenses in order to encourage SMEs to invest in R&D activities with a “certain degree” of innovativeness and enhance the momentum for SMEs to upgrade and transform themselves; (II) Deferral the income taxations on the transfer of intellectual properties for equity, in order to encourage application and utilization of such intellectual properties, provide incentives for R&D programs or innovations by individuals and SMEs. This also creates a catalyst for industry upgrade; (III) Tax deductions for the employment of new headcounts or the increase of employee wages during the time the economic indicators have reached a certain threshold and based on the health of the investment environment. This is to encourage company investments and capital increases in Taiwan and mitigate the volatility of economic cycles, in order to get ready for business improvement. The above tax incentive programs, i.e. tax deductions for R&D and innovations; deferral of taxations on the transfer of intellectual properties for equity; tax deductions for the hiring of new headcounts and the increase of employee salaries, are meant to boost the investment from SMEs and the competitiveness of SMEs. The Act for Development of Small and Medium Enterprises seeks to reduce tax burdens of SMEs actively investing for their future and competitive advantages. Tax incentives help to mitigate the adverse effect of the economy on the business environment. It is also the fostering of the sources of business income tax revenues for the government. This is the very purpose of the Act for Development of Small and Medium Enterprises. [1]White Paper on Small and Medium Enterprises in Taiwan, 2018, p21 (November 9, 2018) published by the Ministry of Economic Affairs [2]Pursuant to the authorization conferred by Article 35 of the Act for Development of Small and Medium Enterprises, the Ministry of Economic Affairs has announced the Regulations Governing the Reduction of Expenditures for Small and Medium Enterprises Research and Development as Investment. [3]Article 2 on the definition of SMEs. The abovementioned criterion is universally applicable to the Act for Development of Small and Medium Enterprises. It also applies to the eligibility of tax incentives to be introduced in this paper unless otherwise specified. [4]Official Letter Economic-Business No. 10304605790, Ministry of Economic Affairs [5]Official Letter Taiwan-Finance No. 10300207480, Ministry of Finance [6]“Assessment of the Taxations under Article 35, Article 35-1, the first paragraph and the second paragraph of Article 36-2, the Act for Development of Small and Medium Enterprises” published by the Small and Medium Enterprise Administration, Ministry of Economic Affairs, pages 15-17, https://www.moeasmea.gov.tw/files/2670/93B9AF54-84E2-4293-A5CA-EA7DD9FAA05A(most recently browsed date September 9, 2019). [7]Order of Interpretation Economics-Business No. 104004602510 from the Ministry of Economic Affairs: “Second, on the day when the economic indicator has reached the threshold, the paid-in capital of the new business should be at least NT$500,000 and there is no need to instill additional capital during the period when tax incentives are applicable. For existing businesses, there is no limitation on the number of capital increases during the applicable period. So long as the cumulative increase in capital reaches NT$500,000 and new employees are hired during the same fiscal year or during the prior fiscal year.” [8]Paragraph 1, Article 2 of the Regulations for the Tax Preferences Provided to Small and Medium-sized Enterprises on Additional Wage Payment
Innovative Practice of Israel's Government ProcurementInnovative Practice of Israel's Government Procurement Government procurement is an important pillar of government services. Because of the huge number of government purchases, government procurement management play an important role in promoting public sector efficiency and building citizenship. Well-designed government procurement systems also help to achieve policy such as environmental protection, innovation, start-ups and the development of small and medium-sized enterprises. Nowadays, countries in the world, especially OECD countries, have been widely practiced with innovative procurement to stimulate innovation and start-ups, and call Innovation procurement can deliver solutions to challenges of public interest and ICTs can play a major role in this. However, in the OECD countries, in addition to the advanced countries that have been developed, many developing countries have also used government procurement to stimulate national R & D and innovation with remarkable results. Israel is one of the world's leading technology innovation centers, one of the most innovative economies in the world, continues to leverage its own strengths, support of technology entrepreneurship and unique environment, an international reputation in the high-tech industry, the spirit of technological innovation and novelty. Government procurement is a core element of the activities of Israeli government, agreement with suppliers and compliance with the Mandatory Tenders Law. The main challenge is how to ensure efficiency and maintain government performance while ensuring an equitable and transparent procurement process. Israel’s Mandatory Tenders Law has shown the central role played by the Israeli Supreme Court in creating and developing this law, even in the absence of any procurement legislation, based instead on general principles of administrative law. Once the project of creating a detailed body of public tendering law had been completed, and the legislator was about to step in, the Supreme Court was prepared to step out and transferring the jurisdiction to lower courts. The Knesset passed the Mandatory Tenders Law, and based on it the Government issued the various tendering regulations. Besides, Israel's various international agreements on government procurement, mainly GPA and other bilateral international agreements such as free trade agreements with Mexico and Colombia and free trade agreements and memoranda of understanding with the United States. The practical significance of these commitments can only be understood on the backdrop of Israel’s domestic preference and offset policies. These policies were therefore discussed and analyzed as they apply when none of the international agreements applies. The Challenge Tenders "How to solve the problem of overcrowding in the emergency department and the internal medicine department?" is the first of a series of "problem solicitations" released by the Israeli Ministry of Health which seeks to find a digital solution to the public health system problem, questions from the government while avoiding preconceived prejudices affect the nature of the solution, allowing multiple innovative ideas from different fields to enter the health system, make fair and transparent judgments about the ideal solution to the problem. In order to ensure transparency and integrity, equality, efficiency and competition in the decision-making process, the tender proposed by the Israeli Ministry of Health defines a two-stage tender process. The Ministry of Health of Israel, in order to improve the quality of medical care, shorten the waiting time for hospitalized patients, protect the dignity of patients and their families with patients as its center, and ensure their rights, while alleviating the burden of hospital staff, so as to pass the targeted treatment areas reduce the gap between various residential areas. The Israeli government deals with these issues through challenging tenders and offers a digital solution combined with innovative ideas. The initiative proposed through the development of public service projects can raise the level of public services in the country and help the government to reduce costs and achieve the purpose of promoting innovation with limited conceptual, technical and financial capabilities. In addition, due to the online operation of the challenging tender process throughout the entire process, fair and transparent procedures can be ensured, while public-private partnerships are encouraged to facilitate the implementation of the implementation plan.
- Impact of Government Organizational Reform to Scientific Research Legal System and Response Thereto (1) – For Example, The Finnish Innovation Fund (“SITRA”)
- The Demand of Intellectual Property Management for Taiwanese Enterprises
- Blockchain in Intellectual Property Protection
- Impact of Government Organizational Reform to Research Legal System and Response Thereto (2) – Observation of the Swiss Research Innovation System
- Recent Federal Decisions and Emerging Trends in U.S. Defend Trade Secrets Act Litigation
- The effective and innovative way to use the spectrum: focus on the development of the "interleaved/white space"
- Copyright Ownership for Outputs by Artificial Intelligence
- Impact of Government Organizational Reform to Research Legal System and Response Thereto (2) – Observation of the Swiss Research Innovation System
